Three-state mechanical foot structure
A technology of mechanical feet and hinges, applied in the field of robot structure research, can solve problems such as a single environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
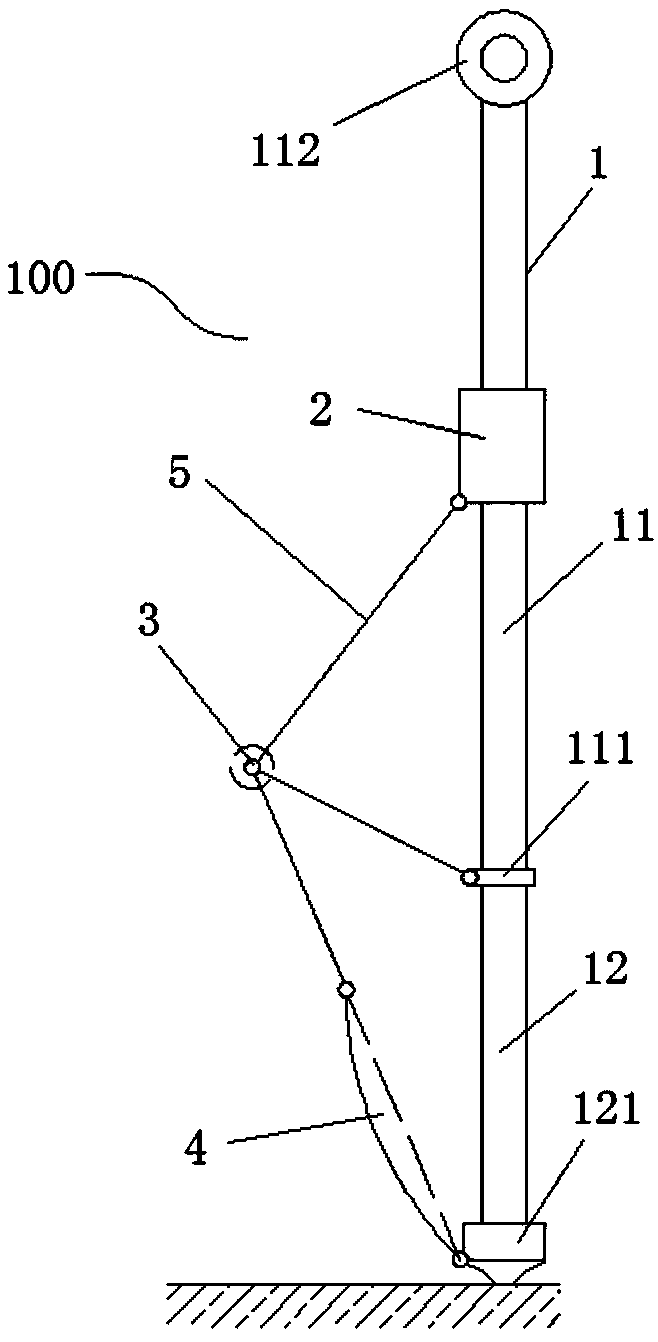
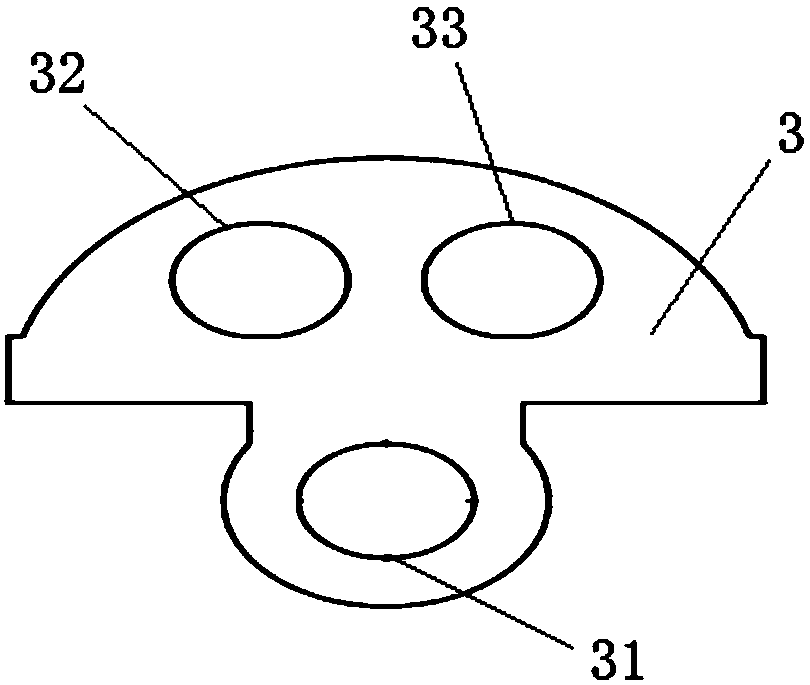
[0036] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a mechanical foot structure 100 for a robot, which mainly includes: a main body 1 of the mechanical foot, a slider 2 and a half-directional hinge 3 .
[0037] The main body 1 is a metal rod, which is divided into two connected sections, including a slide bar 11 and a leg bar 12. The surface of the slide bar 11 is smooth, and one end of the leg bar 12 is The other end of the sliding bar 11 and the leg bar 12 is provided with a first support part 121 ; the first support part 121 includes a foot cover provided at the end of the leg bar 12 .
[0038] The slider 2 is arranged on the slider 11 and is slidably connected to the slider 11. The junction of the slider 11 and the leg bar 12 is provided with a lower limit block 111 corresponding to the slider 2. An upper limit structure 112 is provided on the slide bar 11 corresponding to the lower limit block 111, and the slider 2 slides on the slide bar 11 section between the upper...
Embodiment 2
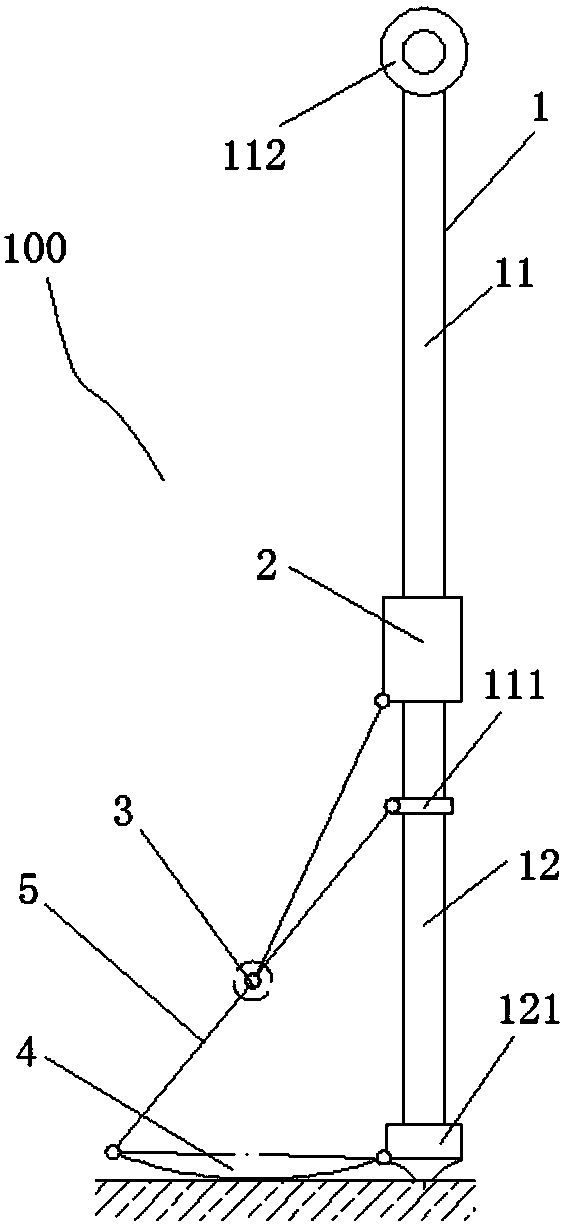
[0044]The same as in Embodiment 1 will not be repeated, in this embodiment, such as figure 2 As shown, the slider 2 is moved to the limit position along the lower limit block 111, at this time, the half-directional hinge 3 is connected with the lower limit block 111, and the half-directional hinge 3 is connected with the second supporting part. The connecting rod 5 of 4 is on the same straight line, and due to the tightening effect of the connecting rod 5 between the slider 2 and the half hinge 3, the disc is in a horizontal state, and the lowest point of the arc-shaped convex surface on the disc is The lowest point of the foot cover on the first supporting part 121 is on the same plane and touches the ground. At this time, the contact surface between the mechanical foot and the ground will gradually become larger, which is suitable for walking on soft ground. The second supporting part 4 can also be set in an oval or spherical shape to improve walking adaptability on soft gr...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The difference from Embodiment 2 is that the mechanical foot structure 100 in this embodiment is not installed on the robot, but on a structure with a certain buoyancy of its own, such as Image 6 The hull structure shown in 6.
[0047] In this embodiment, in order to facilitate the main body 1 rod of the mechanical foot to be arranged on the hull structure 6, the other end of the annular bushing provided on the upper limit structure 112 can be provided with an extension corresponding to the main body 1 rod (in the figure not shown), so as to facilitate the user's hand-held control; the mechanical foot structure 100 is set to a swingable form similar to a paddle through an annular bushing, so as to facilitate the mechanical foot to cooperate with the propulsion movement of the hull structure 6 in water. Further, the mechanical foot structure 100 can also be in the form of a mechanical arrangement, such as through the rotating shaft socketed with the annular bushing, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com