Direct-current relay for resisting short-circuit current
A DC relay and anti-short circuit technology, applied in the direction of electromagnetic relays, relays, electromagnetic relay details, etc., can solve the problems that the contact pressure is not enough to resist the electric repulsion of the moving spring, cannot provide sufficient suction, and the DC relay is small in size, etc., to achieve The magnetic circuit is not easy to be saturated, the cost is low, and the effect of high magnetic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
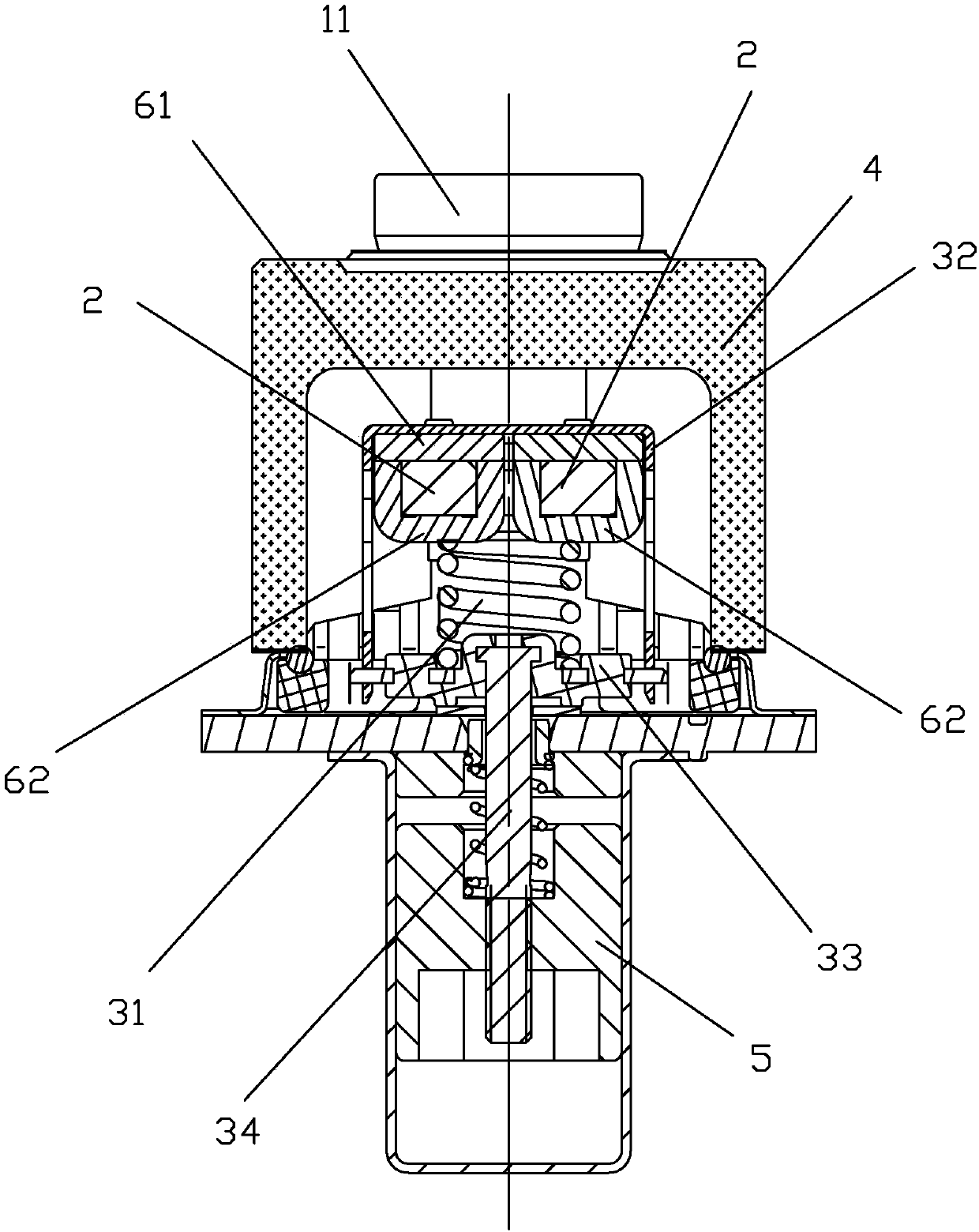
[0044] see Figure 1 to Figure 11 As shown, a kind of short-circuit current DC relay of the present invention includes two static contact terminals 11, 12 for current inflow and current outflow respectively, a straight-type movable reed 2 and a Drive the moving reed 2 to move to realize the moving contact at the two ends of the moving reed and the static contact at the bottom of the static contact lead-out end to contact or disconnect the push rod part 3; On the casing 4, a part of the moving reed 2 and the push rod part 3 is accommodated in the casing 4, and the push rod part 3 is also connected with the moving iron core 5 in the magnetic circuit structure, and under the action of the magnetic circuit, the push rod Part 3 drives the movable reed 2 to move upwards, so that the movable contacts at both ends of the movable reed 2 are respectively in contact with the static contacts at the bottom ends of the two static contact lead-out ends 11 and 12, so as to realize the connect...
Embodiment 2
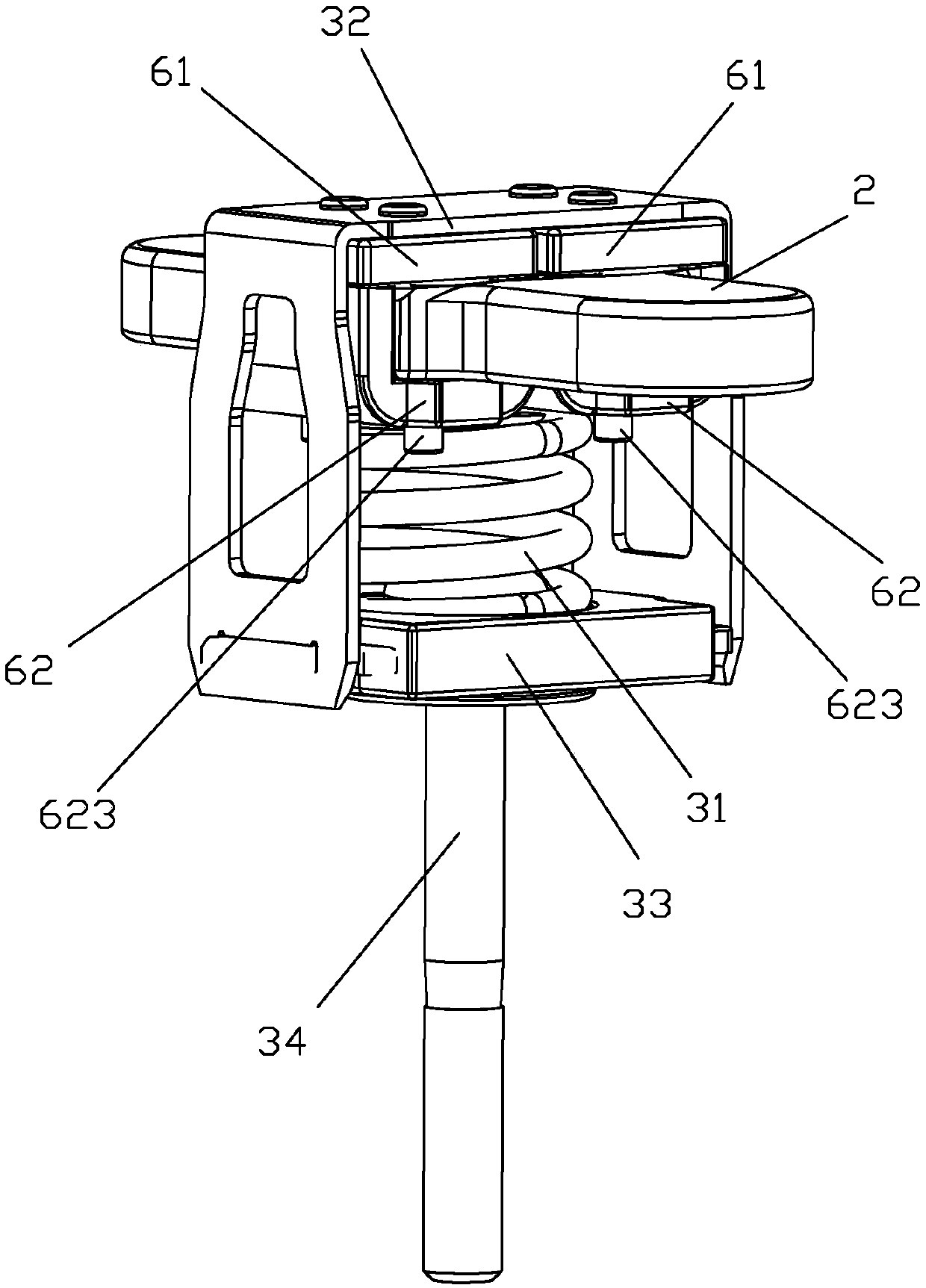
[0064] see Figure 12 to Figure 13 As shown, a DC relay against short-circuit current of the present invention differs from Embodiment 1 in that the upper magnetic conductor 61 is an upper yoke, and the upper yoke is fixed on the On the housing of the lead-out end, like this, when the movable contact of movable reed 2 and the static contact of static contact lead-out 11,12 did not contact and cooperate (that is, when the contacts were disconnected), the upper magnetic conductor 61 (upper There is a preset gap between the lower magnetic conductor 62 (lower armature), and when the movable contact of the movable reed 2 is in contact with the static contacts of the static contact lead-out ends 11 and 12, the upper The magnetic conductor 61 is in contact with the lower magnetic conductor 62 , that is, there is basically no gap between the upper magnetic conductor 61 and the lower magnetic conductor 62 .
Embodiment 3
[0066] see Figure 14 to Figure 16 As shown, a DC relay with short-circuit current resistance of the present invention is different from Embodiment 1 in that there are three magnetic conduction circuits, and the moving reed 2 is provided with two through holes 22, and three U-shaped The lower magnetic conductors 62 are arranged sequentially along the width of the moving reed 2, wherein the two side walls 621, 622 of a U-shaped lower magnetic conductor 62 in the middle pass through the two through holes 22 of the movable reed respectively, and the two through holes 22 on both sides Each side wall 621 of the U-shaped lower magnetic conductor 62 is attached to the corresponding side of the width of the moving reed respectively, and each other side wall 622 of the two U-shaped lower magnetic conductors 62 on both sides passes through the two sides of the movable reed respectively. There is a through hole 22, and there is a gap between the side walls 622 of the two U-shaped bottom ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com