Method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) through sterilization-free fermentation
A technology of polyhydroxyalkanoate and hydroxybutyrate, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of high production cost of PHA, restrict the development and promotion of PHA, etc., and reduce energy consumption. consumption, reduce production costs, and reduce costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
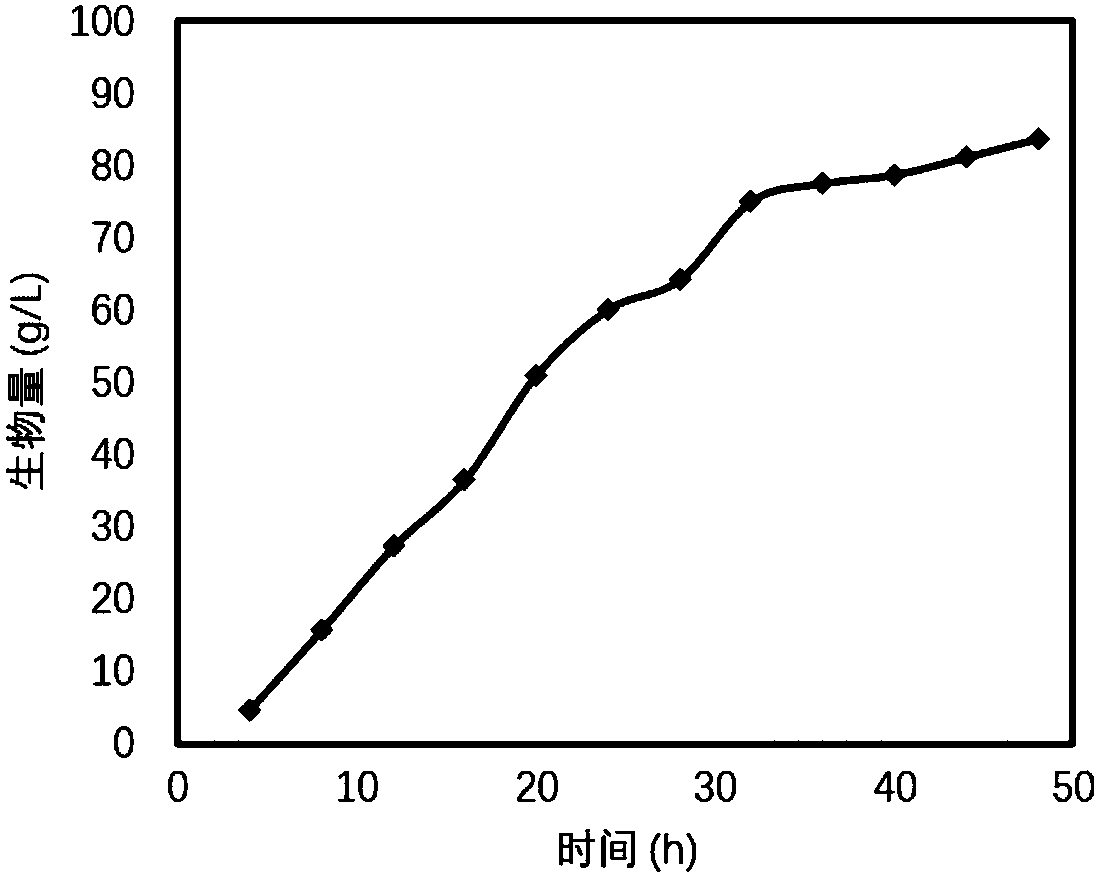
[0046] Example 1 Halomonas (halomonas TD01) produces PHB in a 7.5L fermenter
[0047] Strain culture
[0048] 1. Strain activation: put the glycerol tube of Halomonas TD01 [preservation number: CGMCC No.4353, authorized in the patent application (patent announcement number: CN102120973B)] stored in the refrigerator at -80°C on a 60LB solid plate Single clones were isolated by streaking on the medium, and cultured in a 37°C incubator for 18-24h.
[0049] 2. First-class seeds: Take a single colony from the activated halomonas TD01 plate and place it in a 100mL shaker flask filled with 20mL60LB, and culture it in a shaking table at a temperature of 37°C and a rotation speed of 200rpm for 12h.
[0050] 3. Second-level seeds: The first-level seed solution is inoculated into a 500mL shaker flask filled with 100mL 60LB according to the inoculum amount of 1%, and cultivated in a shaker at a temperature of 37°C and a rotation speed of 200rpm for 10-12h.
[0051] 60LB medium compositi...
Embodiment 2
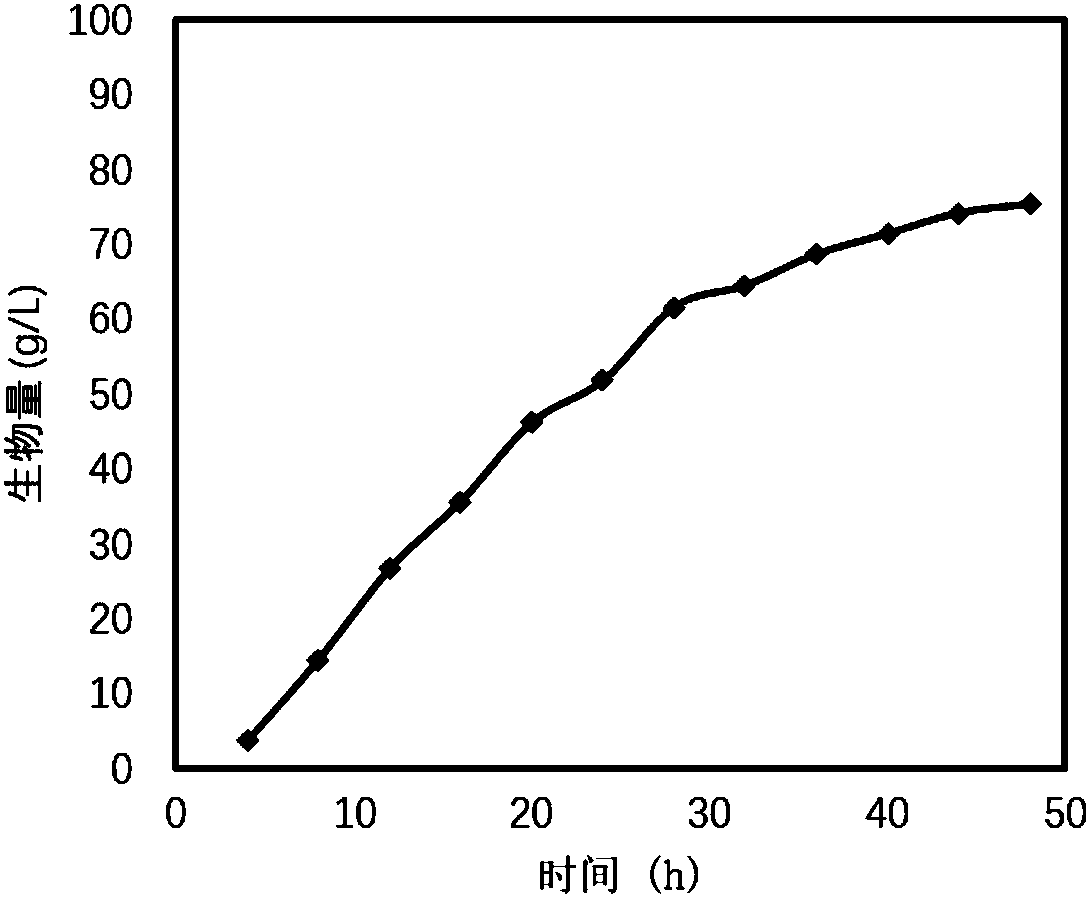
[0073] Example 2 Halomonas (halomonas TD40) produces P3HB4HB in a 7.5L fermentation system
[0074] Halomonas TD40 is based on the wild bacteria halomonas TD01 by synthetic biology technology, and introduces the 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA transferase gene into the genome of TD01, so that it has the ability to synthesize P3HB4HB.
[0075] Strain culture
[0076] 1. Strain activation: Halomonas TD40 stored in a -80°C refrigerator (this strain has been disclosed in the following non-patent literature: Chen, X., Yin, J., Ye, J., Zhang, H., Che ,X.,Ma,Y.,Li,M.,Wu,L-P.,Chen,G-Q.,Engineering Halomonas bluephagenesis TD01for Non-sterile Production of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate),Bioresource Technology(2017 ), and provided by Beijing Blue Crystal Microbiology Technology Co., Ltd.) Glycerol tubes were streaked on 60LB solid plate medium to isolate single clones, and cultured in a 37°C incubator for 18-24h.
[0077] 2. First-class seeds: Inoculate a single colony from the act...
Embodiment 3
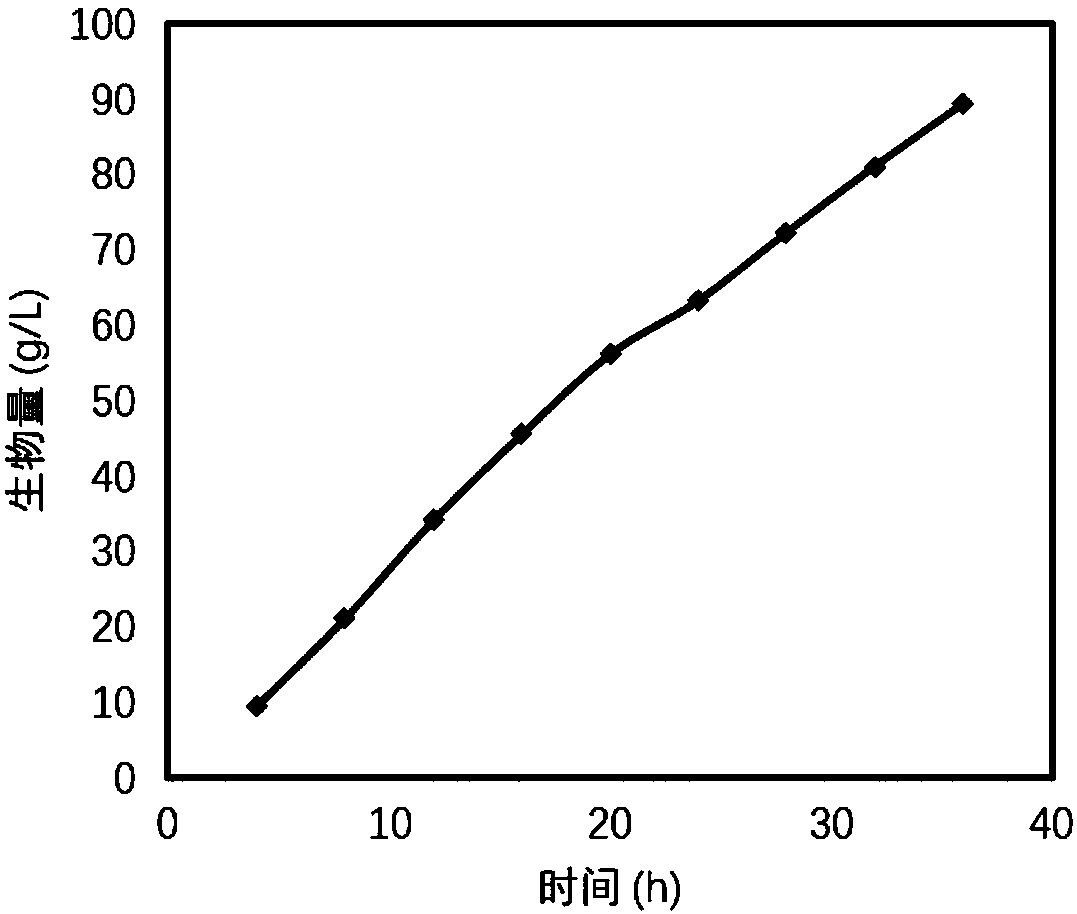
[0104] Embodiment 3 halomonas (halomonas TD40) in 1m 3 Production of P3HB4HB in fermentors
[0105] Strain culture
[0106] 1. Strain activation: Streak the glycerol tubes of Halomonas TD40 stored in -80°C refrigerator on a 60LB solid plate medium to isolate single colonies, and culture them in a 37°C incubator for 18-24h.
[0107] 2. First-class seeds: Take a single colony from the activated Halomonas TD40 plate and place it in a 100 mL shaker flask filled with 20 mL60LB, and culture it in a shaker at a temperature of 37° C. and a rotation speed of 200 rpm for 12 hours.
[0108] 3. Second-level seeds: The first-level seed liquid is inoculated in a 2L shaker flask with 400mL 60LB according to the inoculum amount of 1%, and cultivated in a shaker at a temperature of 37°C and a rotation speed of 200rpm for 10-12h.
[0109] 4. Third-level seeds: The second-level seed liquid is inserted into a 100L fermenter according to the inoculum amount of 2%. Reduce the speed to 30% or les...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dry cell weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dry weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com