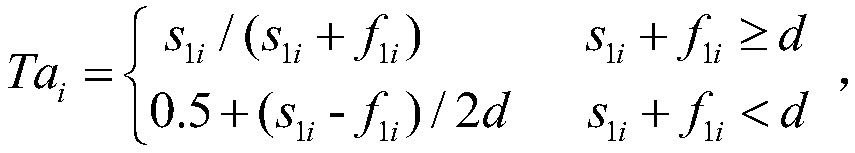Method for detecting malicious node in wireless ad-hoc network based on behavioural cognition
A wireless self-organizing and malicious node technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of non-malicious node credibility reduction, high delay, congestion, etc., to avoid the reduction of trust, improve network reliability, and reduce negative effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
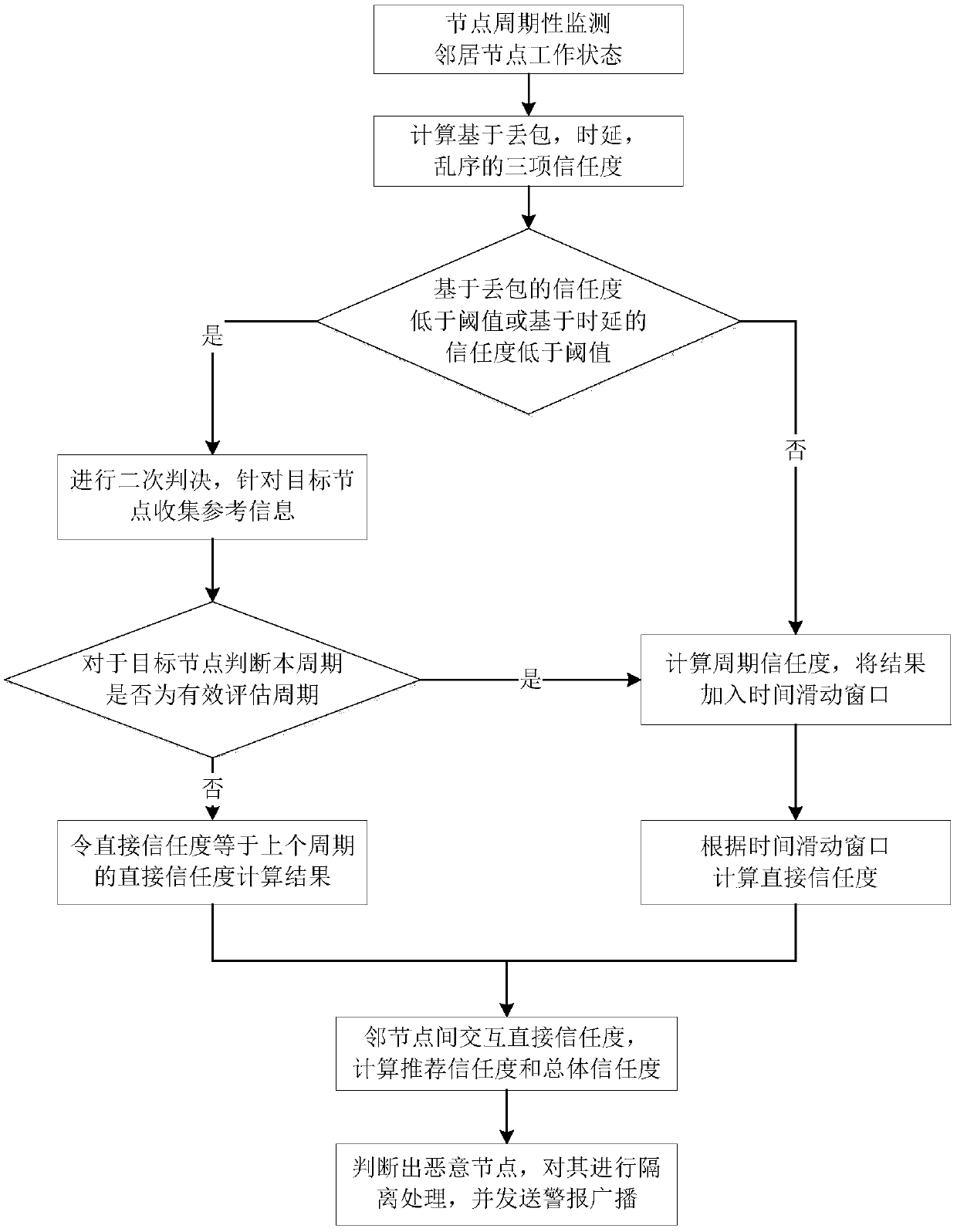
[0029] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows.
[0030] Step 1, the node periodically monitors the working status of the neighboring nodes.
[0031] (1a) Each node in the network is set in the promiscuous listening mode, that is, the node can receive all data packets within the communication range, regardless of whether it is the next-hop node of the data packet;
[0032] (1b) The node periodically monitors the behavior of all neighbor nodes, that is, monitors the following three situations:
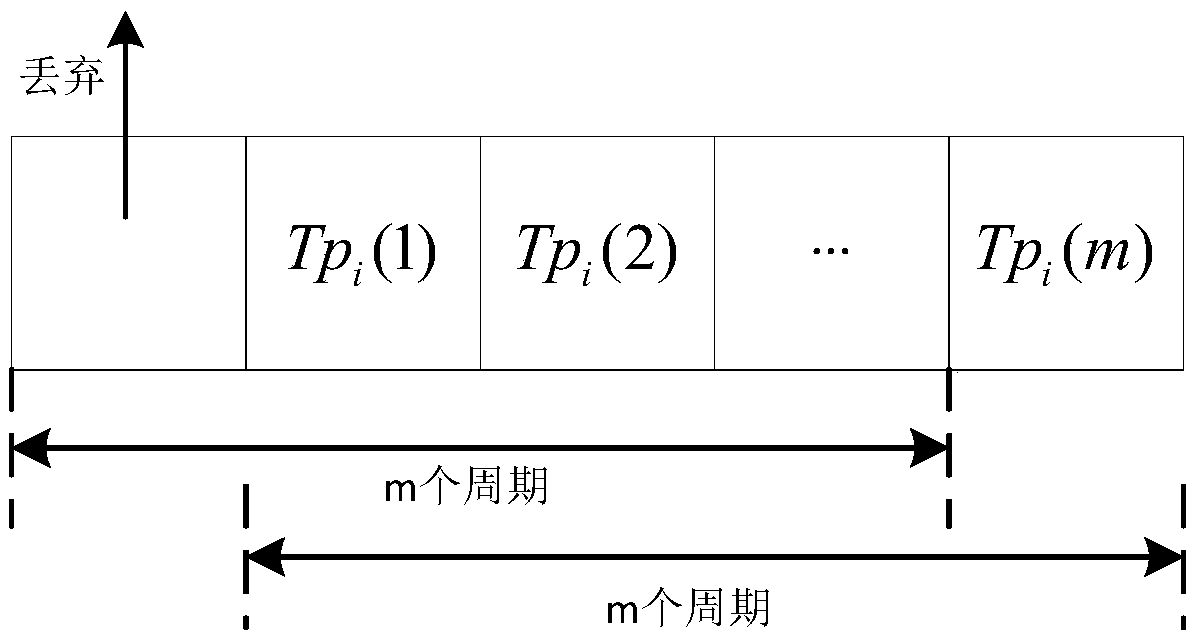
[0033] Packet loss: The specific statistical parameter is the number s of correctly forwarded data packets among the data packets sent by this node and forwarded by node i 1i and the number of lost packets f 1i ;
[0034] Delay: The specific statistical parameter is the number of data packets that have not timed out among the da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com