A kind of purification method of long-chain dibasic acid
A long-chain dibasic acid and purification method technology, applied in the field of biochemical industry, can solve the problems of product color and nitrogen content, limited removal effect, etc., and achieve high product yield, improved removal rate, and environmentally friendly effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
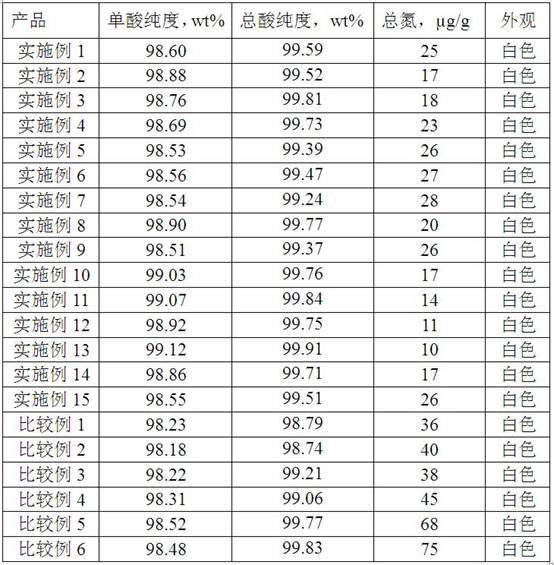
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Using n-dodecane as substrate, use Candida tropicalis to ferment and produce dodecane dibasic acid. At the end of the fermentation, the concentration of dodecanedibasic acid was 150g / L, and the pH was 7.0. Take 1000ml of fermentation broth, heat it to 90°C, let it stand to room temperature, separate the residual alkanes in the upper layer, filter to remove the bacteria, and obtain the fermentation supernatant. While stirring, slowly add 6 mol / L sulfuric acid to the fermentation clear liquid to adjust the pH to 5.0, continue stirring for 30 minutes, then add 10 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the fermentation clear liquid while stirring, adjust the pH to 8.0, and continue stirring for 30 minutes , and then add 5g of sodium lauryl sulfate to the clear liquid, and continue to stir for 60min. Use a membrane with a pore size of 10 -2 μm membrane filter to remove the precipitate. Add 5 g of activated carbon to the filtered clear liquid, stir and decolorize for 20 min, a...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Tridecane dibasic acid was produced by fermenting Candida tropicalis with n-tridecane as substrate. At the end of the fermentation, the tridecanedioic acid concentration was 145g / L, and the pH was 7.2. Take 1000ml of fermentation broth, heat it to 95°C, let it stand to room temperature, separate the residual alkanes in the upper layer, filter to remove the bacteria, and obtain the fermentation supernatant. While stirring, slowly add 8 mol / L nitric acid to the fermentation clear liquid to adjust the pH to 4.0, continue stirring for 20 minutes, then add 10 mol / L potassium hydroxide solution to the fermentation clear liquid under stirring, adjust the pH to 9.0, and continue stirring for 20 minutes , and then add 15g isomeric tridecanol polyoxyethylene ether to the clear liquid, and continue to stir for 3h. Use a membrane with a pore size of 10 -2 μm membrane filter to remove the precipitate. Add 10 g of activated carbon to the filtered clear liquid, stir and decolorize ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Tetradecane dibasic acid was produced by fermenting Candida tropicalis with n-tetradecane as substrate. At the end of the fermentation, the tetradecanedibasic acid concentration was 135g / L, and the pH was 7.4. Take 1000ml of fermentation broth, heat it to 95°C, let it stand to room temperature, separate the residual alkanes in the upper layer, filter to remove the bacteria, and obtain the fermentation supernatant. While stirring, slowly add 4 mol / L hydrochloric acid to the fermentation clear liquid to adjust the pH to 4.5, continue stirring for 40 minutes, then add 6 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the fermentation clear liquid while stirring, adjust the pH to 9.5, and continue stirring for 40 minutes , and then add 20g of sodium dodecylsulfonate to the clear liquid, and continue to stir for 2h. Use a membrane with a pore size of 10 -2 μm membrane filter to remove the precipitate. Add 3g of activated carbon to the filtered clear liquid, stir and decolorize for 40m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com