Preparation method of nanocellulose-based high-efficiency electromagnetic shielding porous material
A nano-cellulose, electromagnetic shielding technology, applied in the fields of magnetic/electric field shielding, metal material coating technology, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of huge application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
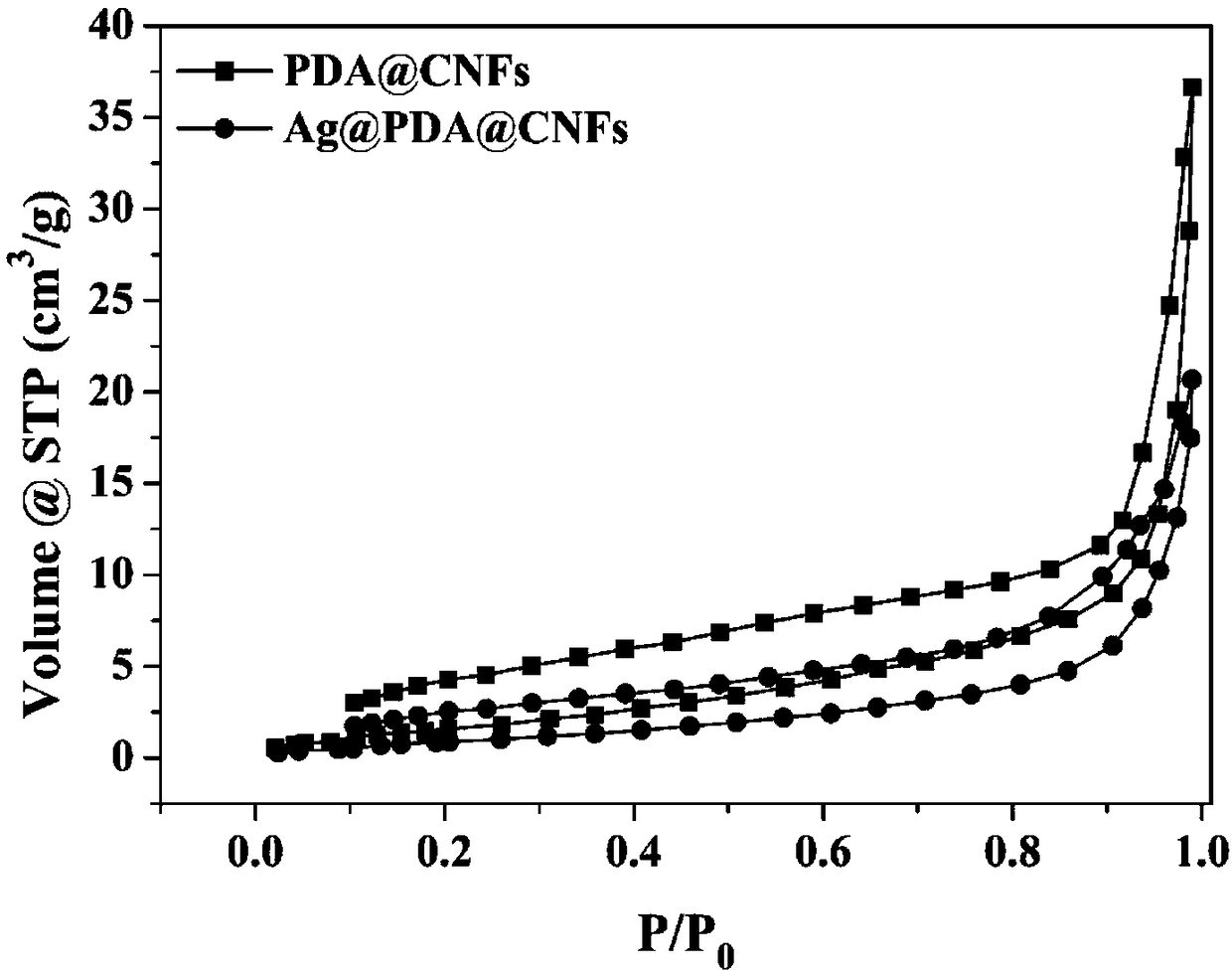
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
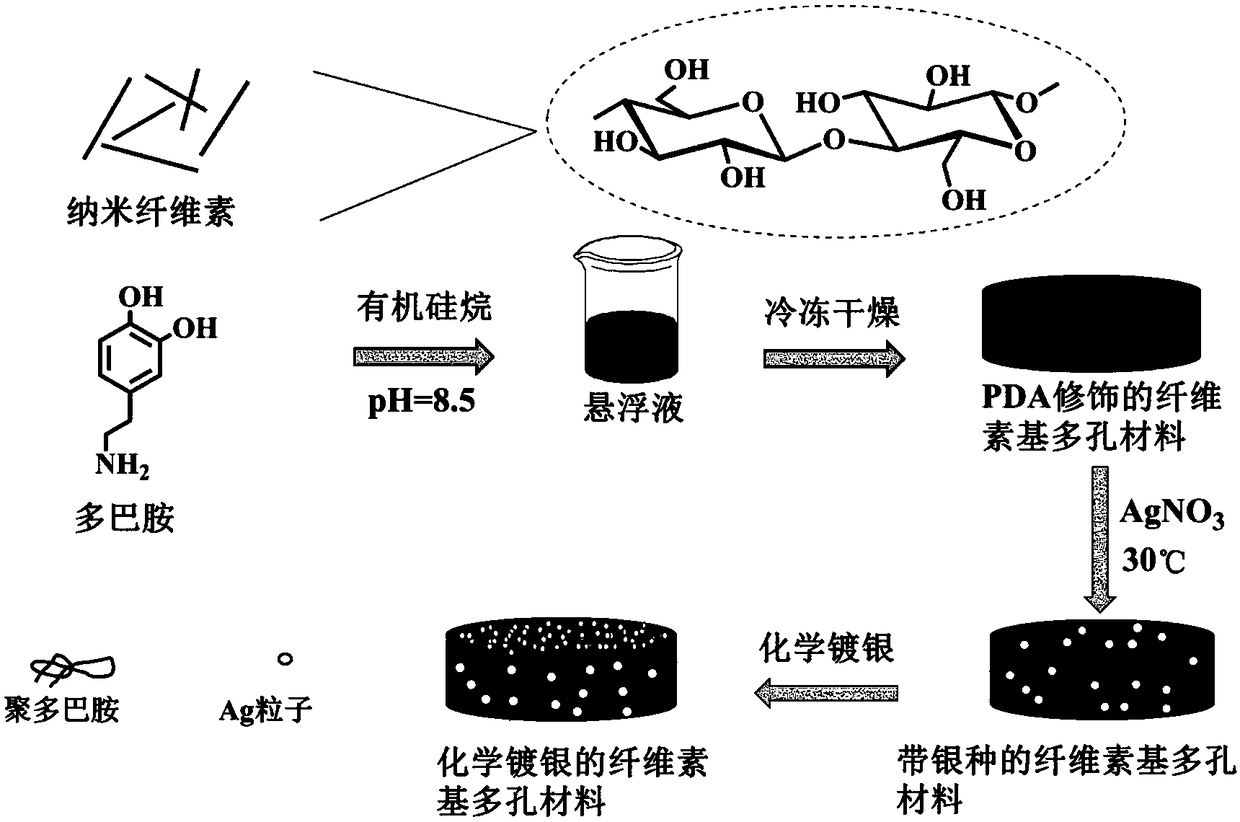
[0030] (1) Preparation of polydopamine-modified cellulose-based porous materials
[0031] Weighing 10 grams of the wood pulp cellulose nanowire suspension with a mass fraction of 1.3% was placed in a 50ml beaker, and at room temperature, 28.9mg of dopamine hydrochloride (dissolved in 1ml of water, slowly dropwise) was added under the effect of magnetic stirring Add), and adjust the pH to 8.5 with Tris-HCl buffer solution, keep the reaction at room temperature for 20h, add 130mg KH560 and continue to stir for 2h. Subsequently, the suspension was frozen with liquid nitrogen for 8 min and then freeze-dried on a freeze-drying agent for 48 h to obtain a polydopamine-modified cellulose-based porous material, which was baked at 110° C. for 30 min to increase the degree of crosslinking. Wherein, the porous material preparation method of the organosilane-modified cellulose-based porous material (ie, without PDA) was used as a blank control as described above.
[0032] (2) Silver-seedi...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Preparation of polydopamine-modified cellulose-based porous materials
[0040] Weighing 10 grams of the wood pulp cellulose nanowire suspension with a mass fraction of 1.3% was placed in a 50ml beaker, and at room temperature, 28.9mg of dopamine hydrochloride (dissolved in 1ml of water, slowly dropwise) was added under the effect of magnetic stirring Add), and adjust the pH to 8.5 with Tris-HCl buffer solution, keep the reaction at room temperature for 20h, add 130mg KH560 and continue to stir for 2h. Subsequently, the suspension was frozen with liquid nitrogen for 8 min and then freeze-dried on a freeze-drying agent for 48 h to obtain a polydopamine-modified cellulose-based porous material, which was baked at 110° C. for 30 min to increase the degree of crosslinking. Wherein, the porous material preparation method of the organosilane-modified cellulose-based porous material (ie, without PDA) was used as a blank control as described above.
[0041] (2) Silver-seedi...
Embodiment 3
[0048] (1) Preparation of polydopamine-modified cellulose-based porous materials
[0049] Weighing 10 grams of the wood pulp cellulose nanowire suspension with a mass fraction of 1.3% was placed in a 50ml beaker, and at room temperature, 28.9mg of dopamine hydrochloride (dissolved in 1ml of water, slowly dropwise) was added under the effect of magnetic stirring Add), and adjust the pH to 8.5 with Tris-HCl buffer solution, keep the reaction at room temperature for 20h, add 130mg KH560 and continue to stir for 2h. Subsequently, the suspension was frozen with liquid nitrogen for 8 min and then freeze-dried on a freeze-drying agent for 48 h to obtain a polydopamine-modified cellulose-based porous material, which was baked at 110° C. for 30 min to increase the degree of crosslinking. Wherein, the porous material preparation method of the organosilane-modified cellulose-based porous material (ie, without PDA) was used as a blank control as described above.
[0050] (2) Silver-seedi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com