Posterior probability distribution calculation method and system for mountain fire disaster failure in power network
A technology of posterior probability distribution and failure probability distribution, applied in calculation, complex mathematical operations, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to accurately analyze the risk of mountain fire disasters in power grids, and achieve high practical value, convenient operation, and clear principles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The method for calculating the posterior probability distribution of the grid mountain fire disaster fault in the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0035] S1: Statistics of transmission line mountain fire trip data under different mountain fire disaster conditions; analysis of the relationship between the key elements of transmission line faults and the number of mountain fire trips; elements related to mountain fire trips (including but not limited to: number of fire points, precipitation, wind speed , relative humidity, etc. Since the factors associated with wildfire tripping may vary in different regions, here are just a few general factors that may be related to wildfire tripping).
[0036] S2: Construct the fault probability distribution function of the transmission line relevant with a plurality of fault probability distribution parameters;
[0037] S3: Obtain the prior probability distribution of each failure probability distrib...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A method for calculating the posterior probability distribution of a power grid mountain fire disaster fault in this embodiment includes:
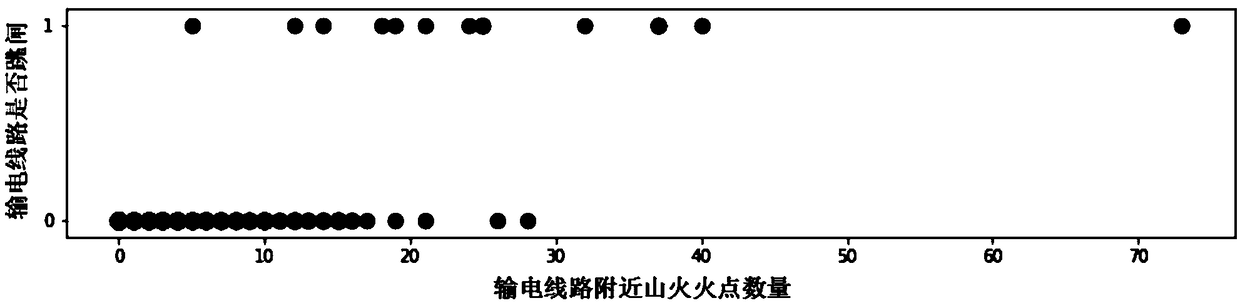
[0045] S1: Calculated the mountain fire trip data of 500kV and above transmission lines of a power grid from 2012 to 2018, and calculated the number of fire points in the 5km corridor of each 500kV transmission line according to the fire point data of the University of Maryland Mountain Fire Database, as follows figure 2 shown.
[0046] S2: According to the relationship between the number of fire points and the line mountain fire trip, the logistic distribution function is selected to fit the relationship between the number of fire points and the line mountain fire trip, the formula is as follows:
[0047]
[0048] In the formula, T is the number of fire points in the transmission line corridor; α and β are the two parameters of the distribution function; P is the trip probability of line mountain fire.
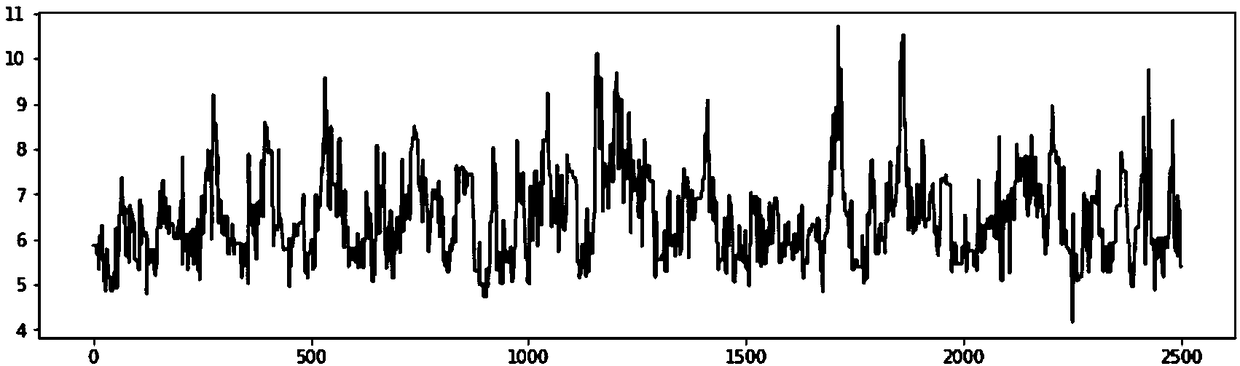
[0049] S3: Since there...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com