Method for rapidly synthesizing hierarchical pore ZIF-61 material from bimetal salt at normal temperature
A ZIF-61, bimetallic salt technology, applied in the field of rapid preparation of hierarchical porous metal-organic frameworks, can solve the problems of reduced stability of MOFs, penetration of pore channels, etc., and achieve the effects of mild conditions, energy saving and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Dissolve 0.198g of zinc acetate dihydrate and 0.081g of zinc oxide in 1mL of N,N-dimethylformamide and 2mL of deionized water, and stir for 10h to obtain a (Zn-Zn) double metal salt solution; 0.402g of imidazole , 0.320g dimethylimidazole and 0.342g benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt were dissolved in 40mL methanol and stirred for 5 minutes to obtain a mixed solution of imidazole, dimethylimidazole and benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt; Add bimetallic salt solution to the benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt mixed solution, stir for 1 minute; then filter the obtained product with suction, activate at 90°C for 40h (soaked in ethanol), and finally put it in a vacuum oven at 110°C for 10 hours to dry. A hierarchically porous ZIF-61 material was obtained, marked as sample A.
Embodiment 2
[0033]Dissolve 0.220g of zinc acetate dihydrate and 0.090g of zinc oxide in 1mL of N,N-dimethylformamide and 2mL of deionized water, and stir for 11h to obtain a (Zn-Zn) double metal salt solution; 0.408g of imidazole , 0.328g dimethylimidazole and 0.36g benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt were dissolved in 40mL methanol, stirred for 7.5 minutes to obtain a mixed solution of imidazole, dimethylimidazole and benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt; Add bimetallic salt solution to the mixed solution of benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt, stir for 1 minute; then filter the obtained product with suction, activate at 95°C for 44h (soaked in ethanol); finally put it into a 115°C vacuum oven and dry for 11h to obtain Hierarchically porous ZIF-61 material, labeled Sample B.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Dissolve 0.241g of zinc acetate dihydrate and 0.098g of zinc oxide in 1mL of N,N-dimethylformamide and 2mL of deionized water, and stir for 12h to obtain a (Zn-Zn) double metal salt solution; 0.415g of imidazole , 0.337g dimethylimidazole and 0.378g benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt were dissolved in 40mL methanol and stirred for 10 minutes to obtain a mixed solution of imidazole, dimethylimidazole and benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt; Add bimetallic salt solution to the mixed solution of benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt, stir for 1 minute; then filter the obtained product with suction, activate at 100°C for 48h (soaked in ethanol); finally put it in a vacuum drying oven at 120°C for 12 hours, A hierarchically porous ZIF-61 material was obtained, designated as sample C.
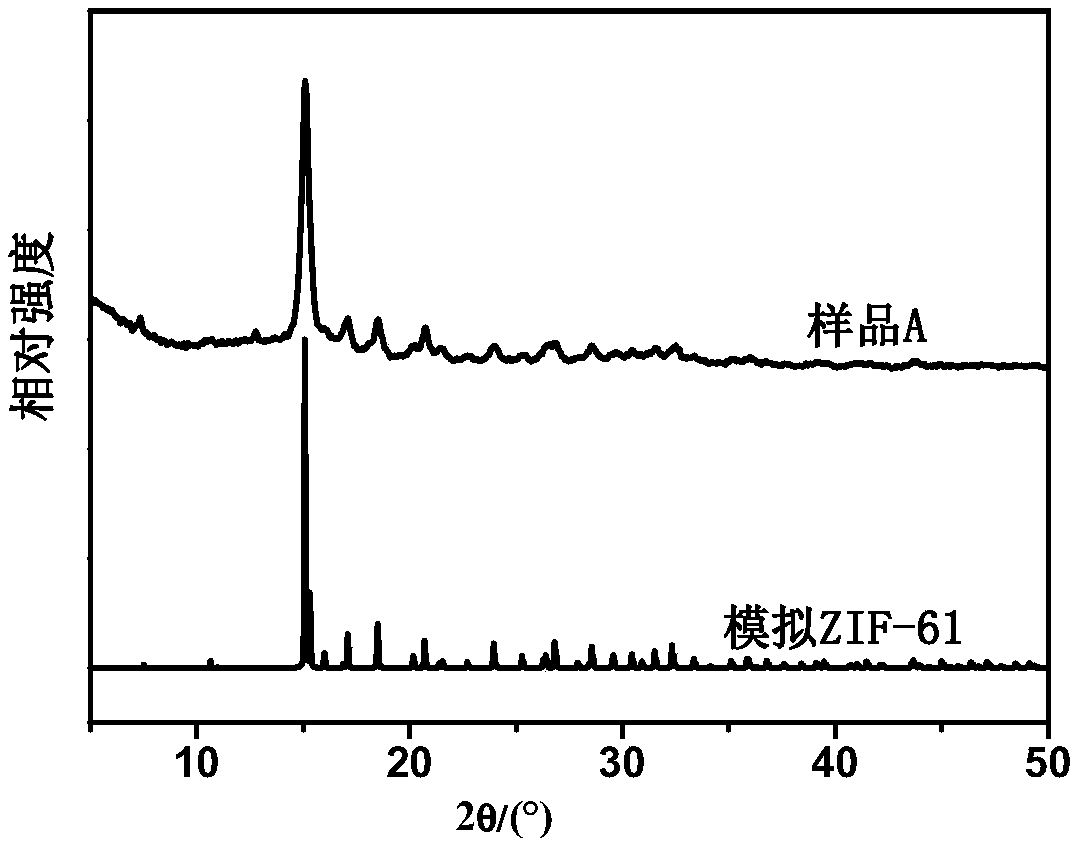
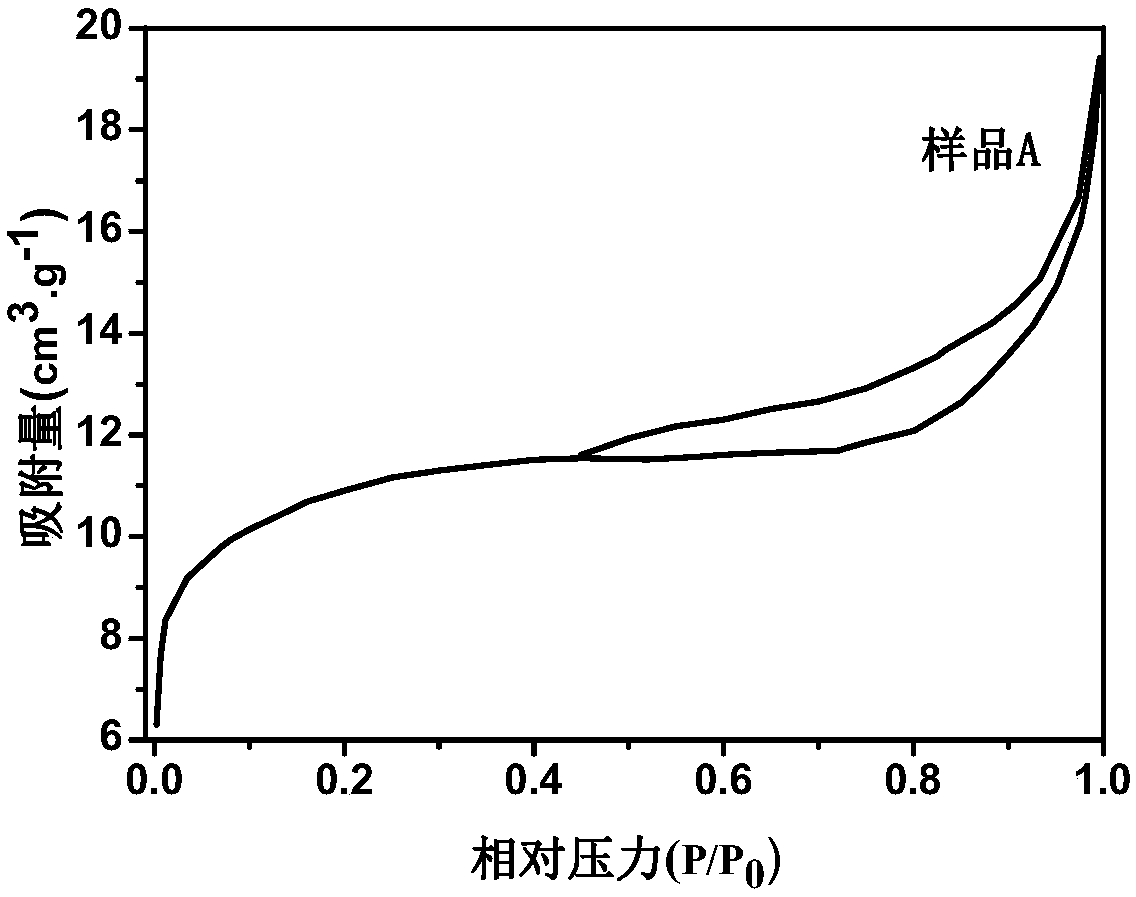
[0036] The hierarchically porous ZIF-61 material prepared in Example 1 was used as a representative for analysis, and the analysis results of the hierarchically porous ZIF-61 material prepared in other ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com