Traffic control method of weaving vehicles in road merging area
A technology for interweaving vehicles and control methods, which is applied to the traffic control system of road vehicles, traffic control systems, roads, etc., can solve problems such as traffic delays and vehicle congestion, and achieve improved safety levels, reduced delay rates, and improved overall traffic efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
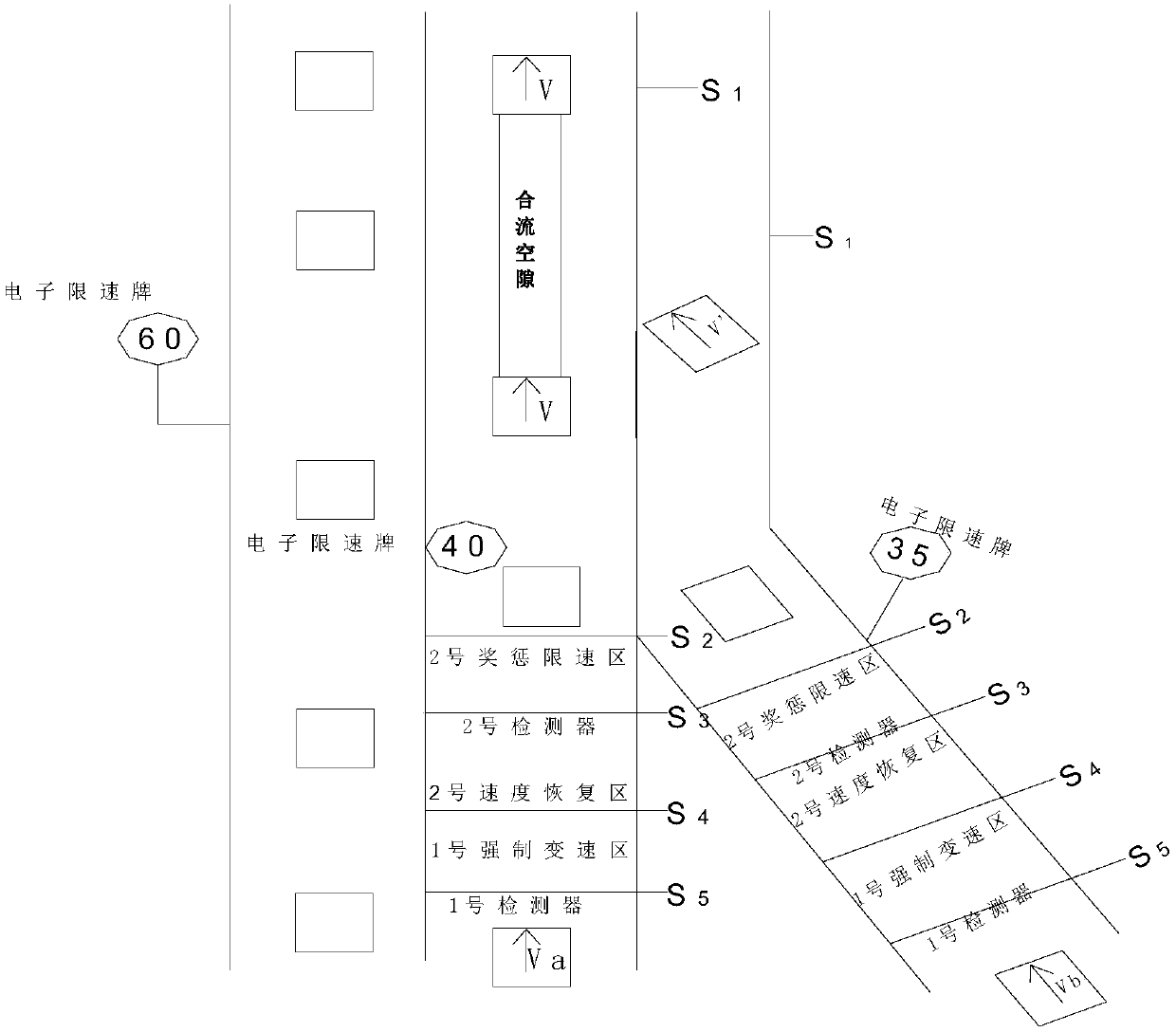
[0016] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 As shown, a traffic control method for weaving vehicles in a road merging area is realized through the following steps:
[0017] Step 1. Investigate the merging speed of vehicles on the main road in the road merging area, the merging speed of vehicles on the auxiliary road, the maximum speed limit of the main road, the maximum speed limit of the auxiliary road, and road geometric conditions;
[0018] Step 2, determining the positions of the detector, the forced speed change area, the speed recovery area, the reward and punishment speed limit area, and the variable speed limit device;
[0019] Step 3: According to the positions of the detector, the forced speed change area, the speed recovery area, the reward and punishment speed limit area, and the variable speed limit device determined in step 2, determine the traffic control rules for the weaving vehicles in the merge area.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0020] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the specific process of the step 1 is: the merging speed of the vehicles on the main road and the merging of vehicles on the auxiliary roads in the road merging area to be controlled before and after peak hours The speed is collected for 3 hours, and the width of the road in the merge area and the length of the acceleration lane in the merge area are measured.
[0021] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0022] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that: in the step two, the specific steps for determining the position of the detector, the forced speed change area, the speed recovery area, the reward and punishment speed limit area, and the variable speed limit device are as follows: The process is:
[0023] set S 1 is the location of the merging area; the forward direction of the vehicle is taken as the positive direction, and the end position of the reward and punishment speed limit area of the main road and auxiliary road is S 2 , and at S 2 Position setting variable speed limiting device;
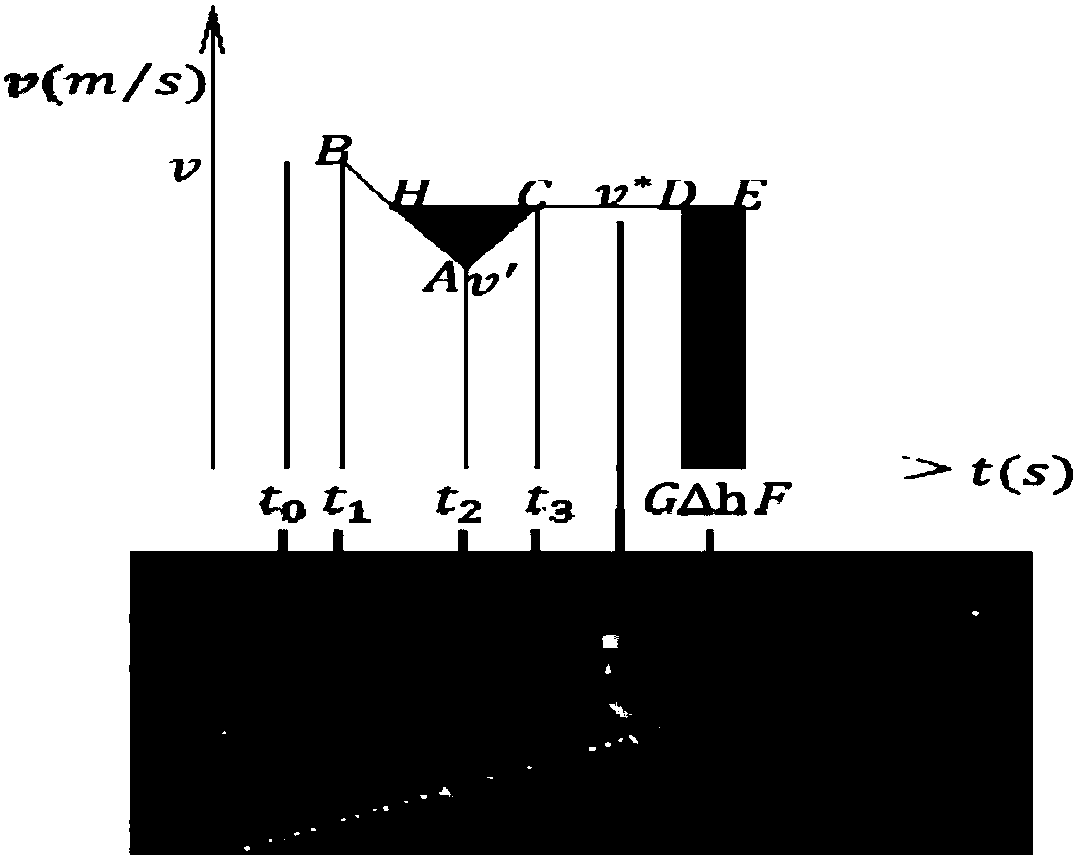
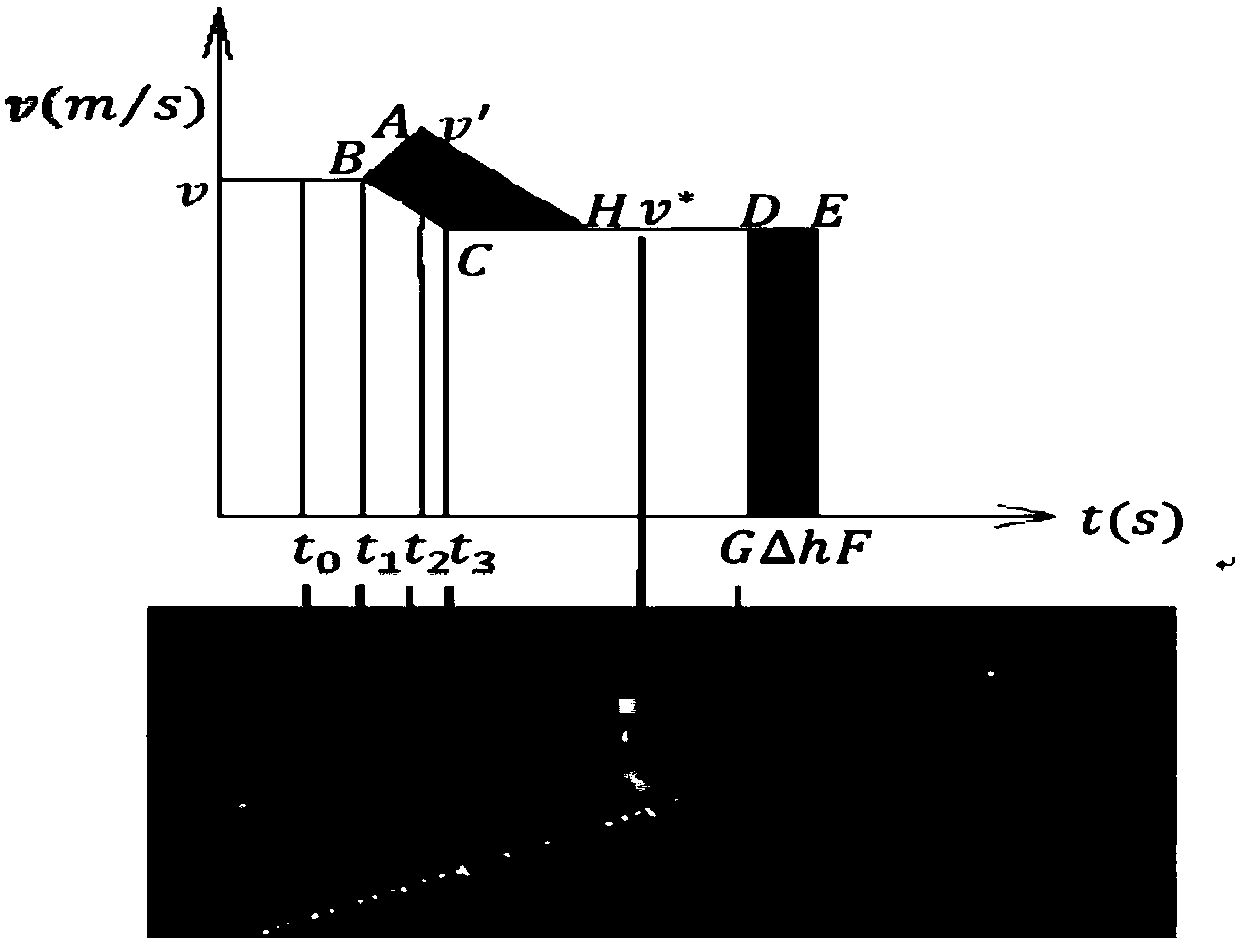
[0024] If the vehicle is leaving the variable speed limiter position S 2 To the merge position S 1 Unauthorized speed change during the period will make the merge impossible to complete as required, so S 1 S 2 In order for the vehicle to be adjusted by deceleration acceleration or acceleration deceleration model, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com