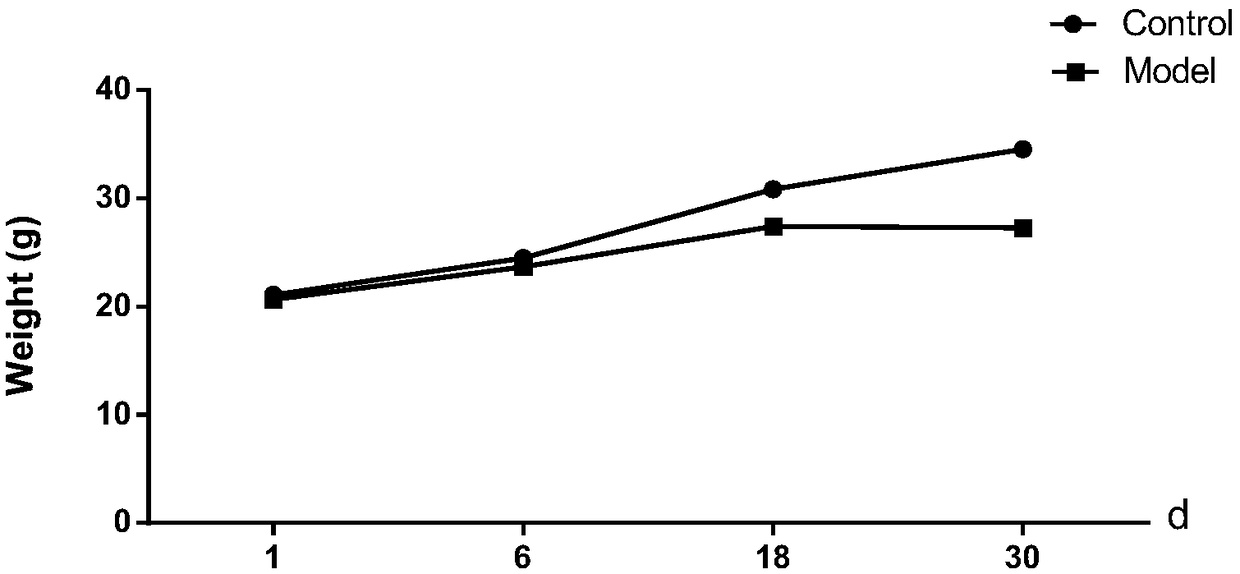
Method of establishing mouse model of functional dyspepsia
A technology of indigestion and mouse models, which is applied in the field of medical animal model modeling, can solve problems such as irritability, incompletely consistent clinical patient disease process, and mouse tail injury, and achieve moderate stress intensity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] This embodiment provides a method for establishing a mouse model of functional dyspepsia, comprising the following steps:
[0056] S1, animal selection and pretreatment;
[0057] Twenty SPF grade Kunming mice were selected, each weighing about 20 g, and the mice were adaptively reared for 7 days before modeling. During rearing, water and feed were supplied adequately and the mice were allowed to drink freely.
[0058] After the adaptive feeding, the mice were divided into two groups, one group was the normal group and the other group was the modeling group, with 10 mice in each group.
[0059] S2, animal model establishment;
[0060] After the adaptive feeding, the modeling was started, and restraint, electric shock, and forced swimming were given in sequence every day. The three stimuli were as follows: After the mice were successfully restrained by restraint tubes, the mice were electroshocked for 5 minutes, and the mice were restrained continuously for 6 hours, and...
Embodiment 2-3
[0083] The modeling methods provided in Examples 2-3 are identical to the modeling methods provided in Example 1, except that the conditions are different.
Embodiment 2
[0085] The mice were reared adaptively for 5 days. The first electric shock was to shock the mouse's tail for 3 minutes, and the duration of restraint was 5.5 hours. The second electric shock was to shock the mouse's tail for 3 minutes.
[0086] Fatigue swimming is 45 minutes after the release of restraint, control mice to swim in water at 19°C, and the standard of fatigue is that the mouse's nose is submerged in the water for 2-4 seconds and cannot be lifted. Modeling for 28 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com