Measurement method of turning point of thermomechanical analysis curve based on Pearson correlation coefficient
A technique of Pearson correlation and thermomechanical analysis, which is applied in the field of evaluation of low temperature performance of asphalt mixture, and can solve problems such as difficulty in determining the turning point of asphalt
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0016] Specific embodiment one: the method for measuring the turning point of the thermomechanical analysis curve based on the Pearson correlation coefficient in this embodiment is implemented according to the following steps:
[0017] 1. Measure the thermomechanical parameters that change with temperature, and establish a temperature array T [i] , i∈[1,N] and thermomechanical parameter array Y [i] ,i∈[1,N];
[0018] 2. The temperature array and thermomechanical parameter array obtained in step 1 are sorted in ascending order according to the size of the temperature measurement value, and the sorted data is recorded as the temperature-thermomechanical parameter data group {T j ,Y j}(j=1,2,…,N), where T j-1 j j+1 , and take the temperature T as the abscissa and the thermomechanical parameter Y as the ordinate to draw the temperature-thermomechanical parameter relationship curve;
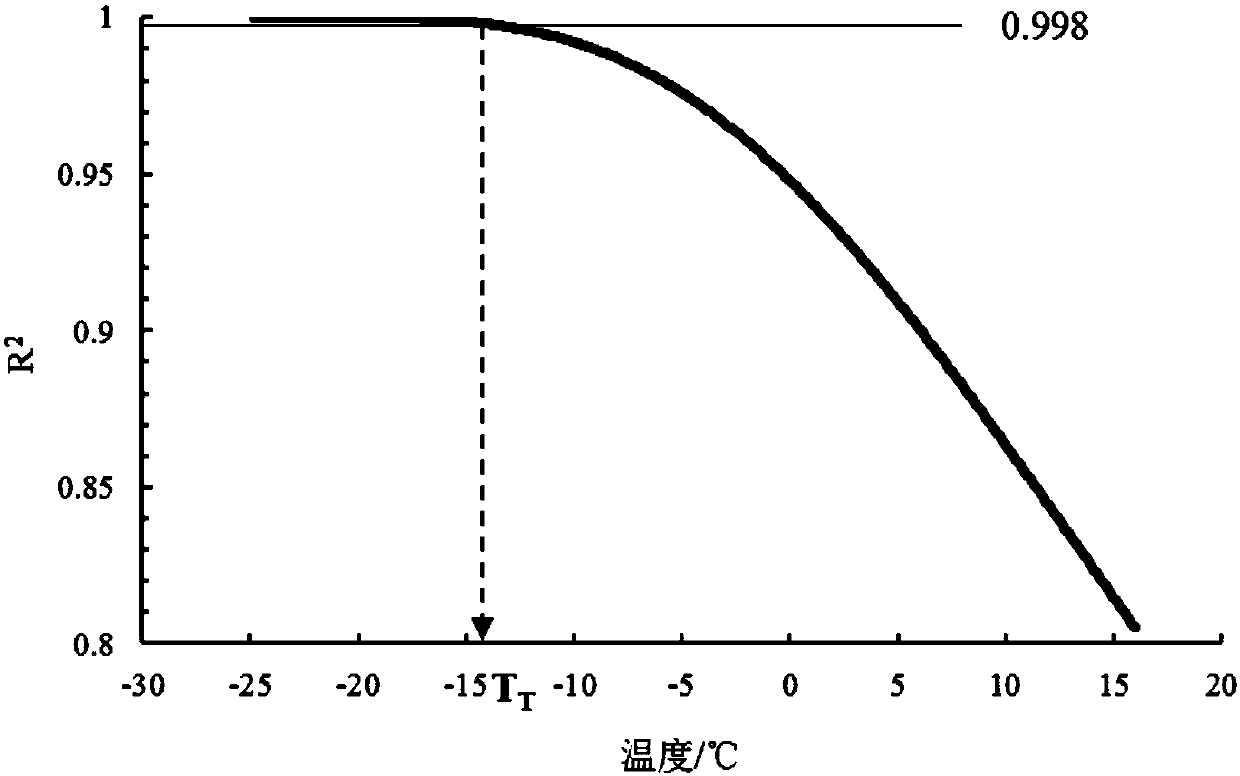
[0019] Three, based on the temperature-thermomechanical parameter data set of step 2, calculat...
specific Embodiment approach 2
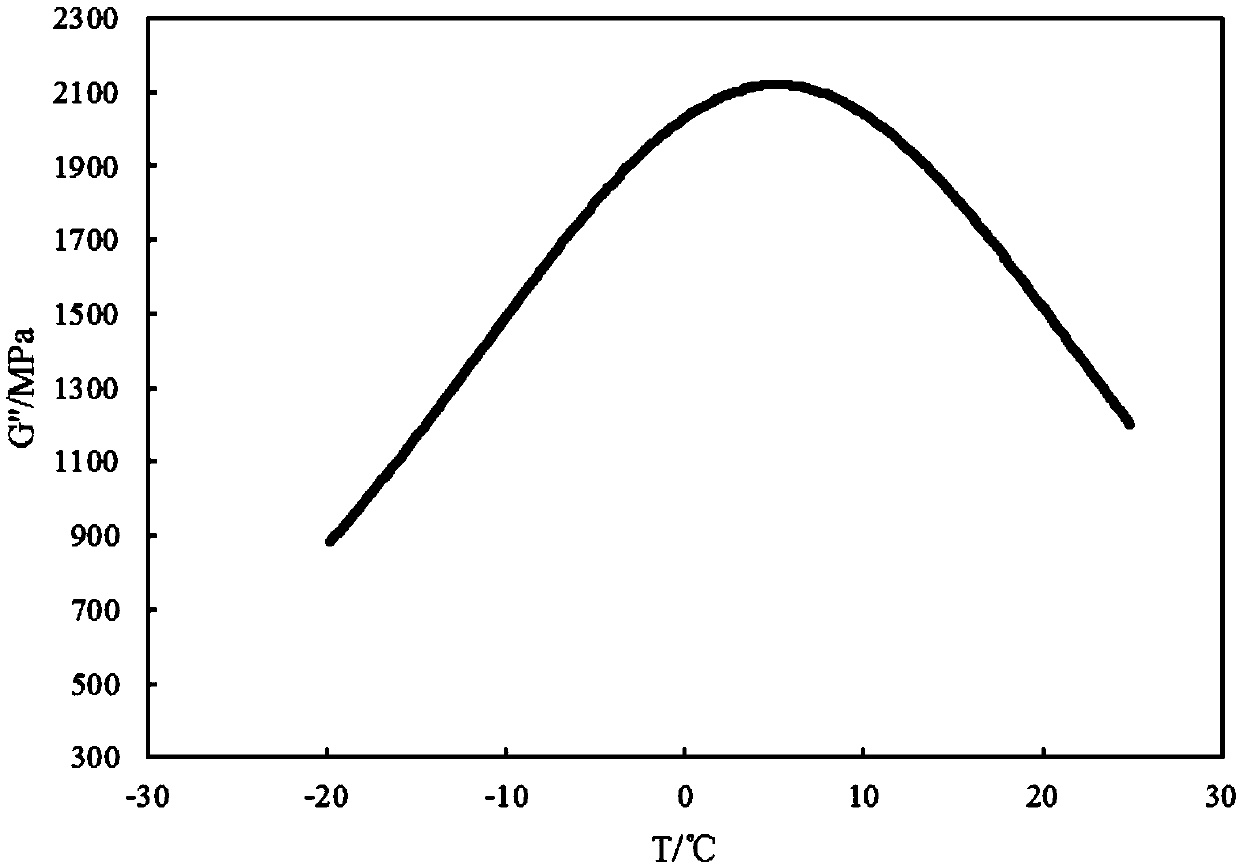
[0023] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the thermomechanical parameters described in step 1 are stress value, loss shear modulus or temperature shrinkage strain.
specific Embodiment approach 3
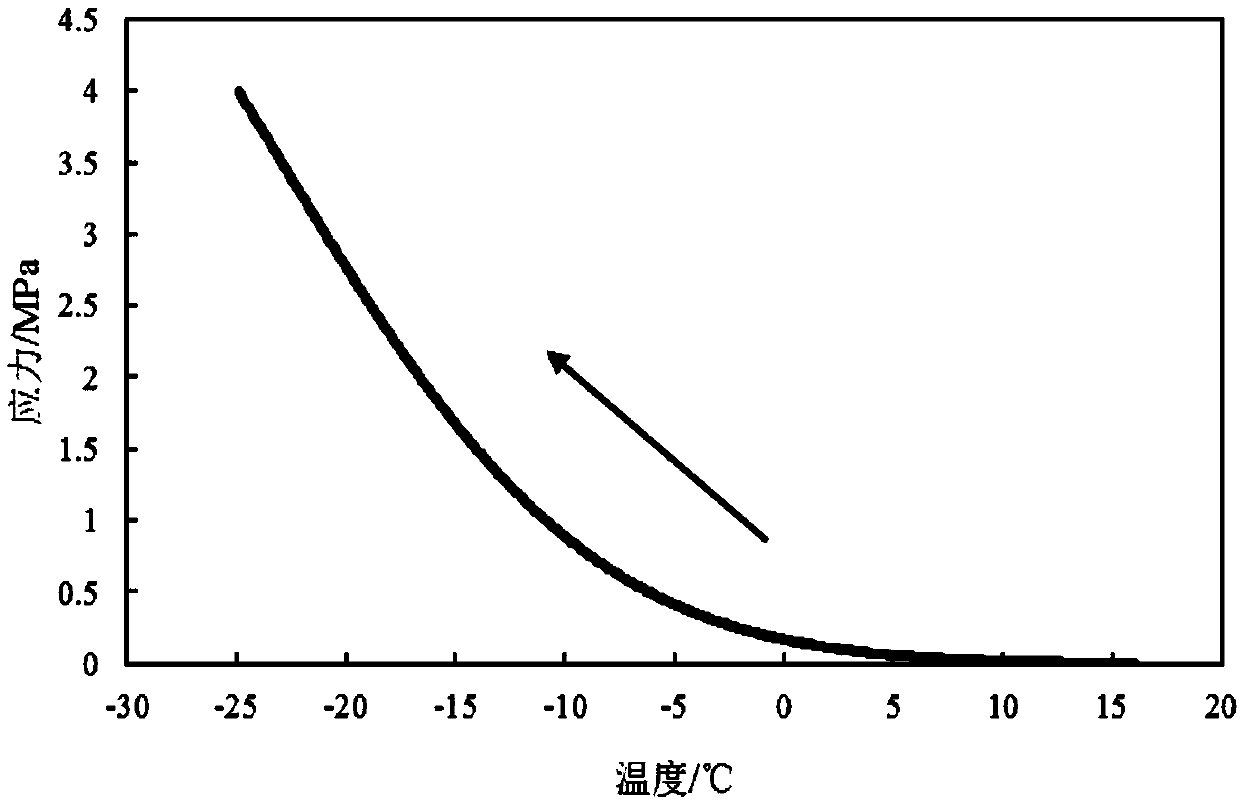
[0024] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that when the thermomechanical parameter is the stress value, the low-temperature freeze-break experimental device is used to carry out the temperature stress test of the restrained specimen on the asphalt mixture test specimen, and the initial temperature is set and cooling rate, and then start the program to collect and record the temperature data and stress data during the test, and obtain the temperature array T [i] , i∈[1,N] and the stress array σ [i] ,i∈[1,N], when the specimen freezes, the test ends.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com