Method for repairing heavy metal pollution in culture pond bottom mud
A technology for breeding ponds and heavy metals, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve problems such as poor results, and achieve remarkable effects, low cost, and simple operation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Use passivation agent to restore heavy metals Cd, Cu, As in sediment, the specific method is as follows:
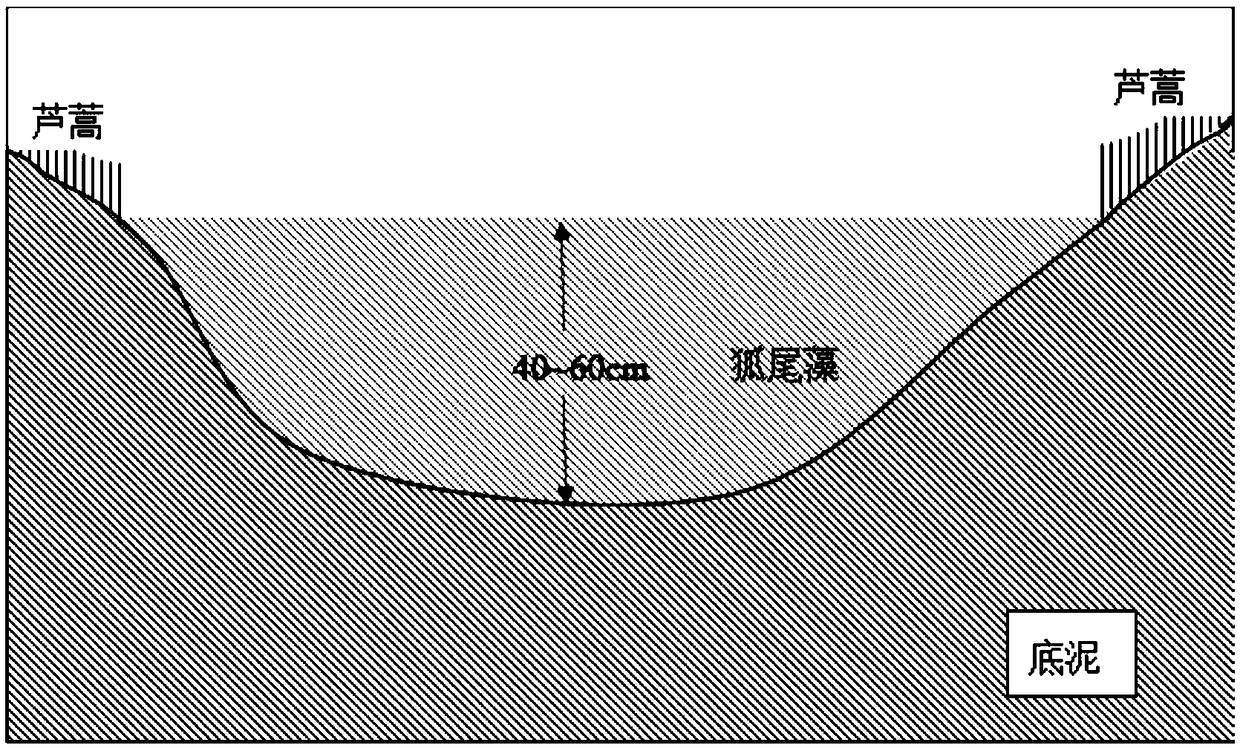
[0035] The first step is to drain the pond water, remove the sundries in the bottom mud, and keep the bottom mud flat.
[0036] The second step is to evenly spread nano-iron oxide on the surface of the bottom mud, and the content of nano-iron oxide is 40g / m 2 , Stir the bottom mud to mix the nano-iron oxide and the bottom mud evenly.
[0037] The third step is to turn the bottom mud every other week, and keep the water content of the bottom mud between 50% and 95%, and the passivation time is 21 days.
[0038] The results after the sediment restoration are shown in Table 1:
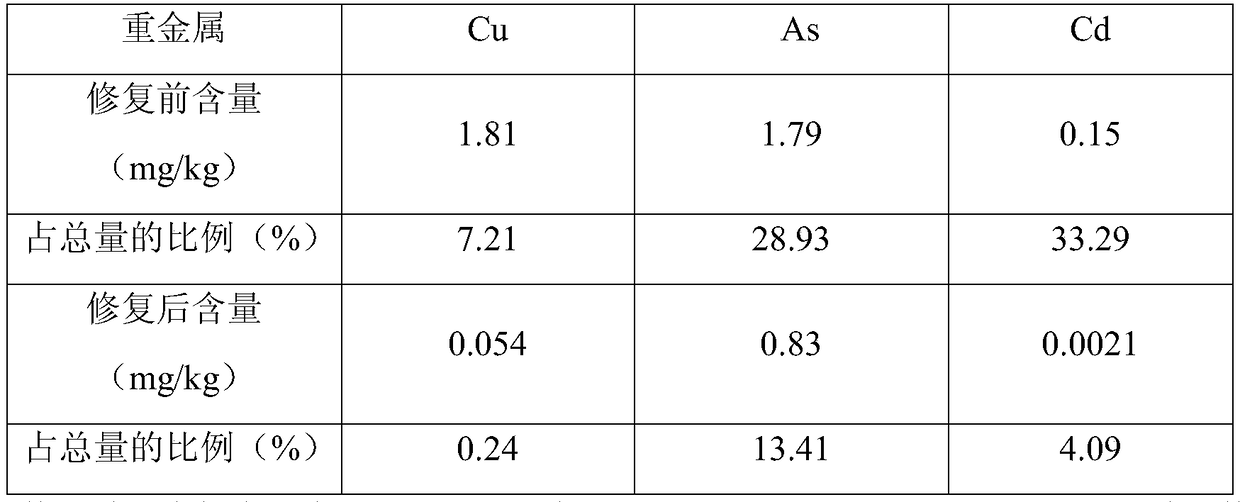
[0039] Table 1 Bioavailable heavy metal content in sediment
[0040]
[0041] Before restoration, the contents of bioavailable Cu, As, and Cd were 1.81, 1.79, and 0.15 mg / kg, respectively. After passivation restoration, the contents of bioavailable Cu, As, and Cd were reduced to 0.054, 0...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Use passivation agent to restore heavy metals Cd, Cu, As in sediment, the specific method is as follows:
[0044] The first step is to drain the pond water, remove the sundries in the bottom mud, and keep the bottom mud flat.
[0045] The second step is to evenly spread nano-iron oxide on the surface of the bottom mud, and the content of nano-iron oxide is 200g / m 2 , Stir the bottom mud to mix the nano-iron oxide and the bottom mud evenly.
[0046] The third step is to turn the bottom mud every other week, and keep the water content of the bottom mud between 50% and 95%, and the passivation time is 21 days.
[0047] The results after sediment repair are shown in Table 2:
[0048] Table 2 Bioavailable heavy metal content in sediment
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Before restoration, the contents of biologically available Cu, As, and Cd were 1.81, 1.79, and 0.15 mg / kg, respectively; Respectively reduced 97.73%, 46.37%, 98.87%.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Use passivation agent to restore heavy metals Cd, Cu, As in sediment, the specific method is as follows:
[0054] The first step is to drain the pond water, remove the sundries in the bottom mud, and keep the bottom mud flat.
[0055] The second step is to evenly spread nano-iron oxide on the surface of the bottom mud, and the content of nano-iron oxide is 1000g / m 2 , Stir the bottom mud to mix the nano-iron oxide and the bottom mud evenly.
[0056] The third step is to turn the bottom mud every other week, and keep the water content of the bottom mud between 50% and 95%, and the passivation time is 21 days.
[0057] The results after the sediment repair are shown in Table 3:
[0058] Table 3 Bioavailable heavy metal content in sediment
[0059]
[0060] Before restoration, the contents of bioavailable Cu, As, and Cd were 1.81, 1.79, and 0.15 mg / kg, respectively. After passivation restoration, the contents of bioavailable Cu, As, and Cd were reduced to 0.013, 1.00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com