High-sensitivity soil heavy metal element detection device and detection method
A detection device and high-sensitivity technology, applied in the field of LIBS detection, can solve the problems of low sensitivity of heavy metal elements, continuous background interference, low analysis accuracy, etc., so as to reduce the influence of uneven doping and the influence of ablation instability , the effect of high analysis accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1 highly sensitive soil heavy metal element detection device
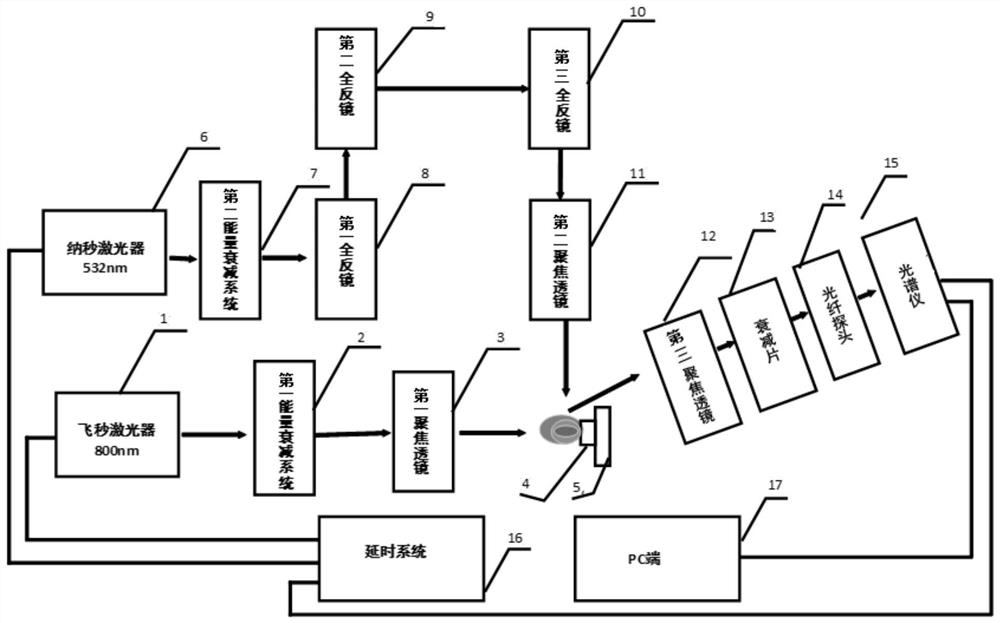
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a heavy metal element detection device in soil based on double-beam LIBS, including: a femtosecond laser 1, a first energy attenuation system 2, a first focusing lens 3, a nanosecond laser 6, a second energy attenuation system 7, Climbing system, second focusing lens 11, two-dimensional translation stage 5, soil target clamp 4, third focusing lens 12, attenuation sheet 13, fiber optic probe 14, spectrometer 15, time delay system 16 and PC terminal 17;
[0051] Wherein, the femtosecond laser 1 is used to output femtosecond pulsed laser, and the femtosecond pulsed laser output by it is focused by the first energy attenuation system 2 and the first focusing lens 3 to form a section of plasma filament in the air, The plasma filament acts on the surface of the soil target, and the plasma generated by the soil target undergoes expansion a...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2 highly sensitive soil heavy metal element detection method
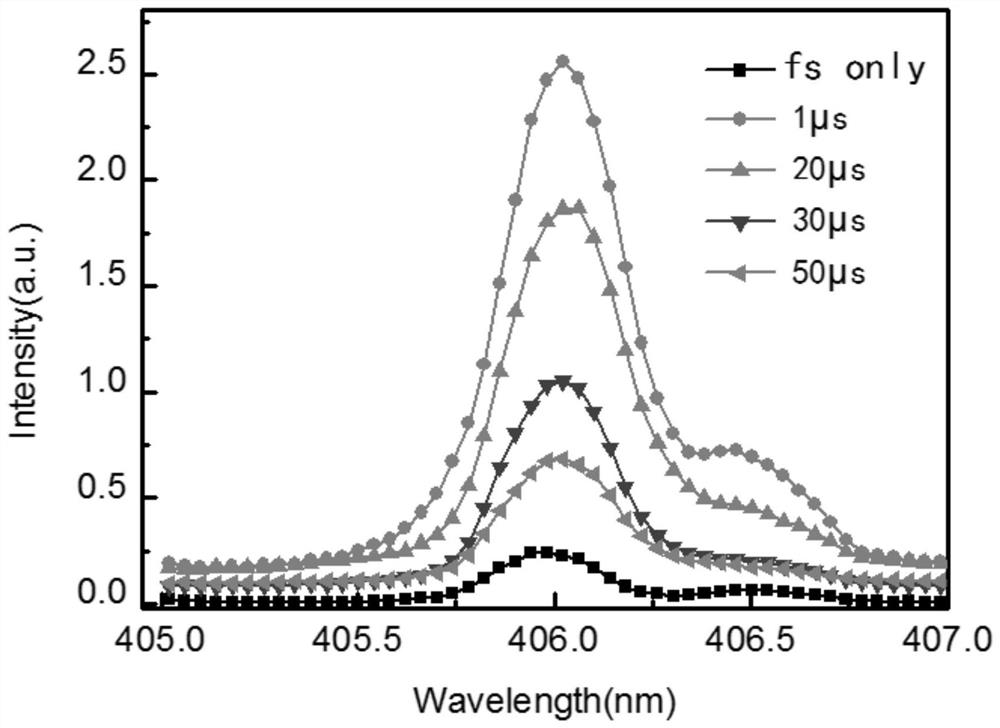
[0068]Step S1: femtosecond pulse laser 1 outputs femtosecond pulse laser, and femtosecond pulse laser is transmitted in the air, the first energy attenuation system 2 ensures that the ablation energy of femtosecond pulse laser is fixed for each experiment, and then the femtosecond pulse laser is focused by the first focusing lens 3 After that (the distance from the first focusing lens to the surface of the soil target is 400-600mm), a section of plasma filament is formed in the air, and the plasma filament ablates the soil target, and the soil target remains fixed in the direction of filament formation. Utilize the one-dimensional translation stage under the first focusing lens 3 to control the position of the femtosecond focused filament ablation soil target, and obtain the characteristic spectral radiation intensity space of the filament ablation soil target generated by the femtosecond laser in ...
Embodiment 3
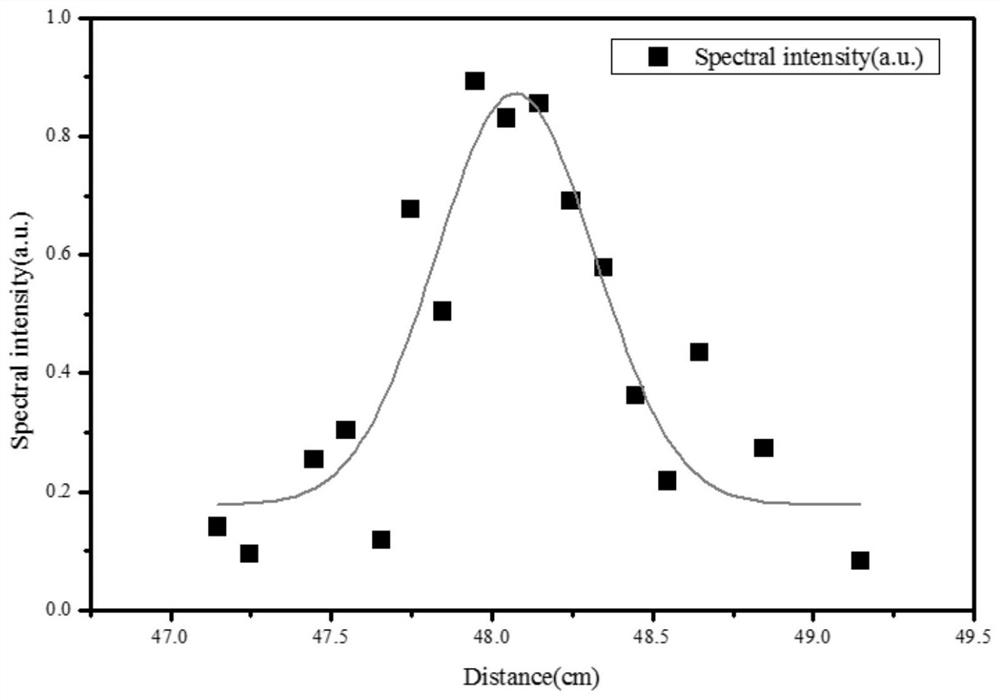
[0075] Example 3 Effect of Femtosecond Laser Focusing Lens Position on Spectral Intensity
[0076] In this embodiment, the soil target material containing heavy metal Pb is detected. During the detection, the femtosecond laser energy is 3.0mJ, and the position of the femtosecond laser focusing lens is changed (the first focusing lens 3 is 472-492mm away from the soil target material position), and the femtosecond laser energy is obtained. Spatial evolution of spectral intensity of soil target by laser filamentation ablation in seconds (such as figure 2 shown); due to the femtosecond filamentation intensity clamping effect, the plasma radiation spectral intensity (PbI405.78nm) does not change much within a certain distance; it can be seen that the use of femtosecond laser characteristics can reduce the surface roughness of the sample The influence brought about improves the detection accuracy.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com