Fast neutron imaging system
An imaging system and neutron technology, applied in the measurement of neutron radiation, instruments, radiation measurement, etc., can solve the problems such as the large size of the translation stage, the difficulty in meeting the requirements of different fields of view and resolution, and the large load. The effect of simple space setting, improving neutron detection efficiency and light collection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
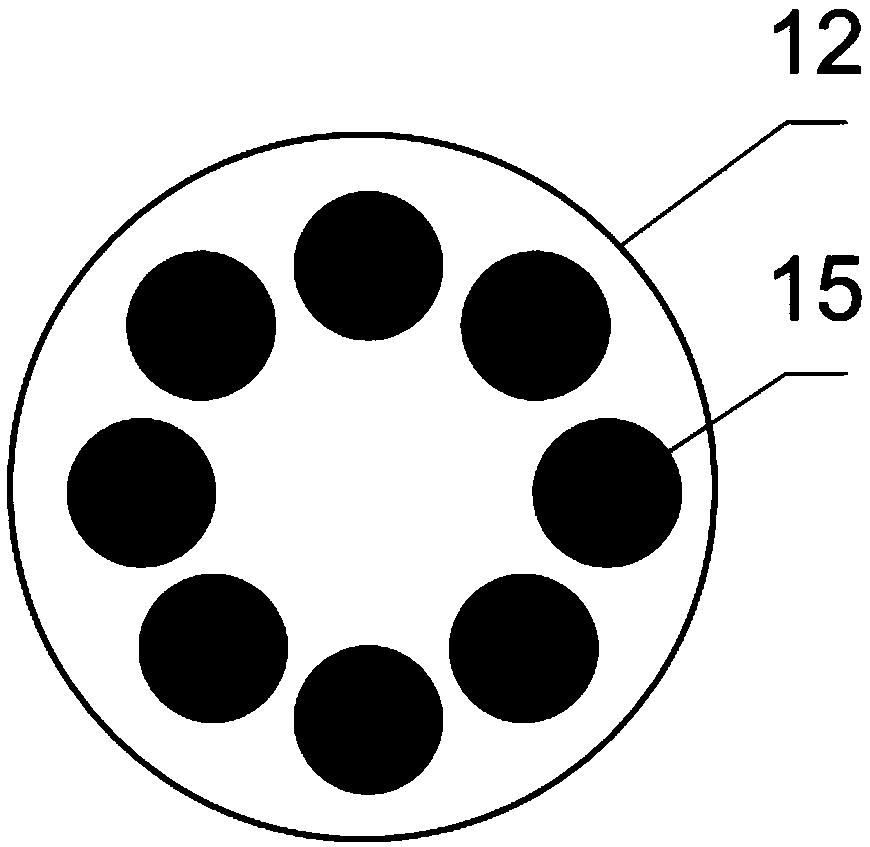
[0040] Such as Figure 1-5 As shown, a fast neutron imaging system in this embodiment includes a neutron conversion screen 1 , a mirror 2 , an image detector 3 , an optical adjustment frame 4 , an obscura 5 , a shielding module 6 and a computer control system 7 . Wherein, the dark box 5 is specifically an "L"-shaped box with a boss extending outward from one side, the extension direction of the boss is facing the neutron beam, and the side wall of the dark box 5 at the side end of the boss is provided with a shielding module 6, and the dark box 5 It contains a neutron conversion screen 1 , a mirror 2 , an image detector 3 and an optical adjustment frame 4 .
[0041] The neutron conversion screen 1 is specifically arranged inside the black box 5 facing the incident direction of the neutron beam. The other side of the neutron conversion screen 1 is provided with a mirror 2 at an angle of 45 degrees to the incident direction of the neutron beam. Equipped with image detector 3 . ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A fast neutron imaging system of this embodiment has basically the same structure as that of Embodiment 1, the main differences are: (1) the neutron conversion screen 1 is circular, with a diameter of 150 mm and a thickness of 32 mm; the neutron-proton conversion layer 11 has a thickness of 2mm, the electron multiplication layer 13 has a thickness of 5mm, and the fluorescent layer 14 has a thickness of 25mm; (2) The channel aperture of the microchannel plate is 20 μm, the channel inclination angle is 8°, and the channel spacing is 50 μm. A voltage of 2 kV is applied at both ends of the microchannel plate.
Embodiment 3
[0053] A fast neutron imaging system of this embodiment has basically the same structure as that of Embodiment 1, the main differences are: (1) the neutron conversion screen 1 is circular, with a diameter of 150 mm and a thickness of 30 mm; the neutron-proton conversion layer 11 has a thickness of 2mm, the electron multiplication layer 13 has a thickness of 4mm, and the fluorescent layer 14 has a thickness of 15mm; (2) the channel aperture of the microchannel plate is 15 μm, and the channel inclination angle is 8 o , the channel spacing is 50 μm, and a voltage of 1kV is applied to both ends of the microchannel plate; (3) the image detector 3 adopts a silicon photomultiplier array; Composed of avalanche photodiodes (APD), it has the characteristics of high single-photon counting detection sensitivity, high gain, low bias voltage, insensitivity to magnetic fields, and compact structure. The neutrons transmitted by the sample react with the neutron conversion screen 1 to generate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com