A roadbed surface dehumidifier
A roadbed surface and dehumidifier technology, applied in roads, roads, buildings, etc., can solve problems such as road diseases, increased maintenance costs, and shortened road service life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] (1) Pour the four components of sodium polyacrylate, polyacrylamide, anhydrous calcium chloride and attapulgite into the mixer and mix for 300s to form a hygroscopic agent, and then put the hygroscopic agent into the material preparation tank.
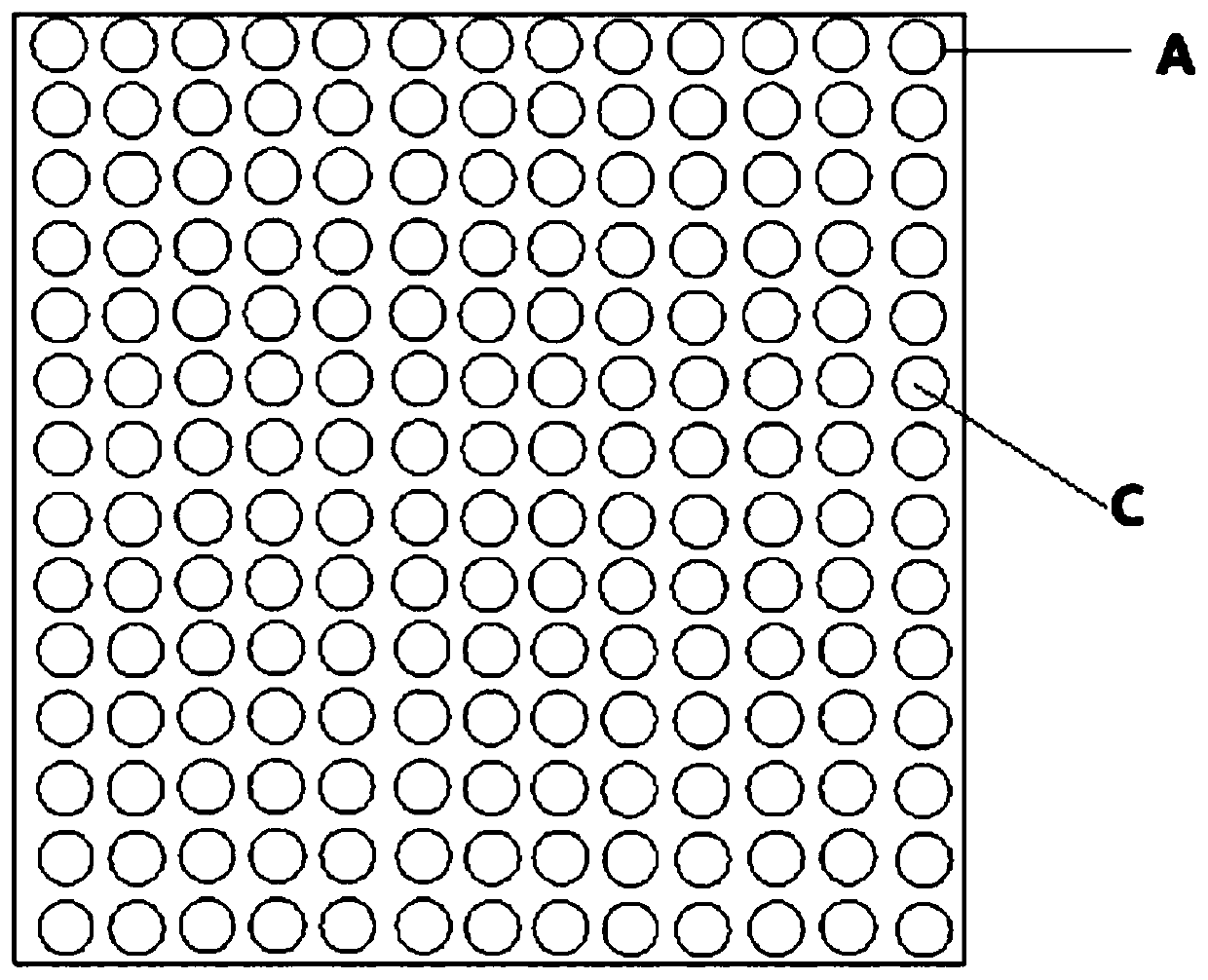
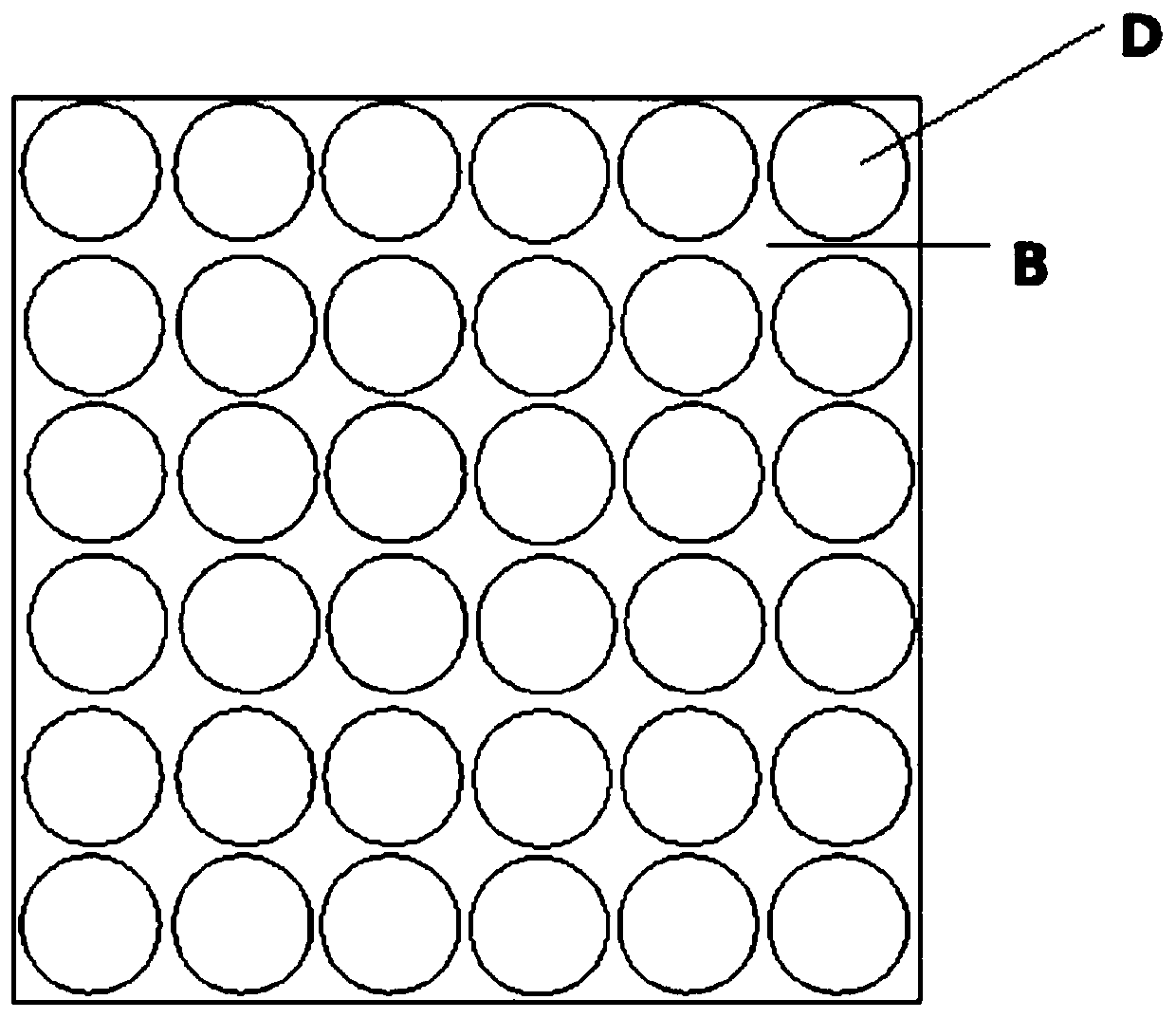
[0071] (2) Take a corresponding mold according to the single hole size of the first substrate, pour the hygroscopic agent in step (1) into the corresponding mold, and use a compression molding machine to press the mixture into a cylindrical hygroscopic agent.
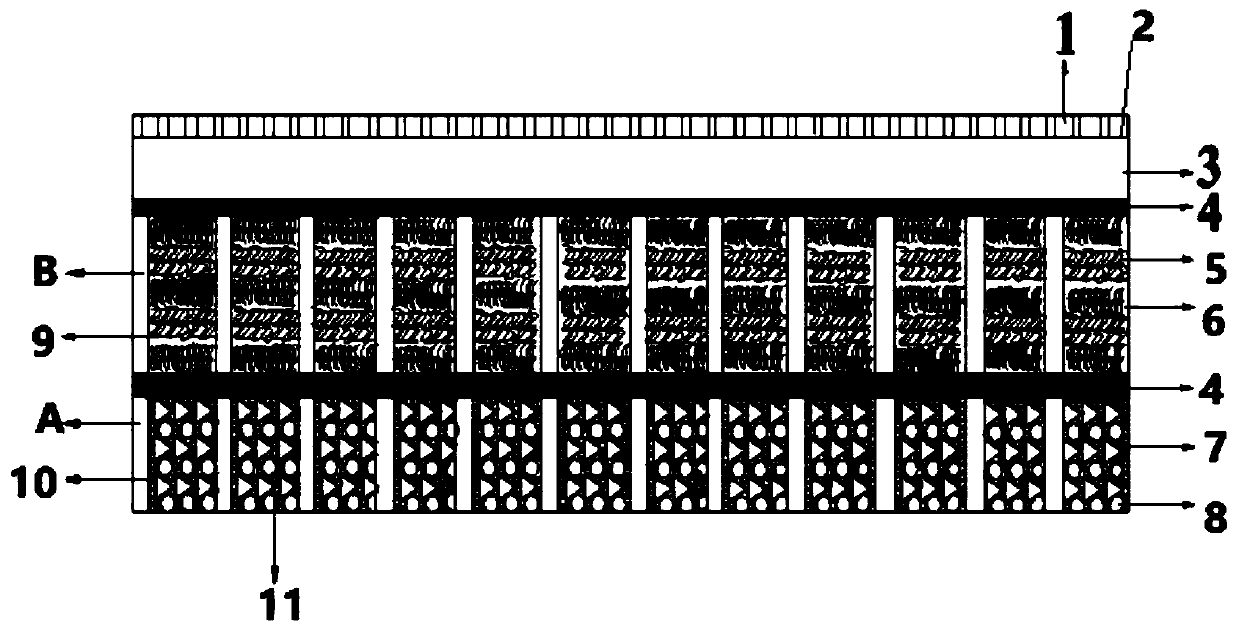
[0072] (3) Insert the pressed cylindrical hygroscopic agent into each cylindrical hole of the first substrate, and evenly coat the first surface (non-hole surface area) and the second surface (non-hole surface area) of the first substrate Acrylate emulsion polymer, with a saturated impregnated nonwoven bonded on the first side for contact with the subgrade surface.
[0073] (4) Take by weighing an appropriate amount of chopped viscose fiber, bamboo fiber and viscose-based...
Embodiment 2
[0078] (1) Pour the four components of sodium polyacrylate, polyacrylamide, anhydrous calcium chloride, and attapulgite into the mixer and mix for 300s to form a hygroscopic agent, and then put the hygroscopic agent into the material preparation tank.
[0079] (2) Take a corresponding mold according to the single hole size of the first substrate, pour the hygroscopic agent in step (1) into the corresponding mold, and use a compression molding machine to press the mixture into a cylindrical hygroscopic agent.
[0080] (3) Insert the pressed cylindrical hygroscopic agent into each cylindrical hole of the first substrate, and evenly coat the first surface (non-hole surface area) and the second surface (non-hole surface area) of the first substrate Acrylate emulsion polymer, with a saturated impregnated nonwoven bonded on the first side for contact with the subgrade surface.
[0081] (4) Take by weighing an appropriate amount of chopped viscose fiber, bamboo fiber and viscose-base...
Embodiment 3
[0086] (1) Pour the four components of sodium polyacrylate, polyacrylamide, anhydrous calcium chloride, and attapulgite into the mixer and mix for 300s to form a hygroscopic agent, and then put the hygroscopic agent into the material preparation tank.
[0087] (2) Take a corresponding mold according to the single hole size of the first substrate, pour the hygroscopic agent in step (1) into the corresponding mold, and use a compression molding machine to press the mixture into a cylindrical hygroscopic agent.
[0088] (3) Insert the pressed cylindrical hygroscopic agent into each cylindrical hole of the first substrate, and evenly coat the first surface (non-hole surface area) and the second surface (non-hole surface area) of the first substrate Acrylate emulsion polymer, with a saturated impregnated nonwoven bonded on the first side for contact with the subgrade surface.
[0089] (4) Take by weighing an appropriate amount of chopped viscose fiber, bamboo fiber and viscose-base...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com