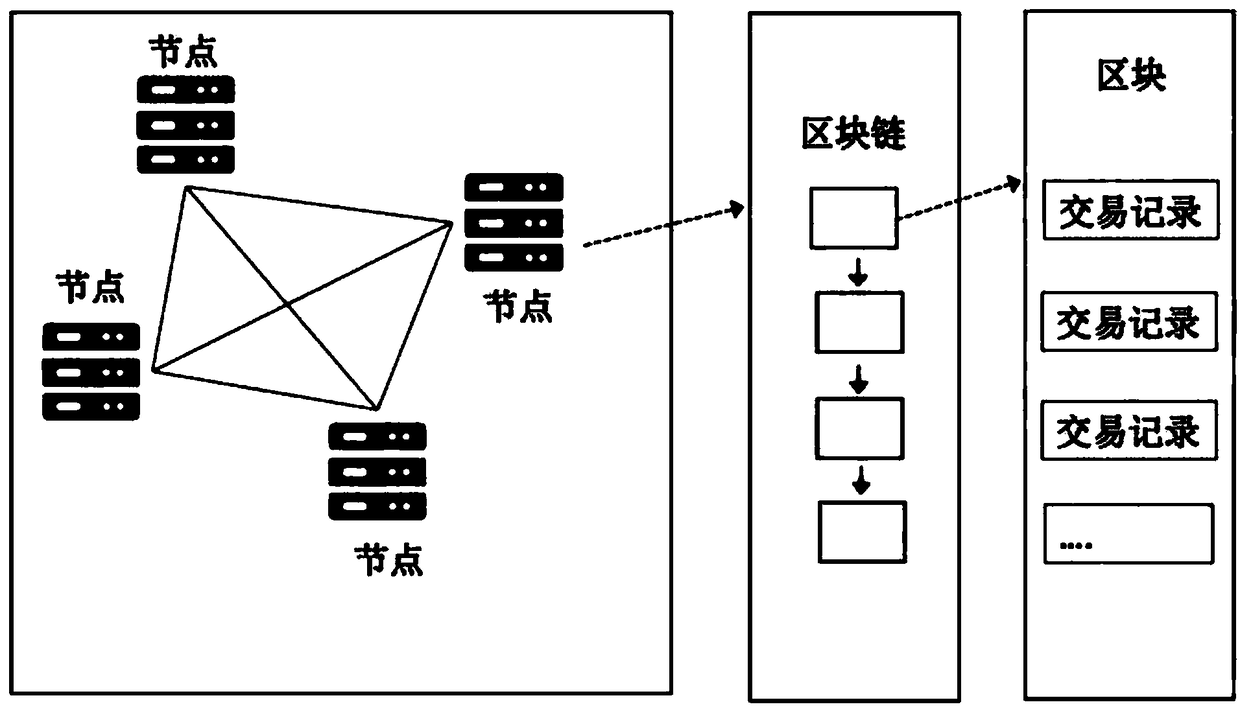
Block chain data lifecycle management method
A technology of life cycle and management method, applied in the field of blockchain data life cycle management, it can solve problems such as slowing down the speed of creating new applications, and achieve the effect of improving synchronization and access efficiency, speeding up transaction speed, and relieving pressure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
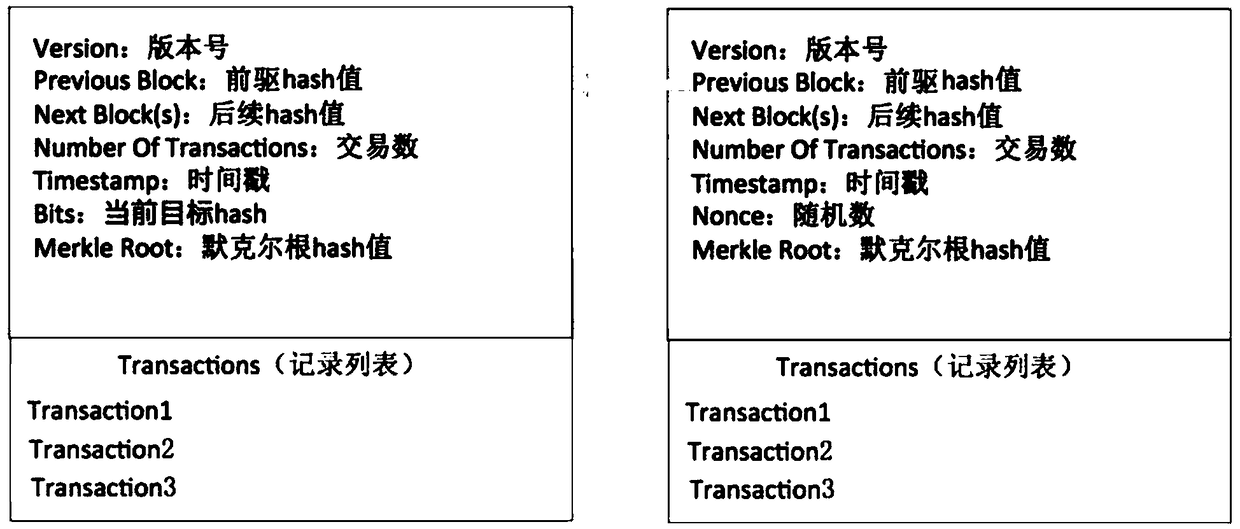
[0037] Invention Example 1: The redesigned block header data structure of the present invention is as follows Figure 4 shown. On the basis of the data structure of the classic block header on the left, the present invention adds variables such as the number of block visits, the last access time of the block, the valid period of block access, the lifetime of the block, the sedimentation mark, and the index value of the sedimentation pool. The number of block visits records the total number of times the block has been accessed since its creation. The validity period of the block records the maximum time allowed for the block to be accessed. The maximum allowable time to be destroyed, the sedimentation mark records whether the block is deposited, and the sedimentation tank index value records the block's position in the sedimentation tank.
example 2
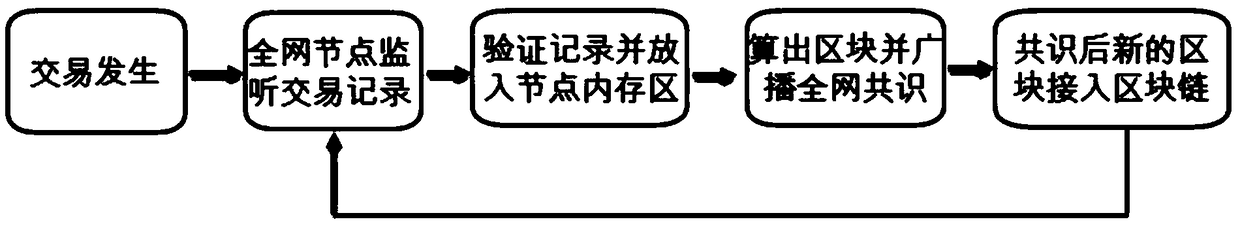
[0038] Invention Example 2: The flow chart of the automatic life cycle management method of the present invention is as follows Figure 5 shown. When a node is ready to perform block synchronization, the system will query the last access time of the block and the number of access times of the block, and based on this, whether the block is still within the access validity period, if it has exceeded the validity period and the access times If it is less than the set threshold v_total, the block will be deposited to the sedimentation tank, and the blocks in the sedimentation tank will no longer be synchronized normally, but the data will still be saved, and the sedimentation tank will be used as a whole for synchronous backup. If the precipitated block needs to be accessed again, it can apply for block recovery. If the sedimentation block has not been accessed within the lifetime, it will be destroyed in the sedimentation pool, its block data will no longer be backed up, and it ...
example 3
[0039] Invention Example 3: The flow chart of the node-initiated life cycle management method in the present invention is as follows Figure 6 shown. When the node is ready to synchronize the block, the user can mark the invalid block according to the demand, and the system will send a block precipitation or destruction request to other nodes after the block is marked. If the agreed number of nodes exceeds the number of requested nodes N_apply, the block can be precipitated or destroyed, and then the block is synchronized; if the number of agreed nodes is insufficient and the number of requested nodes N_apply is required, the block is directly synchronized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com