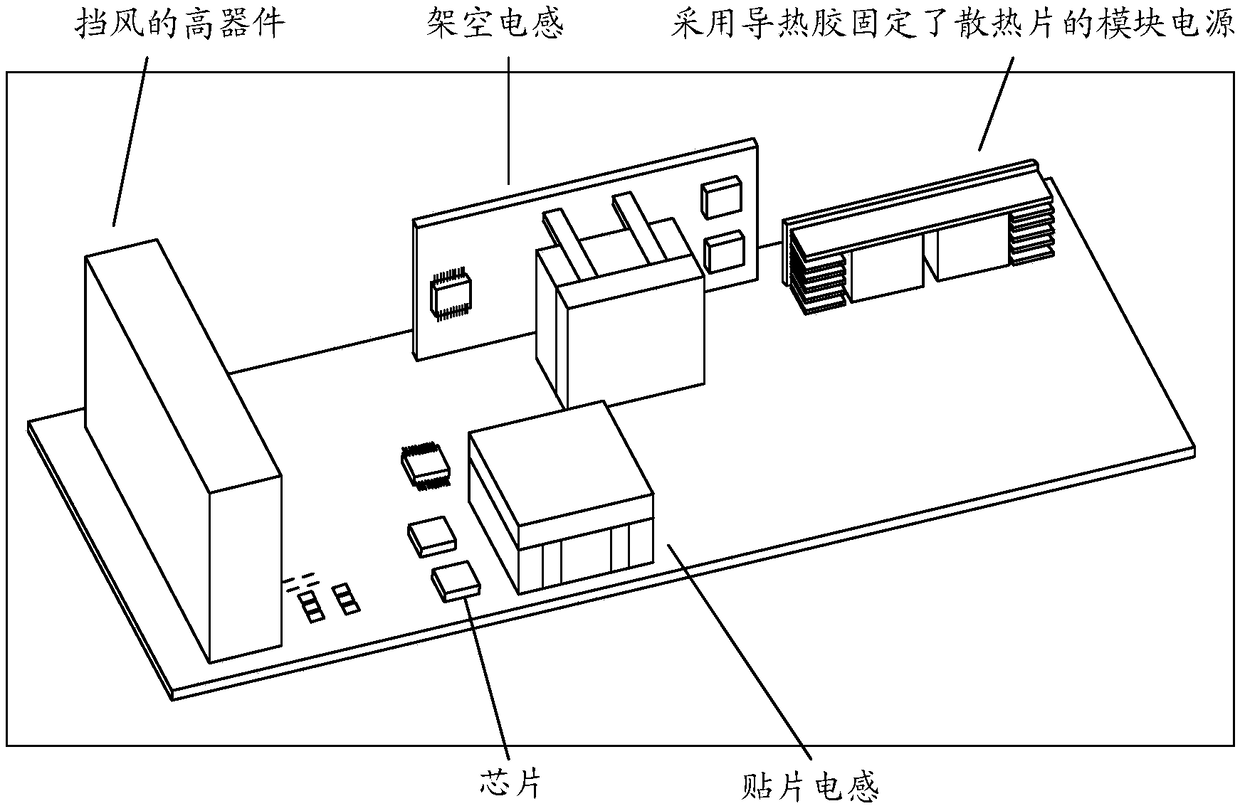
Heat dissipation structure
A technology of heat dissipation structure and heat sink, applied in cooling/ventilation/heating transformation, modification by conduction heat transfer, transformer/inductor cooling, etc. The efficiency, service life and reliability of power components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
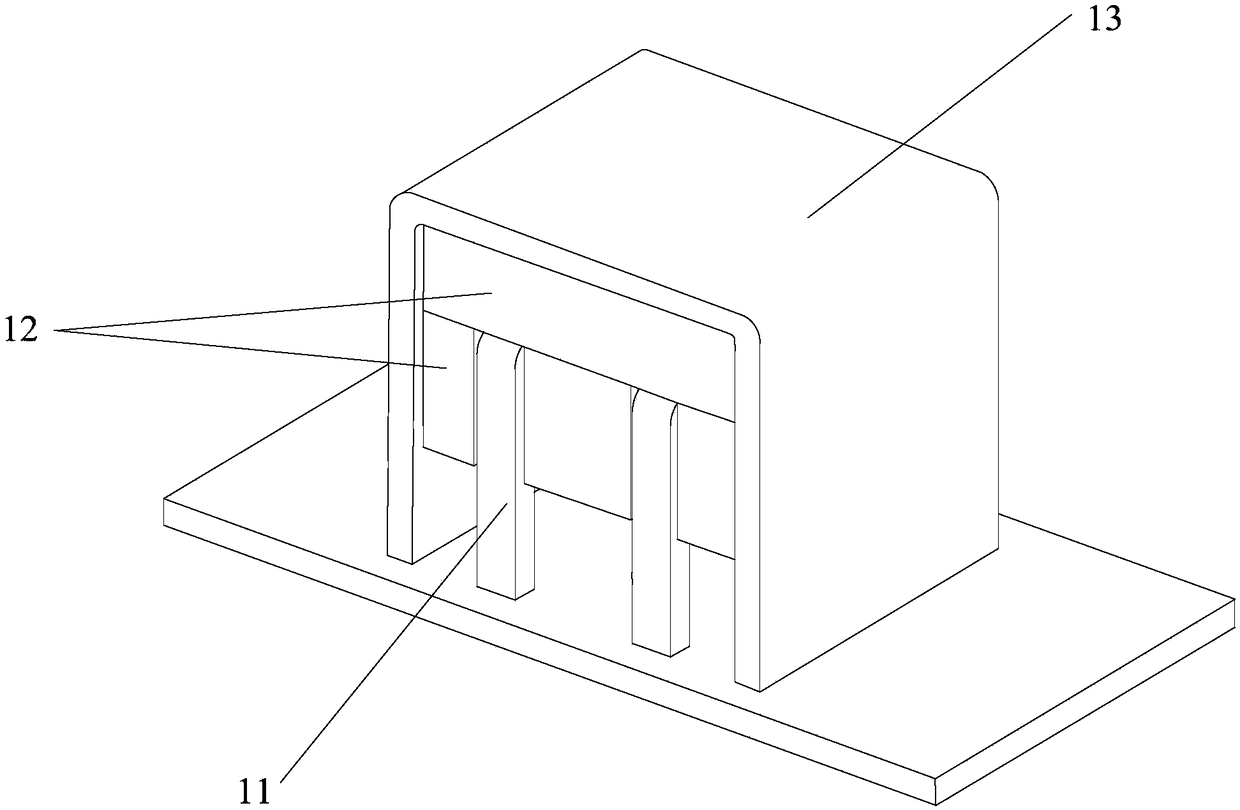
[0096] refer to image 3 , Figure 4 ,in, image 3 An exploded view of the inductor with an integral heat sink, Figure 4 It is an assembly diagram of an inductance with an integral heat sink, and the inductance, as the first type of heating component, includes: winding 11 and magnetic core 12; among them,
[0097] The magnetic core 12 is divided into two parts, the first part of the magnetic core 12 is adjacent to the heat sink 13, and the second part of the magnetic core 12 is adjacent to the circuit board. The second magnetic core 12 is divided into three sub-blocks, with windings 11 arranged between two sub-blocks, and two windings 11 arranged between the three sub-blocks.
[0098] The inductor is supported on the circuit board 14 through the winding 11 and has an overhead structure relative to the circuit board 14 .
[0099] The gap between the magnetic core 12 and the winding 11 of the inductor is filled with a flexible heat-conducting material. A flexible thermally...
Embodiment 2
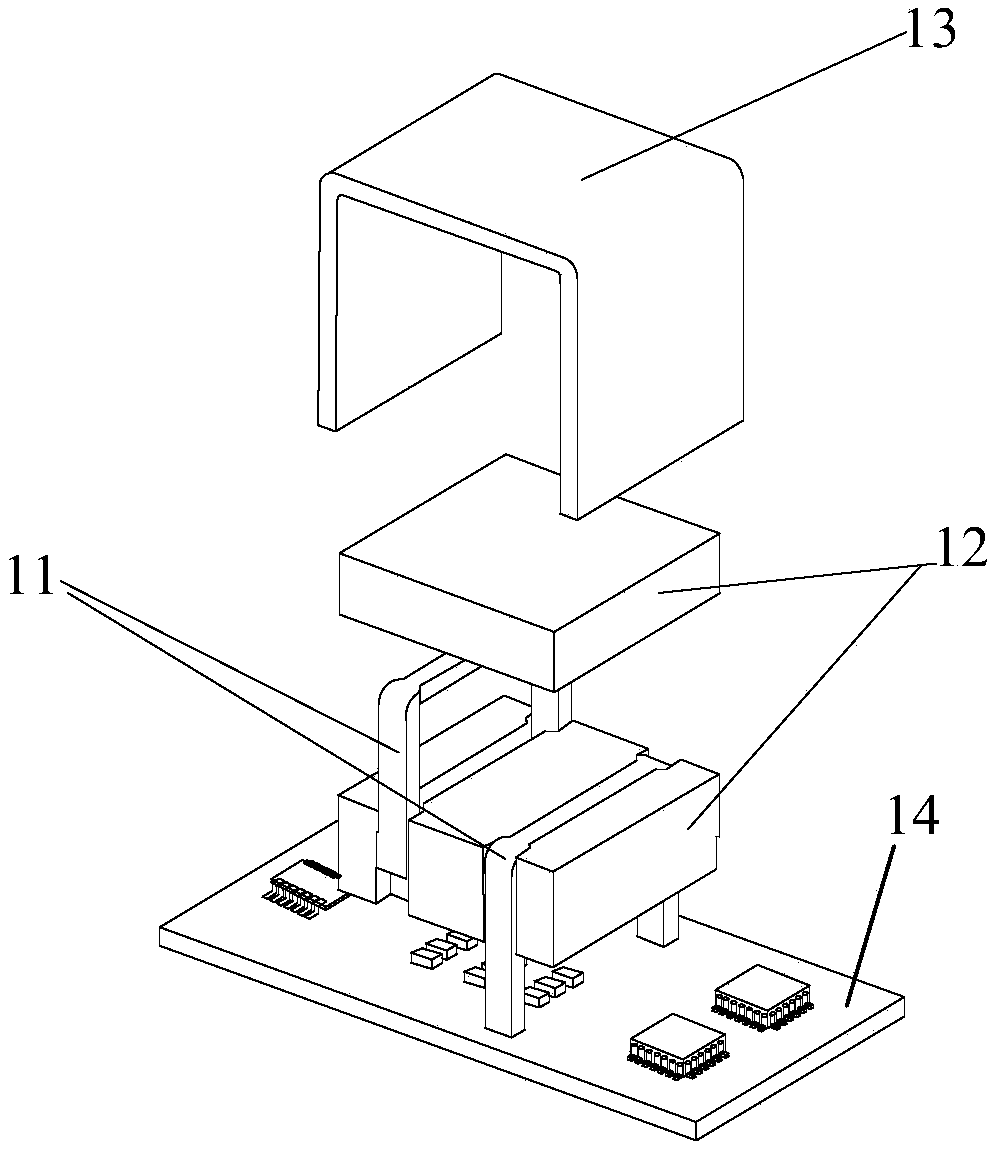
[0103]refer to Figure 5 , Figure 6 ,in, Figure 5 An exploded view of the inductor with an integral toothed heat sink, Figure 6 It is an assembly diagram of an inductance with an integral toothed heat sink, and the inductance as a magnetic device includes: winding 11, magnetic core 12; wherein,
[0104] The magnetic core 12 is divided into two parts, the first part of the magnetic core 12 is adjacent to the heat sink 13, and the second part of the magnetic core 12 is adjacent to the circuit board. The second magnetic core 12 is divided into three sub-blocks, with windings 11 arranged between two sub-blocks, and two windings 11 arranged between the three sub-blocks.
[0105] The inductor is supported on the circuit board 14 through the winding 11 and has an overhead structure relative to the circuit board 14 .
[0106] The gap between the magnetic core 12 and the winding 11 of the inductor is filled with a flexible heat-conducting material. A flexible thermally conducti...
Embodiment 3
[0110] refer to Figure 7 , Figure 8 ,in, Figure 7 An exploded view of the inductor with two discrete toothed heat sinks, Figure 8 It is an assembly drawing of an inductor with two discrete toothed heat sinks, and the inductor as a magnetic device includes: a winding 11 and a magnetic core 12; wherein,
[0111] The magnetic core 12 is divided into two parts, the first part of the magnetic core 12 is adjacent to the heat sink 13, and the second part of the magnetic core 12 is adjacent to the circuit board. The second magnetic core 12 is divided into three sub-blocks, with windings 11 arranged between two sub-blocks, and two windings 11 arranged between the three sub-blocks.
[0112] The inductor is supported on the circuit board 14 through the winding 11 and has an overhead structure relative to the circuit board 14 .
[0113] The gap between the magnetic core 12 and the winding 11 of the inductor is filled with a flexible heat-conducting material. A flexible thermally ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com