Self-starting and stopping method of washing of rubber ball of condenser based on DCS
A condenser, self-start and stop technology, applied in the field of cooling water, can solve the problem of unable to meet the remote monitoring of the condenser, unable to directly monitor the cleaning effect of rubber balls, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
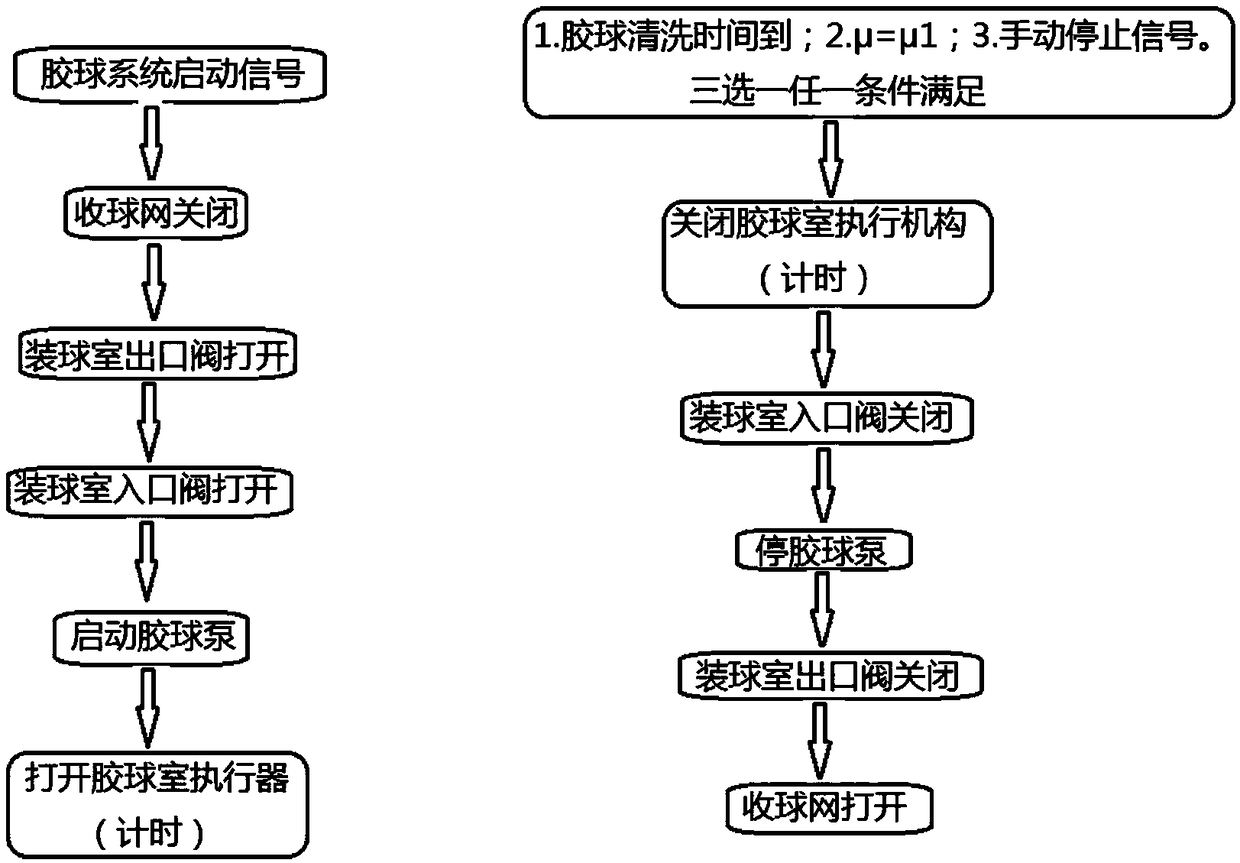
[0092] A DCS-based self-starting and stopping method for condenser rubber ball cleaning, comprising the following steps:
[0093] (1) Preset the cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the side of condenser A in DCS a and the preset cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the B side of the condenser b ;
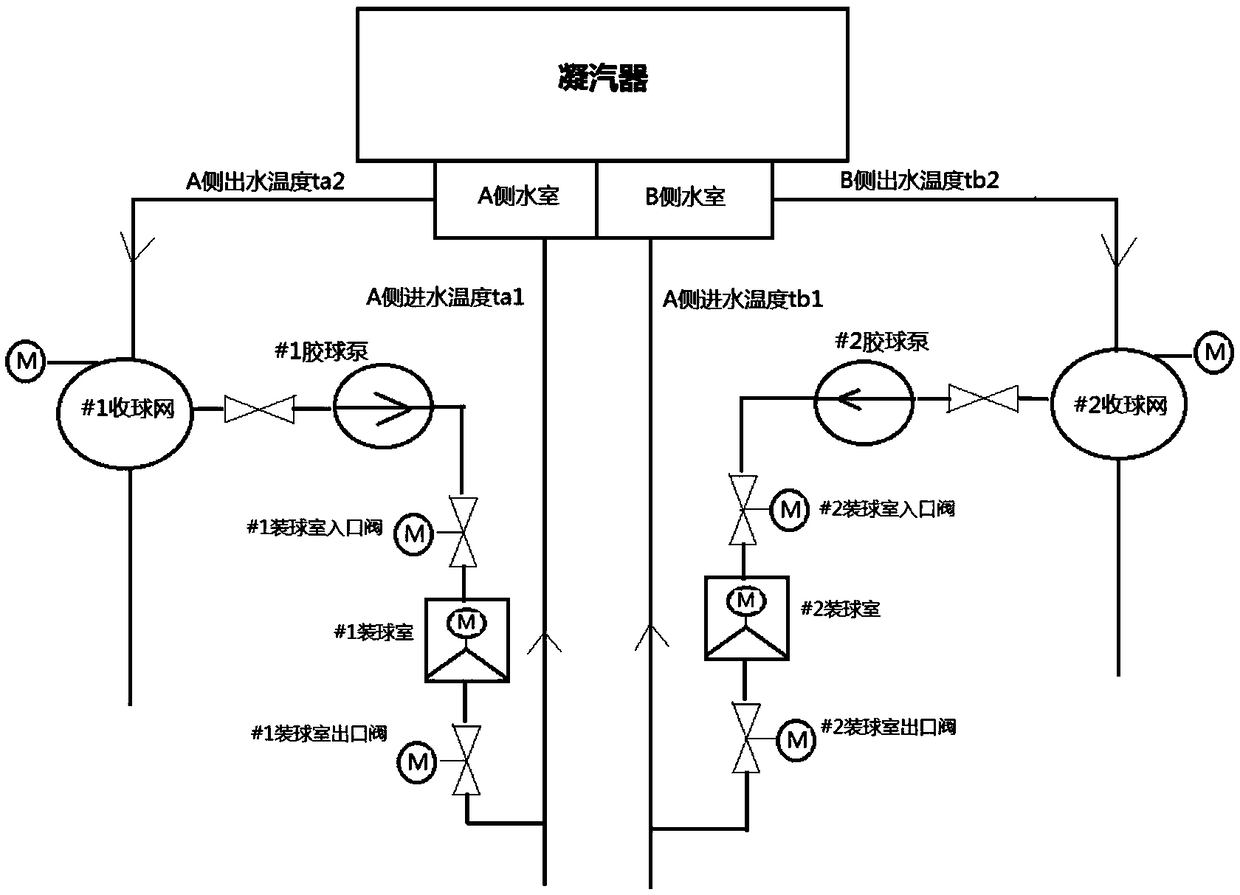
[0094] (2) Collect the working condition data of the condenser, including: high-pressure superheated steam flow q1, medium-pressure superheated steam flow q2, low-pressure superheated steam flow q3, condenser pressure p1, condenser circulating water A side inlet water temperature ta1, Condenser circulating water A side outlet temperature ta2, condenser circulating water B side inlet temperature tb1 and condenser circulating water B side outlet temperature tb2 data;
[0095] (3) Using the condenser working condition data collected in step (2), calculate the actual cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the side A of the condenser circulating water throu...
Embodiment 2
[0167] A DCS-based self-starting and stopping method for condenser rubber ball cleaning, comprising the following steps:
[0168] (1) Preset the cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the side of condenser A in DCS a and the preset cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the B side of the condenser b ;
[0169] (2) Collect the working condition data of the condenser, including: high-pressure superheated steam flow q1, medium-pressure superheated steam flow q2, low-pressure superheated steam flow q3, condenser pressure p1, condenser circulating water A side inlet water temperature ta1, Condenser circulating water A side outlet temperature ta2, condenser circulating water B side inlet temperature tb1 and condenser circulating water B side outlet temperature tb2 data;
[0170] (3) Using the condenser working condition data collected in step (2), calculate the actual cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the side A of the condenser circulating water throu...
Embodiment 3
[0178] A DCS-based self-starting and stopping method for condenser rubber ball cleaning, comprising the following steps:
[0179] (1) Preset the cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the side of condenser A in DCS a and the preset cleaning coefficient μ of the water chamber on the B side of the condenser b ;
[0180] (2) When the condenser needs to run stably with load for more than 10 minutes and / or the load fluctuation of the unit is less than 5MW, collect the working condition data of the condenser, including: high-pressure superheated steam flow q1, medium-pressure superheated steam flow q2, low-pressure superheated steam flow q3 , condenser pressure p1, condenser circulating water A side inlet water temperature ta1, condenser circulating water A side outlet temperature ta2, condenser circulating water B side inlet temperature tb1 and condenser circulating water B side outlet water temperature tb2 data;
[0181] (3) Using the condenser working condition data co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com