Image corner point matching method based on self-adaptive threshold and RANSAC
An adaptive threshold and corner matching technology, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in estimating the threshold size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Embodiment 1: The inventive method is described in detail below:
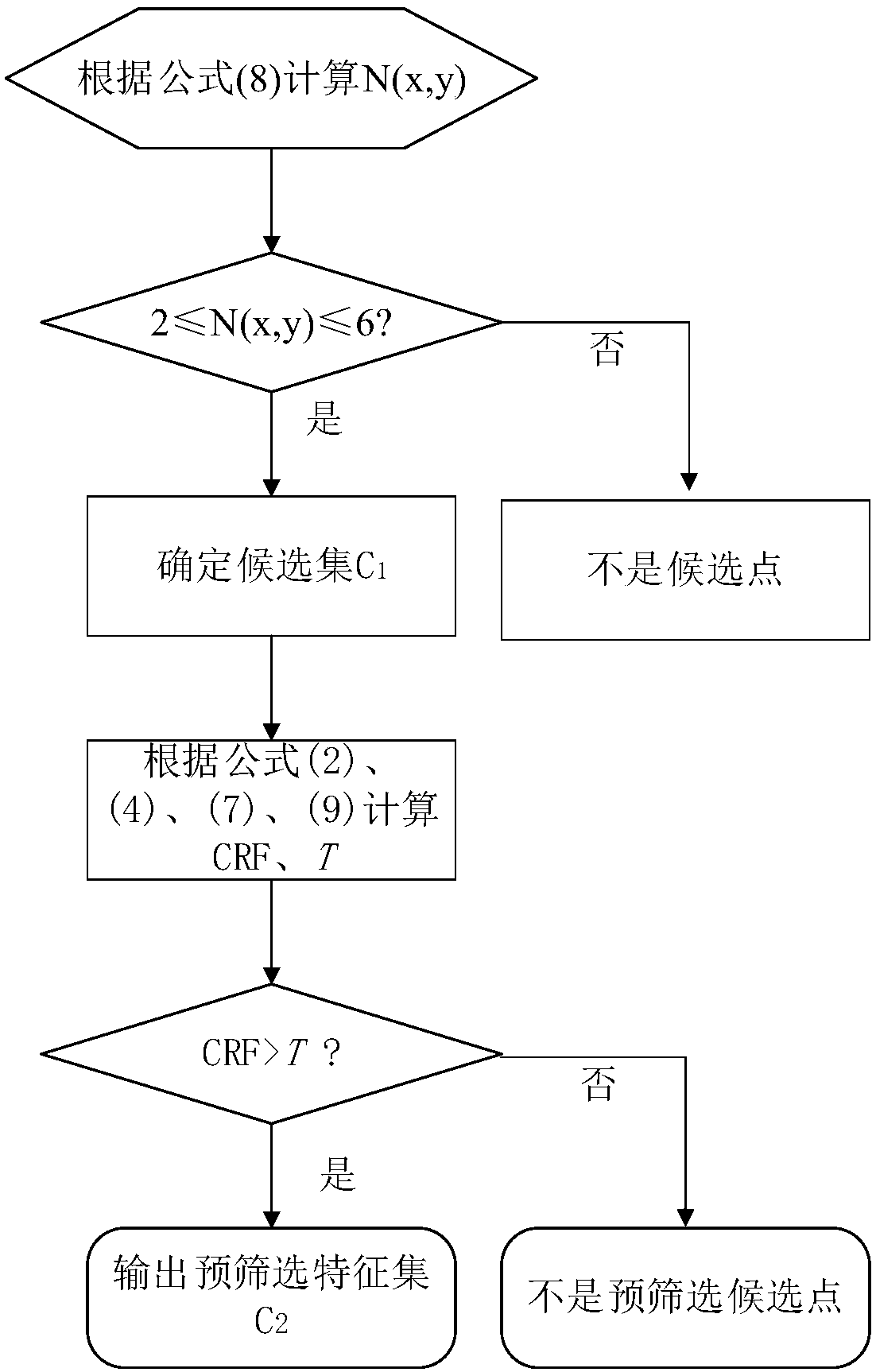
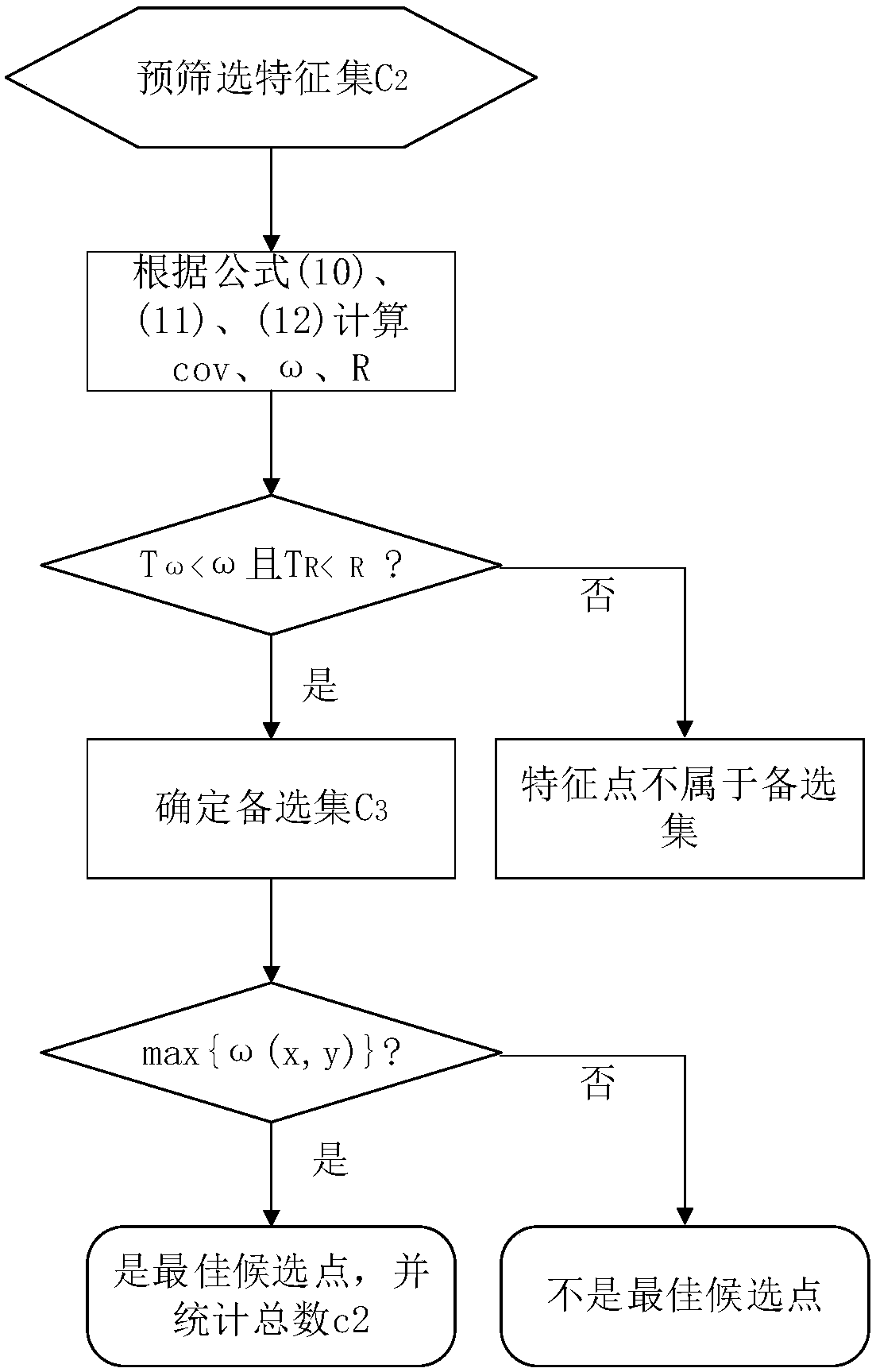
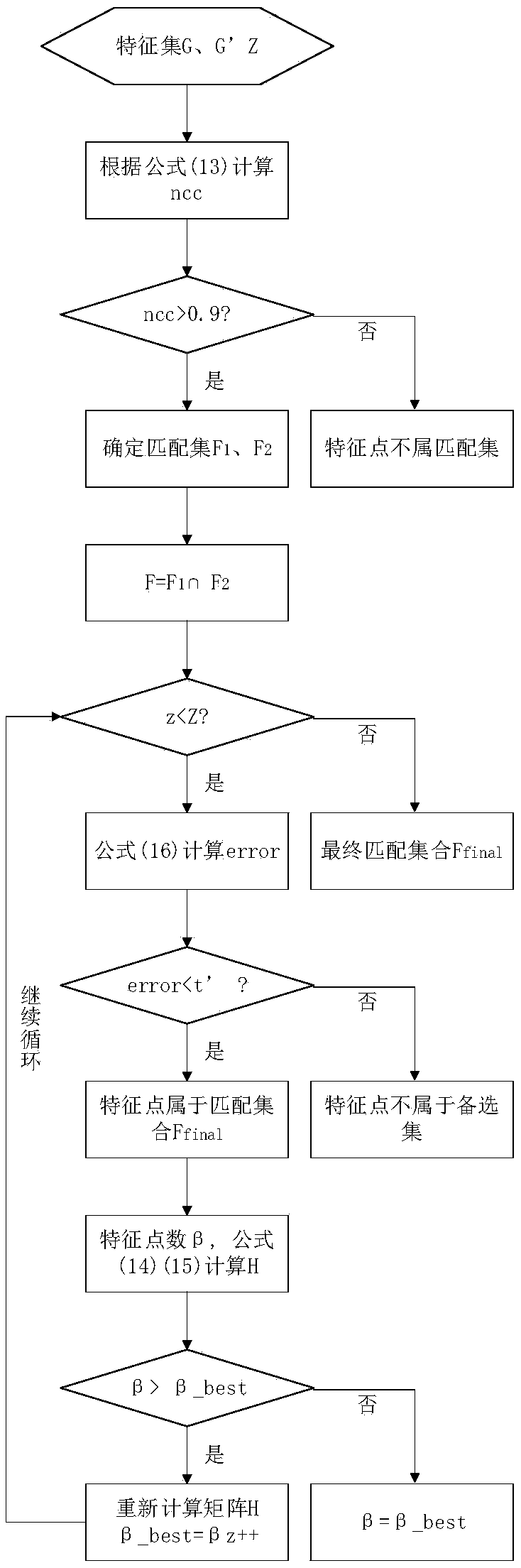
[0069] Harris corner detection principle
[0070] Harris corner detection algorithm is developed on the basis of Moravec algorithm, which was proposed by Harris C and Stephens MJ. Harris improved the Moravec corner detection algorithm by using differential operations and autocorrelation matrices. For an image I(x, y), a small window centered on a certain pixel (x, y) moves u in the x direction and v in the y direction, and the gray intensity change given by Harris is as in the formula (1 ) as shown in:
[0071] E(x,y)=∑w(x,y)[f(x+u,y+v)-f(x,y)] 2 (1)
[0072] Among them, f(x, y) represents the gray value at point (x, y), and f represents the gray function formula (1) is the definition of the Harris algorithm, Harris represents the gray intensity change when the window moves, f is a symbol that facilitates the embodiment of program code. w (x, y) is a Gaussian filter, as shown in formula (2). Acco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com