Differential evolution algorithm-based CRS dip decomposition method
A differential evolution algorithm and population technology, applied in the field of oil and gas exploration seismic data processing, can solve the problems of image quality reduction, three-parameter test infinite coherence value is impractical, affect the stacking section effect, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
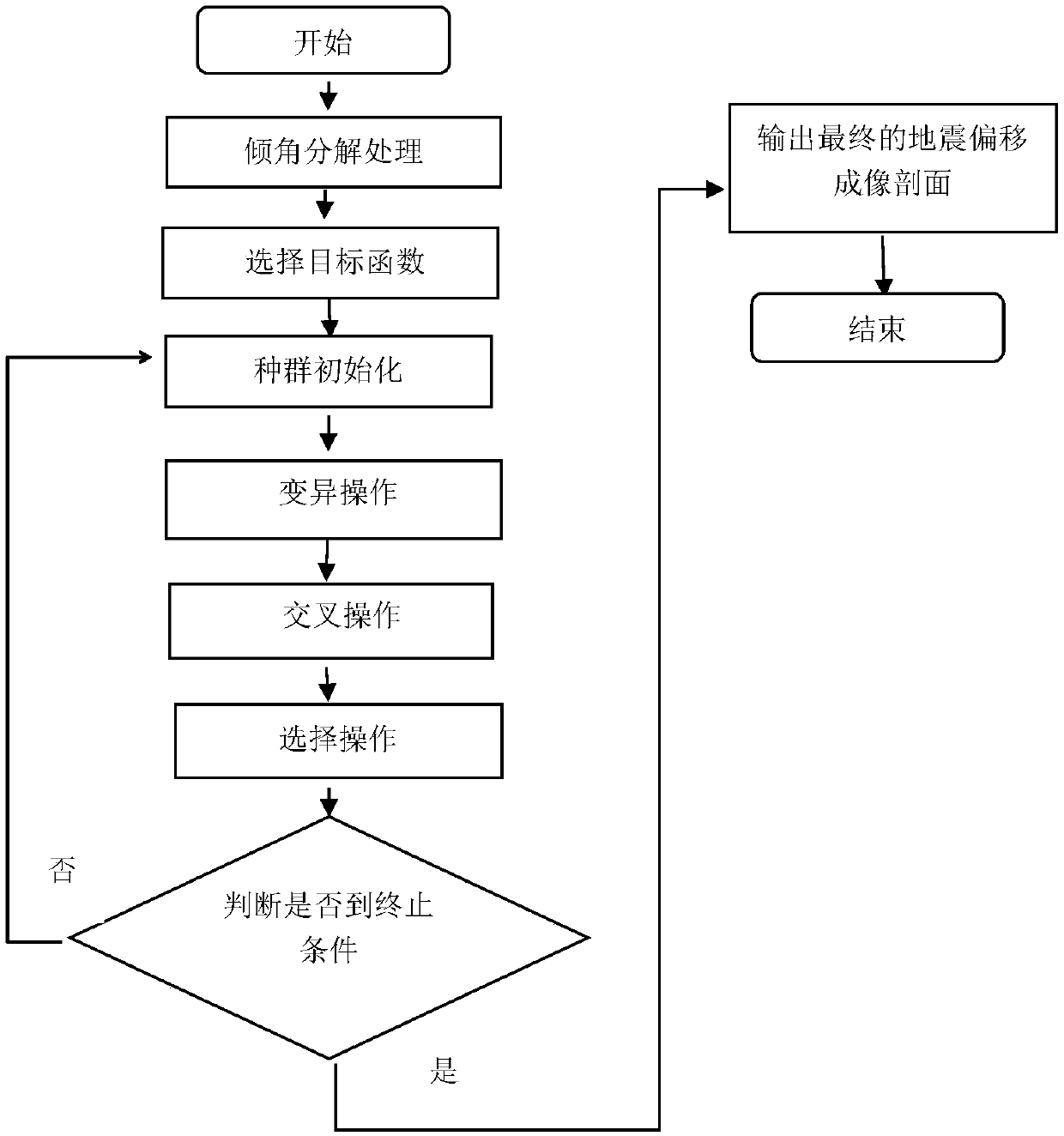
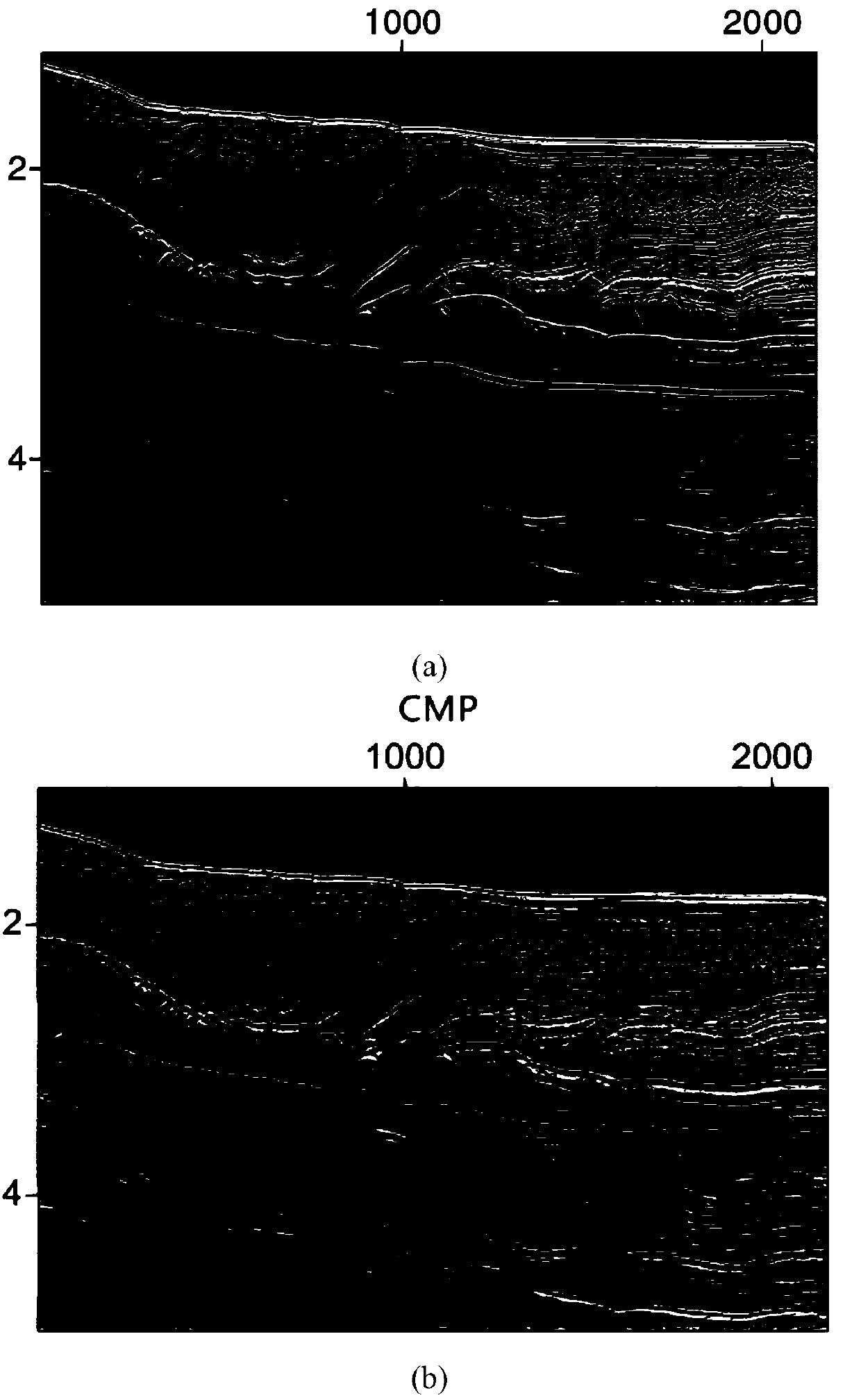
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, a CRS inclination angle decomposition method based on differential evolution algorithm is completed by discretizing the outgoing angle α, and the inclination angle is divided into several parts. For each part, the parameters with the highest similarity are obtained based on the differential evolution algorithm. Finally, each part partially superimposed.
[0040] Before the dip division process, in order to improve the R in the search space NIP The lower limit of , the minimum dynamic correction speed is required, and the lower limit is calculated by the minimum dynamic correction speed
[0041]
[0042] lb is denoted as the lower boundary, α min and alpha max is the boundary of the angle range, v 0 is the ground velocity, V min is the dynamic correction speed, similarly, the maximum dynamic correction speed can be used to calculate R NIP The upper limit of , where the CRS motion correction velocity is obtained using the CRS parameters...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com