Movable in-situ analysis root box and using method thereof
An in-situ analysis and active technology, applied in the field of soil science, can solve the problems of high cost, poor applicability, and difficulty of in-situ and localized analysis of root morphological characteristics and the relationship between roots and soil. To achieve the effect of facilitating post-cleaning and maintenance, and realizing volume size adjustment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
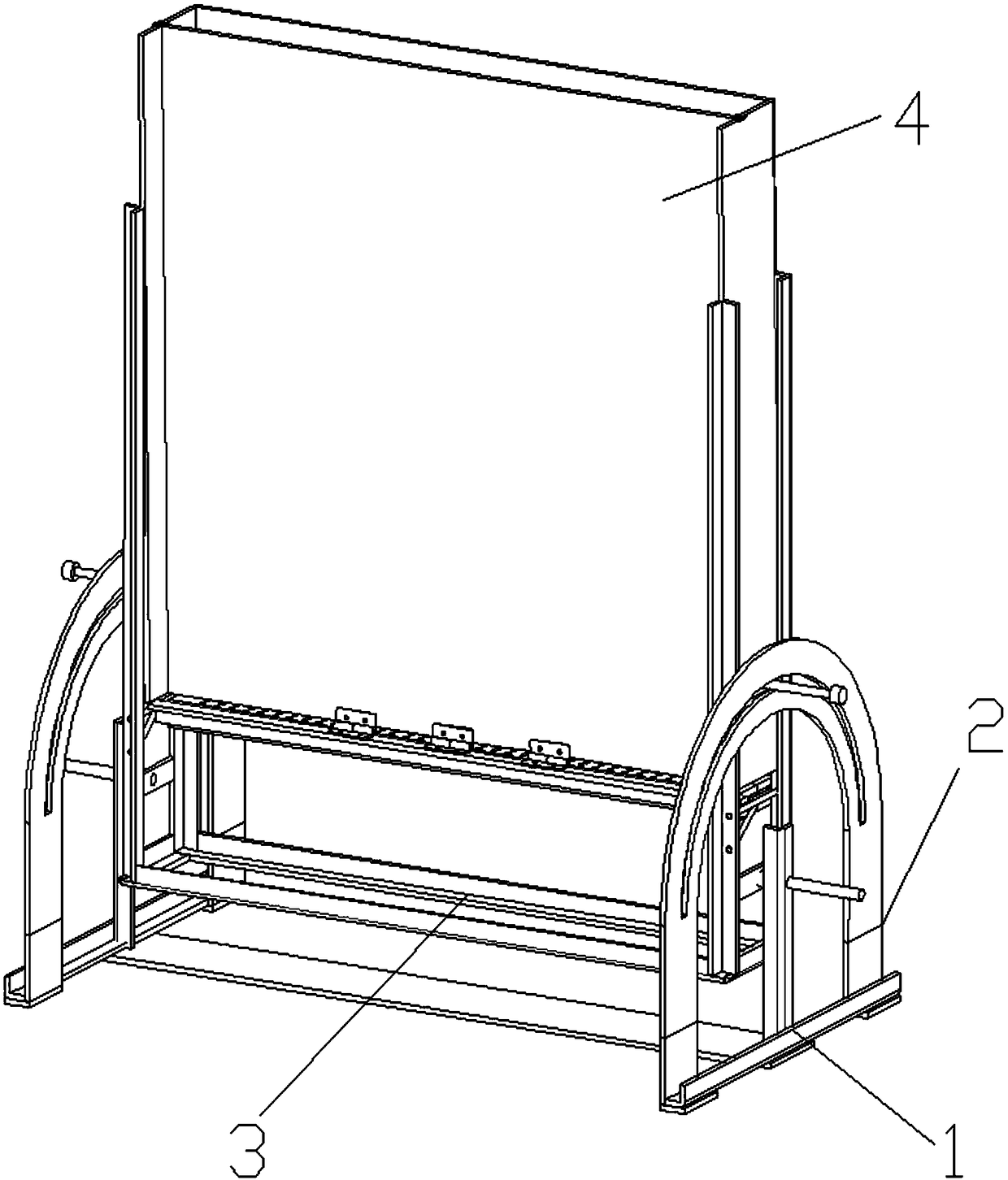
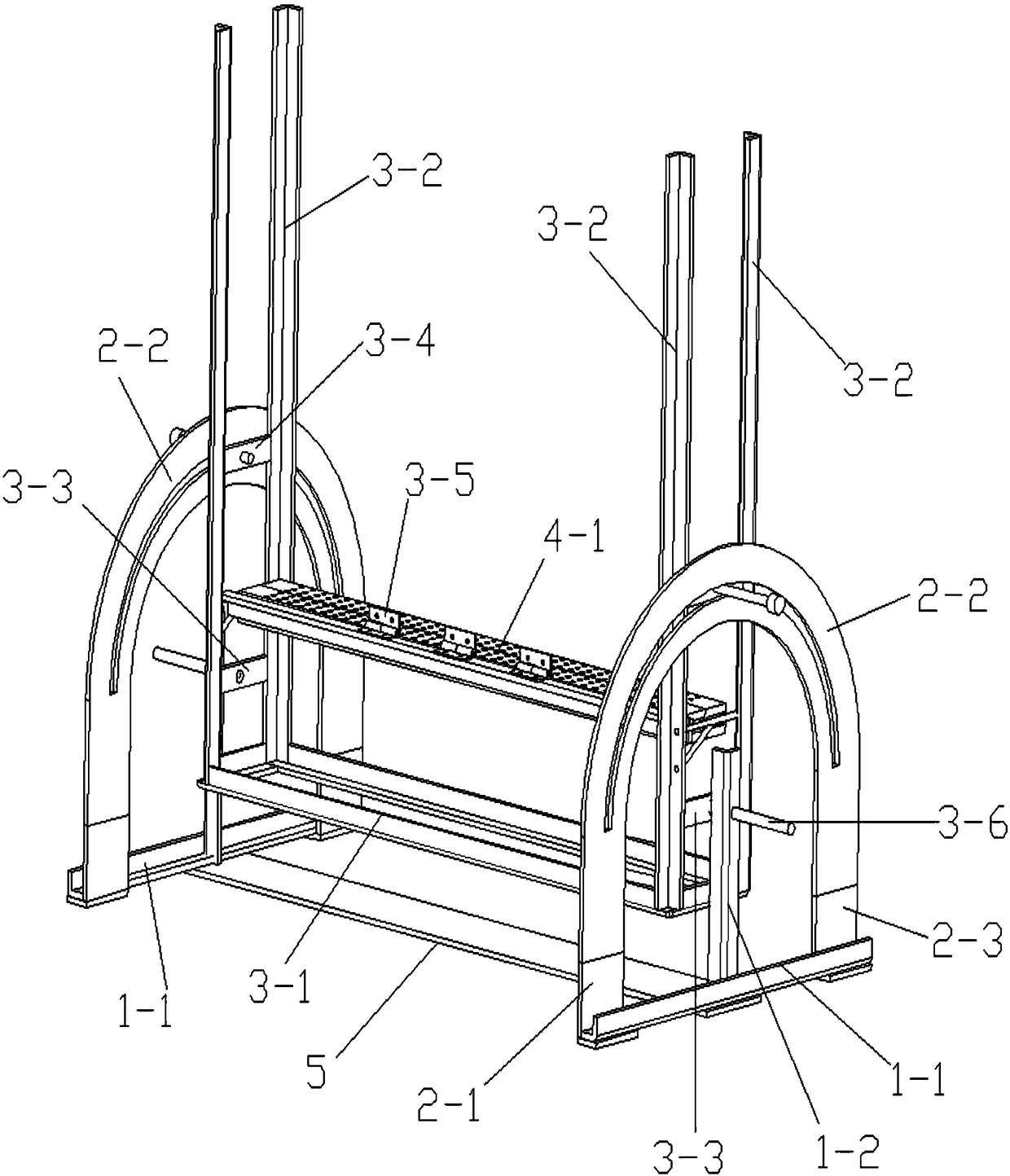
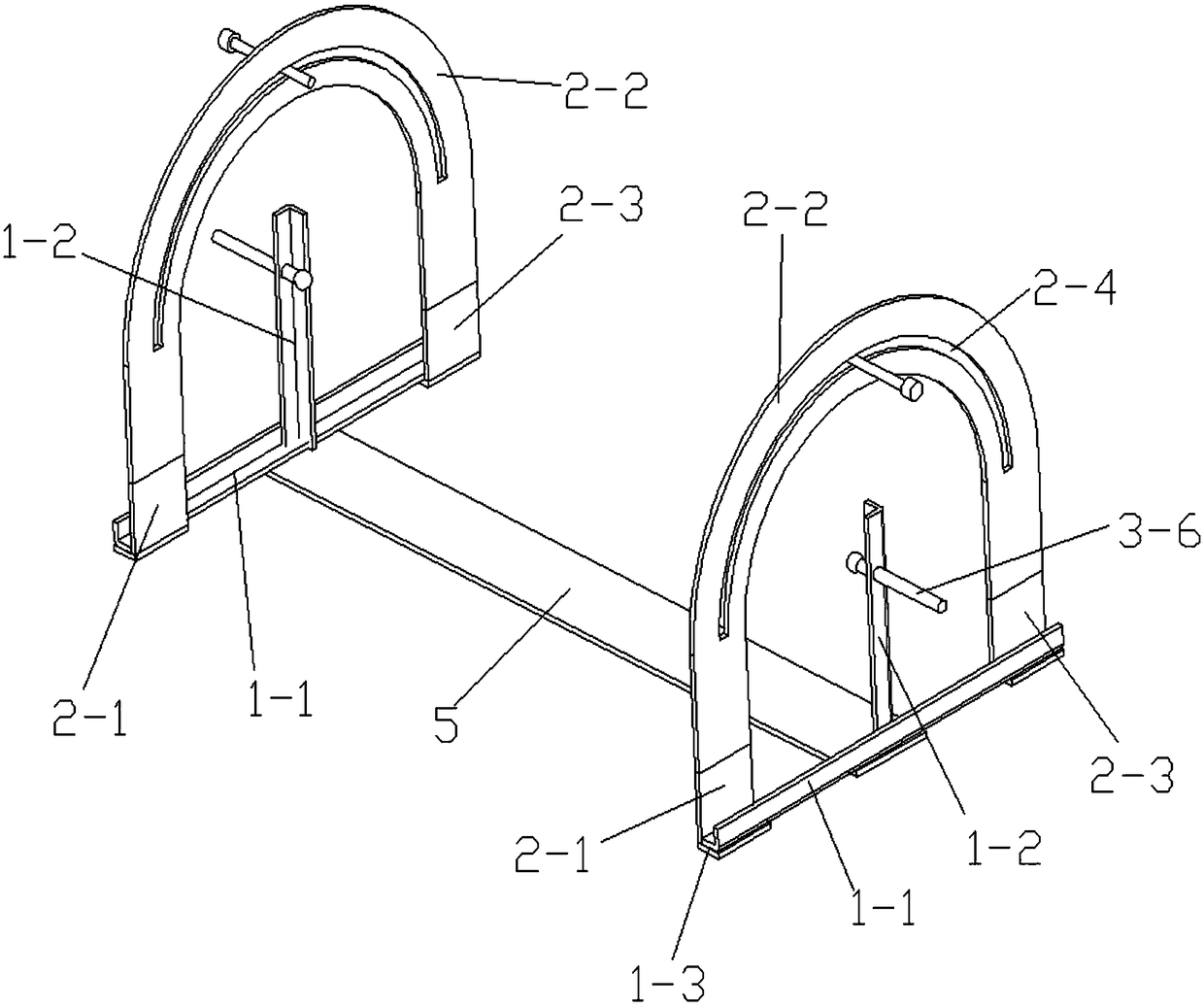
[0043] combine figure 1 As shown, a movable in-situ analysis root box includes a bracket, a box frame rotatably installed on the bracket, a plurality of solid side plates connected in sequence and fixed on the box frame, and a telescopic telescopic box mounted on the box frame. The living side panel installed on the box frame by block and translation. The box frame can rotate around the bracket, and the solid side panels are all set vertically, that is, the solid side panels are vertical, and each solid side panel is fixed on the box frame, and the sides of multiple solid side panels are sequentially connected together. The telescopic block can move up and down along the box frame, and the living side plate can translate back and forth on the box frame. The movable side panels that move horizontally along the inner walls of the fixed side panels are vertically arranged. In contact with each other, from a top view, the movable side panels and multiple fixed side panels form ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Except the following technical features, all the other unmentioned technical features are the same as embodiment 1.
[0065] When using root boxes for in situ analysis, do the following:
[0066] Step 1: Set the volume of the cultivation room to 0.036m by adjusting the moving rod and the tripod 3 (600mm×600mm×100mm);
[0067] The second step: the cutting area is 600mm×100mm nylon cloth (the mesh is 0.025mm), and spread it on the bottom surface of the cultivation room (the upper surface of the telescopic block);
[0068] The third step: put the red soil that has been naturally air-dried and passed through a 2mm sieve into the cultivation room, water it thoroughly, and properly compact the red soil in the cultivation room;
[0069] The fourth step: Transplant the half-year-old yellow beam seedlings into the cultivation room and cover them with shading insulation film; by adjusting the bolts connected to the rotating parts connected to the second longitudinal rod of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Except the following technical features, all the other unmentioned technical features are the same as embodiment 1.
[0076] When using root boxes for in situ analysis, do the following:
[0077] Step 1: Set the volume of the cultivation room to 0.0108m by adjusting the moving rod and the tripod 3 (600mm×300mm×60mm);
[0078] The second step: the cutting area is 600mm×60mm nylon cloth (the mesh is 0.025mm), and spread it on the bottom surface of the cultivation room (the upper surface of the telescopic block);
[0079] Step 3: mix the red soil and urban sewage sludge (both naturally air-dried and passed through a 2mm sieve) in a mass ratio of 1:1, put them into the cultivation room, water them thoroughly, and properly compact the cultivation room matrix;
[0080] Step 4: Transplant the 1-year-old seedlings of Scherichia hemanthus into the cultivation room, cover with shading and thermal insulation film; connect the rotating part connected with the second vertical rod ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com