A program hardening method and device
A technology for hardening devices and programs, which is applied in the direction of program code conversion, program/content distribution protection, decompilation/disassembly, etc., can solve the problem of low security of software products, and achieve the effect of improving security and increasing the difficulty of reverse engineering.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
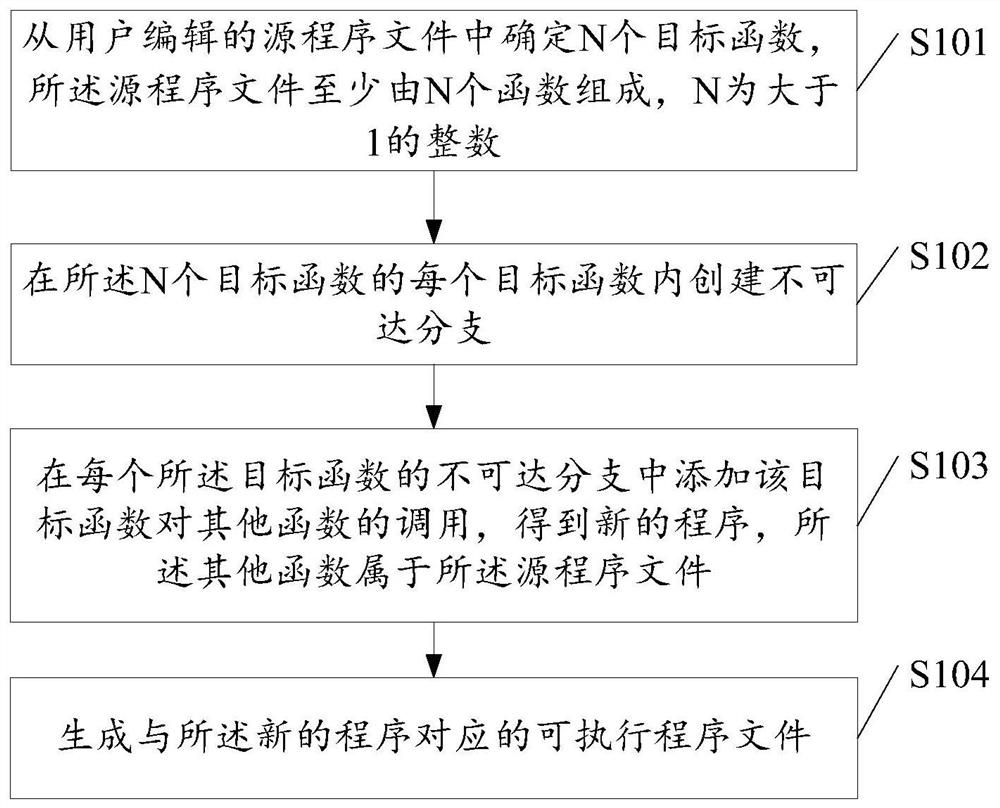
[0133] For each of the target functions, the following steps are respectively performed: in the unreachable branch of the conditional call statement of the target function, adding random calls of other functions by the target function.
[0134] Specifically, in the reachable branch of the conditional call statement of the target function, random calls of functions different from the functions called in the reachable branch by the target function are added.
[0135] For example, the source program file includes function 1, function 1 calls functions 2, 3, and 4, function 3 calls functions 2, 5, and function 4 calls functions 6, 7.
[0136] Create a conditional call statement 1 in the target function 1 (that is, in function 1). In the reachable branch of the conditional call statement 1, function 1 calls functions 2, 3, and 4. In the unreachable branch of the conditional call statement 1 Add random calls of function 1 to functions 1, 5, 6, and 7 in function 1, create conditional...
Embodiment approach 2
[0140] Perform the following steps for each of the target functions: scan the source program file to determine the number of functions in the source program file; judge whether the number of functions in the source program file is greater than a preset value; In the unreachable branch of the conditional call statement of the target function, add the random call of the target function to other functions; otherwise, in the unreachable branch of the conditional call statement of the target function, add the random call of the target function to other functions A one-to-one call.
[0141] Through the second embodiment, it is possible to balance the code size and reverse difficulty of the final generated executable program file.
[0142] In the first and second embodiments above, the random call of the objective function to other functions can be implemented as follows:
[0143] Determine one or more candidate called functions from all the functions in the source program file; in ...
Embodiment approach 3
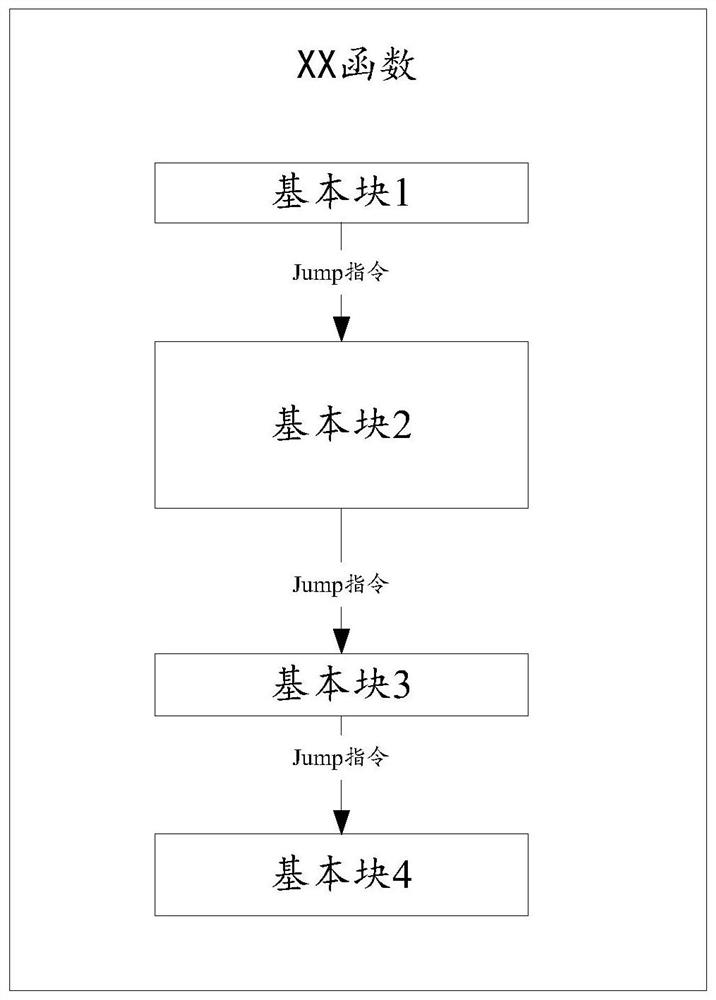
[0166] Embodiment 3: Randomly select more than one basic block from the basic block sequence as the target basic block.
[0167] Through the above three implementation manners, more than one target basic block can be selected from the basic block sequence, and then through step 2, unreachable branches can be respectively created in each target basic block selected from the basic block sequence.
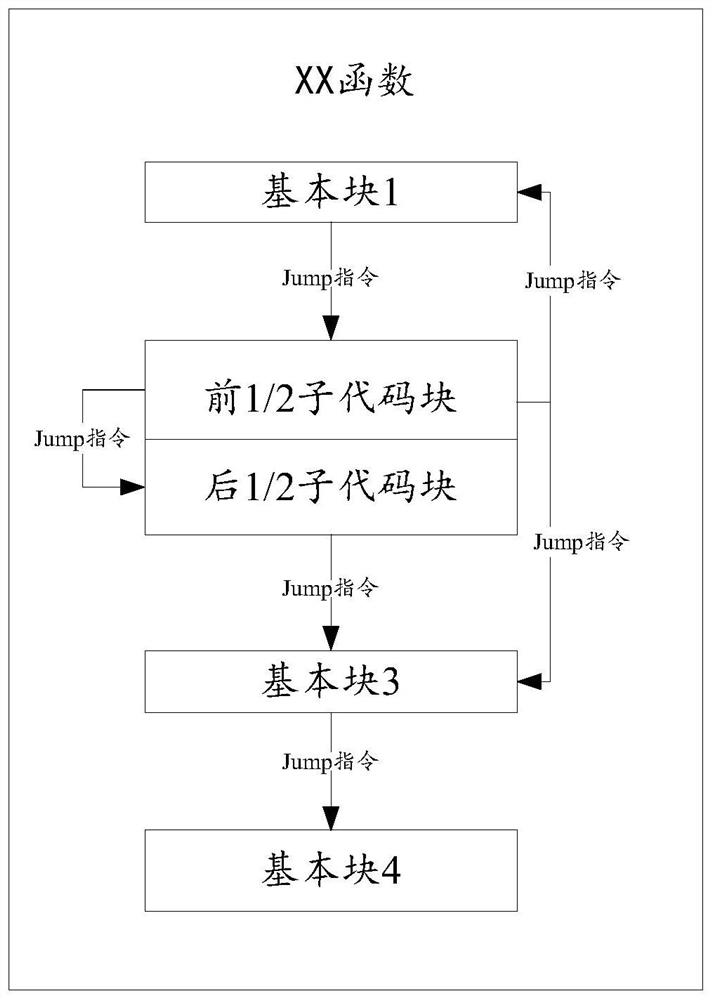
[0168] Specifically, an unreachable branch is created in the target basic block of the basic block sequence, and the implementation may include the following steps 1a-1c:
[0169] Step 1a, dividing the target basic block into M sub-code blocks, where M is an integer greater than 1.
[0170] In the specific implementation process, according to the number of assembly instruction lines of the target basic block, the instructions of the target basic block are equally divided to obtain M sub-code blocks. Specifically, if the basic blocks in the basic block sequence whose size is larger th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com