Method for degrading sulfonylurea herbicides through composite microbial system
A technology for sulfonylureas and herbicides, which is applied in the field of degrading sulfonylurea herbicides, can solve problems such as the ecological environment of pesticide residues and the negative impact on the quality and safety of agricultural products, and achieve the effects of enriching diversity and improving degradation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
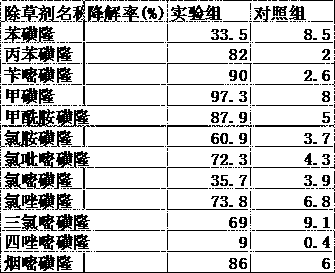
[0044] At a pH of 7.0 and a temperature of 10°C, 15°C, 20°C, 25°C and 30°C, the control group and the experimental group were placed on a constant temperature shaker, and the degradation rate was measured after 20 days of culture. The results show that 20℃ is the best temperature for the compound bacteria to degrade herbicides. At this time, the degradation rate of the four herbicides can reach more than 85%. When the temperature is 15℃, the degradation rate can reach more than 50%. Above 20°C, the degradation rate will decrease, which indicates that the composite strain is suitable for growth in a lower temperature environment.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Set the reaction temperature to 20°C and pH to 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. Place both the control group and the experimental group on a constant temperature shaker, and measure the degradation rate after 20 days of culture. The results show that the composite bacteria have the best degradation effect when pH=7. At this time, the degradation rate of the four herbicides can reach more than 85%, and when it is acid or alkaline, the degradation rate is below 30%. The composition of the compound strain is complex, the pH changes slightly, and some strains are inactivated and die due to inadaptability to the environment.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Set the reaction temperature to 20°C, pH to 7.0, and culture time to 5 days, 10 days, 15 days, 20 days and 25 days respectively. Place the control group and the experimental group on a constant temperature shaker, and measure them after 20 days of culture. Degradation rate. The results show that the degradation rate increases with the increase of time. When it is cultured for 20 days, the degradation rate can reach more than 85%, and when it is cultured for 15 days, the degradation rate can also reach 40%-50%, which shows that when the temperature is 20℃ , The pH is 7.0, and the half-life of the four herbicides is 15 days under the action of the compound strain.
[0049] Conclusion: The present invention utilizes composite bacteria to degrade sulfonylurea herbicides, and it can be known that the present invention can effectively degrade herbicides by measuring the degradation rate of the herbicides. Attaches importance to the synergy between strains, and solves the proble...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com