A method for rapid and simultaneous preparation of lignin nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots
A nanoparticle and carbon quantum dot technology, applied in the field of rapid and synchronous preparation of lignin nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots, can solve the problems of difficult particle size control, complex process, harsh conditions, etc., and achieve high dispersibility and uniform particle size distribution. , the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) The rice straw is crushed and sieved through 60 mesh, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C to a constant weight.
[0037] (2) Put the rice straw treated in step (1) in a digestion tank, and add ethanol-water (ethanol:water 65:35) dissolved in HCl at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml). v / v) The mixed solution is placed in a microwave oven (Galanz P70F20L-DG), and the treated solution is filtered after microwave treatment at 400 W for 10 minutes. The mass fraction of the HCl in the mixed solution is 0.5%.
[0038] (3) Centrifuge the obtained treatment solution at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes, the resulting precipitate is lignin nanoparticles, and the supernatant is a nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot solution.
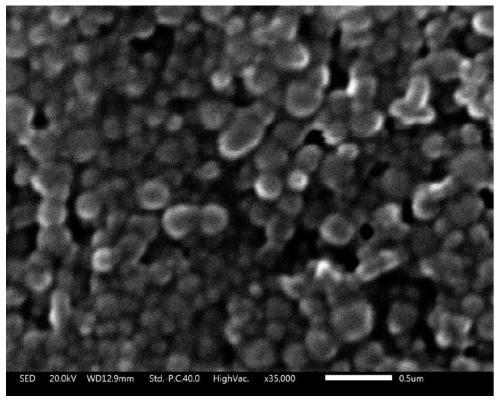
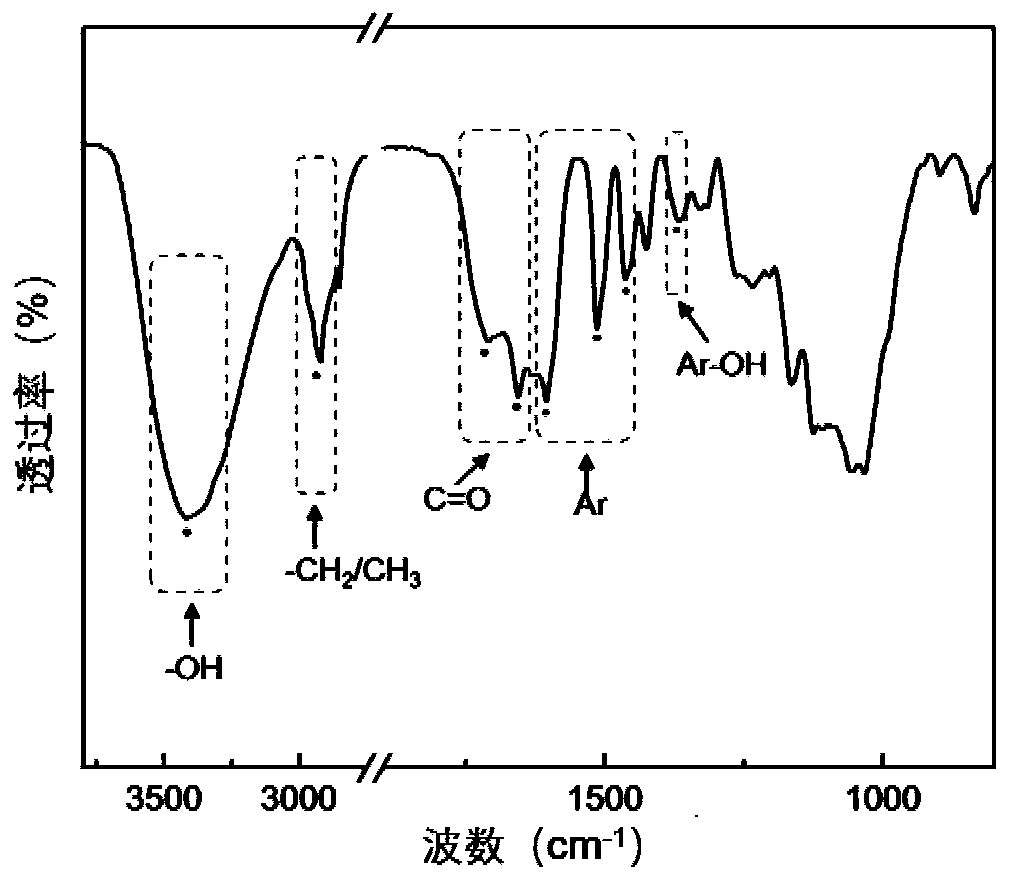
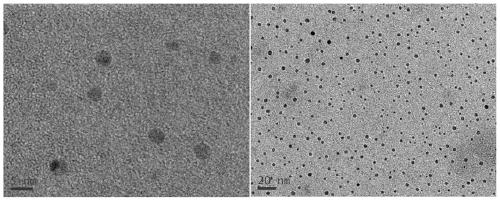
[0039] The lignin nanoparticles (such as figure 1 ) Has an average particle size of 123nm, and the particle size distribution is relatively uniform (dispersion coefficient: 0.173, such as figure 2 ), with typical polyhydroxyl lignin structure (such as ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) The rice straw is crushed and sieved through 60 mesh, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C to a constant weight.
[0042] (2) Put the rice straw treated in step (1) in a digestion tank, and add ethanol-water (ethanol:water 60:40) dissolved in HCl at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:15 (g / ml). v / v) The mixed solution is placed in a microwave oven (Galanz P70F20L-DG), and the treated solution is obtained by filtering after microwave treatment at 500 W for 8 minutes. The mass fraction of the HCl in the mixed solution is 0.5%.
[0043] (3) Centrifuge the obtained treatment solution at 14000 rpm for 5 minutes, the resulting precipitate is lignin nanoparticles, and the supernatant is a nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot solution.
[0044] The average particle diameter of the lignin nanoparticles prepared by this embodiment is 156 nm (dispersion coefficient: 0.201), and has a typical polyhydroxy lignin structure. At the same time, the prepared nitrogen-doped carbon quant...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) The rice straw is crushed and sieved through 60 mesh, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C to a constant weight.
[0047] (2) Put the rice straw treated in step (1) in a digestion tank, and add ethanol-water (ethanol:water 70:30) dissolved in HCl at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:20 (g / ml). v / v) In the mixed solution, then placed in a microwave oven (Galanz P70F20L-DG), after 12 minutes of microwave treatment at 400W, filtered to obtain a treatment solution. The mass fraction of HCl in the mixed solution is 0.8%.
[0048] (3) Centrifuge the obtained treatment solution at 11000 rpm for 10 minutes, the obtained precipitate is lignin nanoparticles, and the supernatant is a nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot solution.
[0049] The average particle diameter of the lignin nanoparticles prepared in this embodiment is 187 nm (dispersion coefficient: 0.165), and has a typical polyhydroxy lignin structure. At the same time, the prepared nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com