Method for extracting microcystis aeruginosa extracellular polymer
A technology of Microcystis aeruginosa cells and extracellular polymers, which is applied in the field of extraction of extracellular polymers of Microcystis aeruginosa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] 1. Samples of Microcystis aeruginosa: Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-469 purchased from the Wild Biological Germplasm Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences—Freshwater Algae Species Bank, placed in a light incubator and cultured with BG11 medium; the culture temperature is 25°C , the time is set to 12Hr day: 12Hr night, and the light condition is 2000Lux. Take 500ml of algae liquid, filter it, and dry it at 105°C until it reaches a constant weight, and the dry matter of the algae liquid is about 0.6g / L. Before the experiment, the density of the algae liquid algae was measured to be about 7×10 8 per L, the chlorophyll content is about 3800mg / L, and the photosynthetic activity (Fv / Fm) is about 0.4.
[0061] 2. Extraction and separation of EPS from Microcystis aeruginosa
[0062] Specific steps are as follows:
[0063] (1) Take 500ml of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-469 algae liquid, centrifuge at 4°C and 2500g centrifugal force for 15 minutes in an ultra-low temperature ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] In this example, different methods are used to extract and separate Microcystis aeruginosa EPS. Except that step (3) is different from Example 1, the rest of the steps are exactly the same as Example 1.
[0068] The processing method of step (3) is as follows:
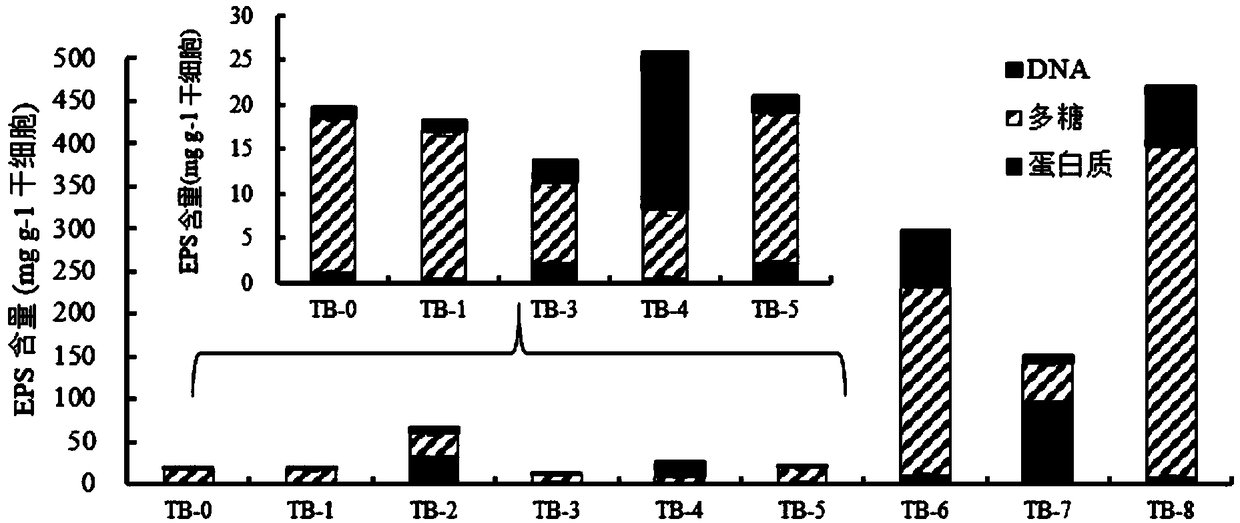
[0069] Treatment 1 (referred to as TB-1): resuspend the residue of the lower layer of step (2) in 0.05% NaCl buffer solution, and sonicate for 2 min under the conditions of 120W and 25kHz; then, place the buffer solution at 4°C to Centrifuge at 15,000 g for 20 minutes, and take the supernatant to obtain a tightly bound extracellular polymer (TB-EPS).
[0070] Treatment 2 (referred to as TB-2): Resuspend the residue of the lower layer in step (2) in 0.05% NaCl buffer solution, heat in a water bath at 60°C for 30min; then, centrifuge the buffer solution at 4°C with a centrifugal force of 15000g After 20 minutes of operation, the supernatant was taken to obtain a tightly bound extracellular polymer (TB-EPS).
[0...
Embodiment 3
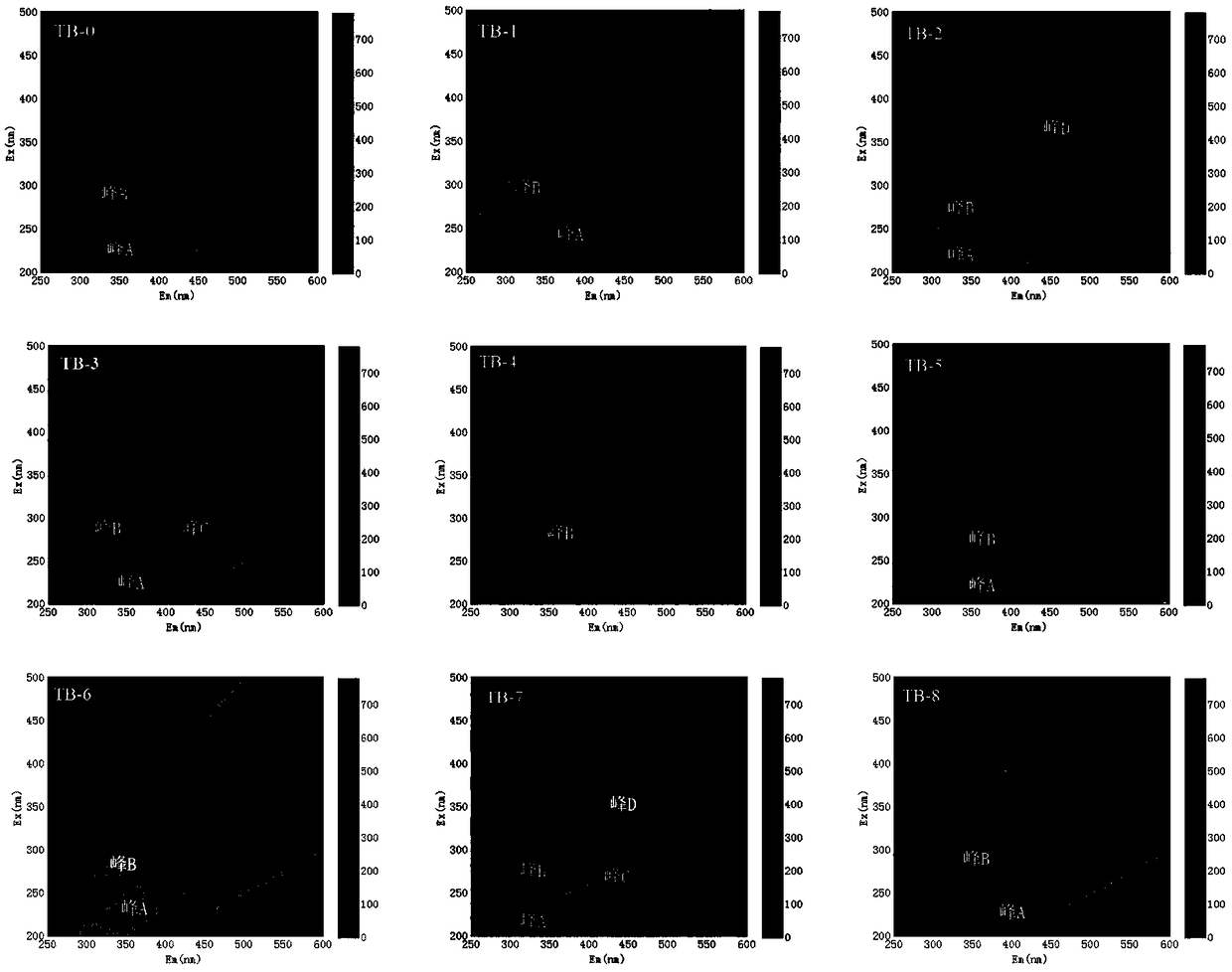
[0093] This example explores the effects of changes in pH value, stirring speed and time, and water bath temperature and time on EPS pollution and three-dimensional fluorescence characteristics. Except that step (3) is different from Example 1, the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1. 1 is exactly the same.
[0094] The processing method of step (3) is as follows:
[0095] Treatment 1: Resuspend the residue of the lower layer of step (2) in 0.05% NaCl buffer, add sodium hydroxide, adjust the pH of the buffer to 8, 9, 10, 11 respectively, at 4°C and 80rpm After stirring for 10 minutes, place it in a water bath at 60°C and heat it for 30 minutes; then, centrifuge the buffer solution at 4°C with a centrifugal force of 15,000 g for 20 minutes, and take the supernatant to obtain a tightly bound extracellular polymer (TB-EPS) .
[0096] Treatment 2: Resuspend the residue of the lower layer of step (2) in 0.05% NaCl buffer solution, add sodium hydroxide, adjust the pH of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com