mmWave multi-cell interference suppression method for minimizing base station transmitting power
A transmission power and interference suppression technology, applied in space transmit diversity, diversity/multi-antenna systems, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as overestimation of performance evaluation, limited energy supply, increased interference, etc., to overcome limitations and overhead Reduced, performance-evaluated accurate effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be described clearly and in detail below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. The described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the invention.
[0032] The technical scheme that the present invention solves the problems of the technologies described above is:
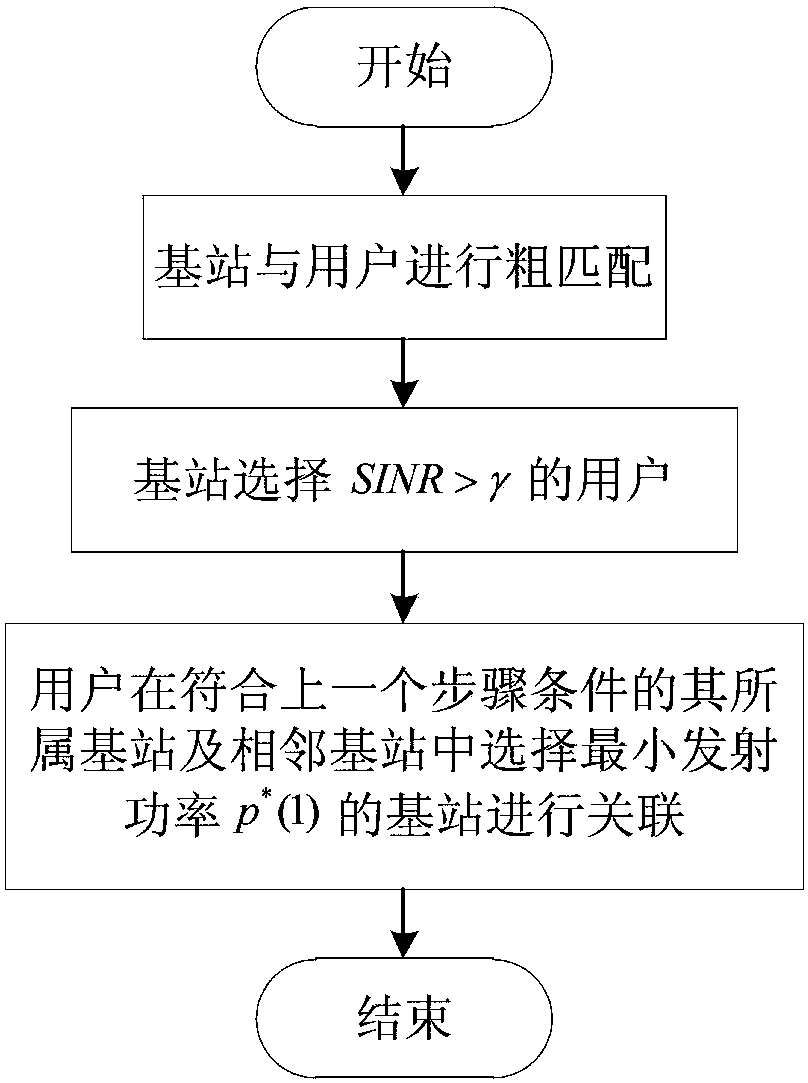
[0033] figure 1 The flow chart of the mmWave multi-cell interference suppression method for minimizing base station transmit power for joint user association and beamwidth selection is described in detail as follows.
[0034] figure 2 is the system model diagram, h t is the height of mmWave base station, h r user height, ξ m is the main lobe beam width, θ represents the reflection angle relative to the ground plane, R is the distance between the base station and the user, and d is the horizontal distance between the base station and the user.
[0035] Step 1: Jointly process the Gauss...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com