Acquiring method for moving distance of gas-liquid phase interface in micrometer capillary passage
A technology for interface movement and acquisition methods, applied in chemical instruments and methods, surface tension analysis, surface/boundary effects, etc., can solve problems such as inability to directly measure contact angle, inability to observe phase interface movement process, and small field of view
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
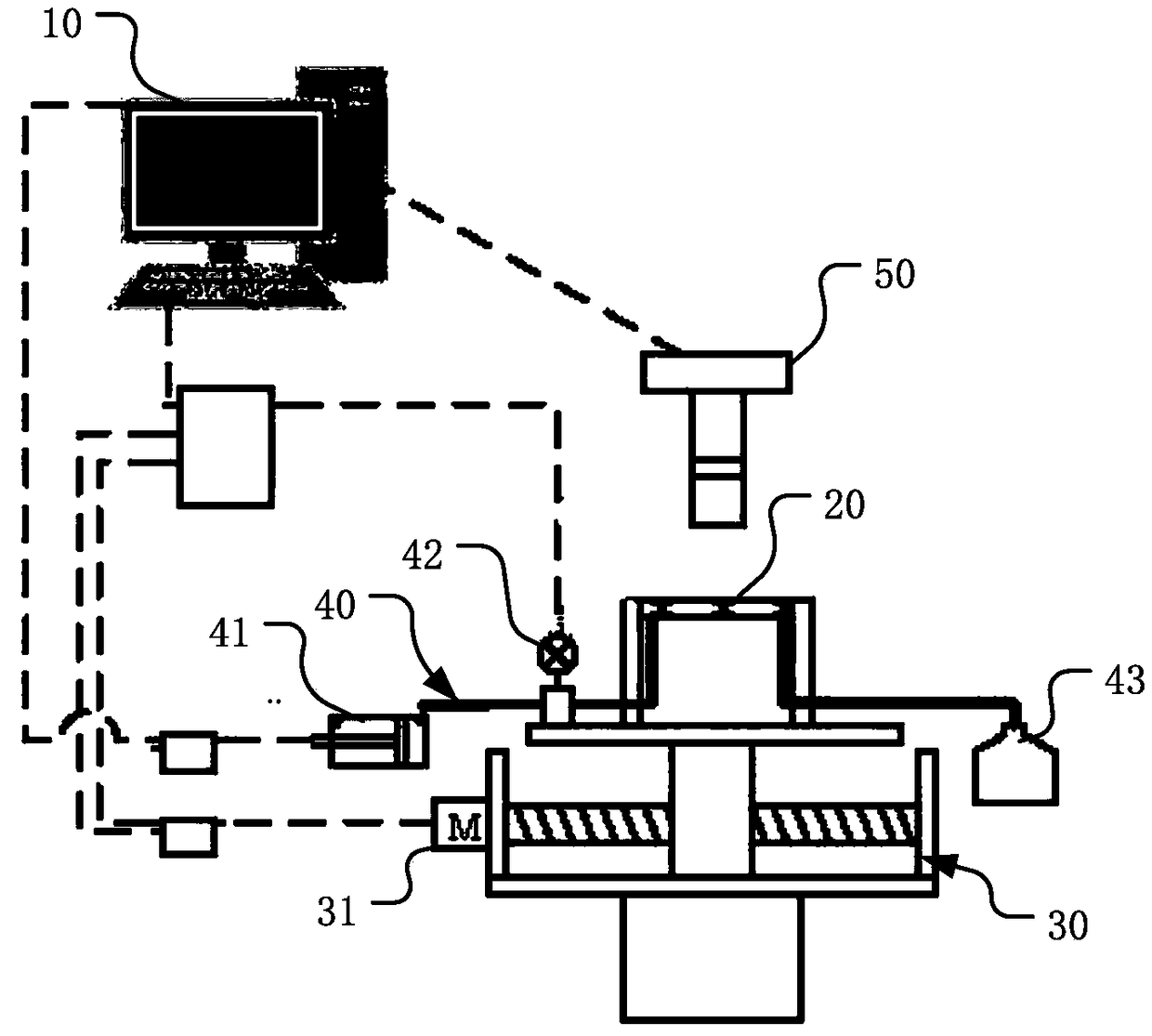
[0110] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for obtaining a gas-liquid phase interface in a micron capillary channel, which generally includes the following steps:
[0111] Step 100, installing the microfluidic chip selected for measurement on the mobile seat of the mobile platform of the dynamic measurement device and connecting the syringe pump, adjusting and installing the camera unit, and connecting each device with the control system at the same time;
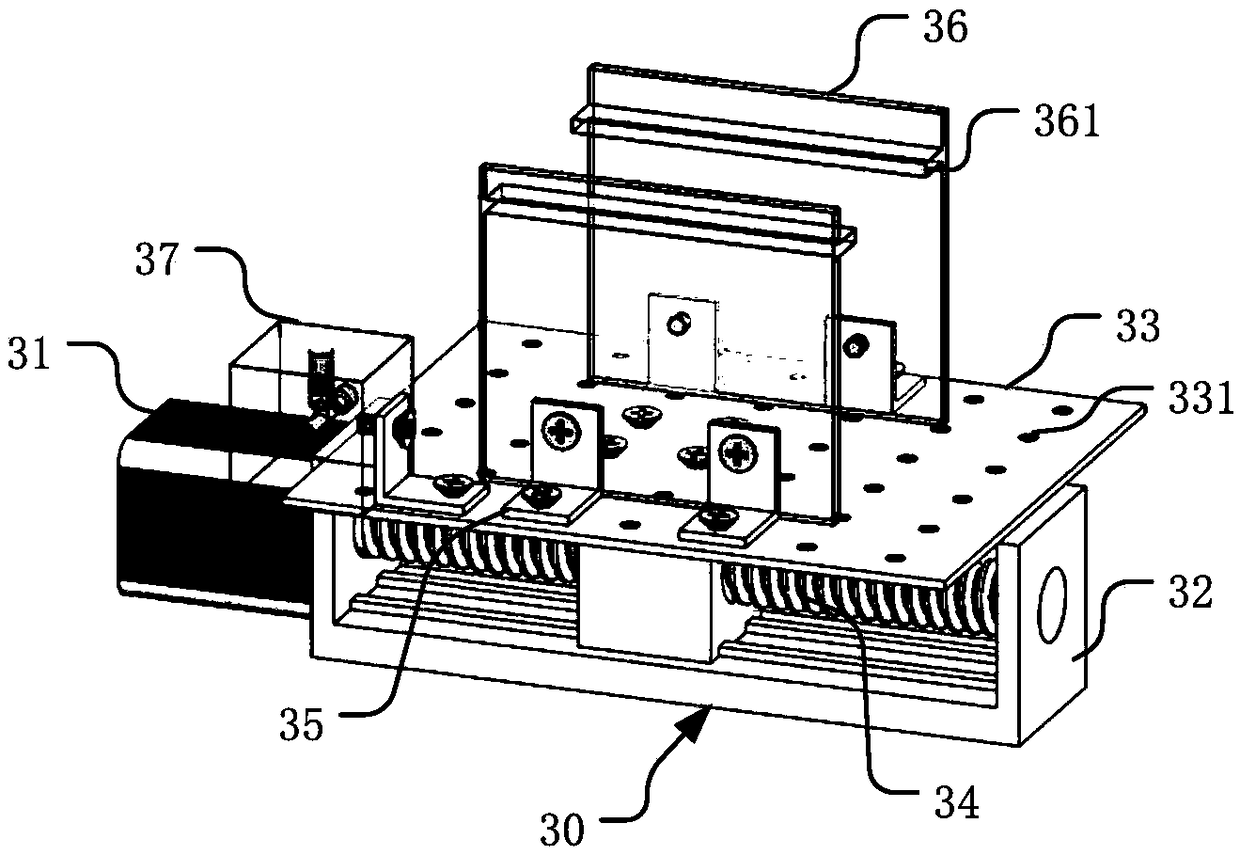
[0112] Such as figure 2 , 3 As shown in , 4 , the dynamic measurement device involved in this embodiment generally includes a microfluidic chip 20 , a pressure control pipeline 40 , a mobile platform 30 , a camera unit 50 and a control system 10 .
[0113] The microfluidic chip 20 is used for passing the test liquid, and is provided with a micron capillary channel 21; the specific microfluidic chip 20 may be a plate-shaped structure made of glass, organic material, or the like. The micron ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com