Construction and applications of a series of efficient heterologous expression hosts of Streptomyces coelicolor
A technology for Streptomyces coelicolor and natural products, which is applied in the field of synthetic biology and can solve the problems that cannot meet the requirements of new compound identification and combined biosynthesis research, and the heterologous expression yield is low.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Example 1: Construction of a series of heterologous high-efficiency expression hosts of Streptomyces coelicolor
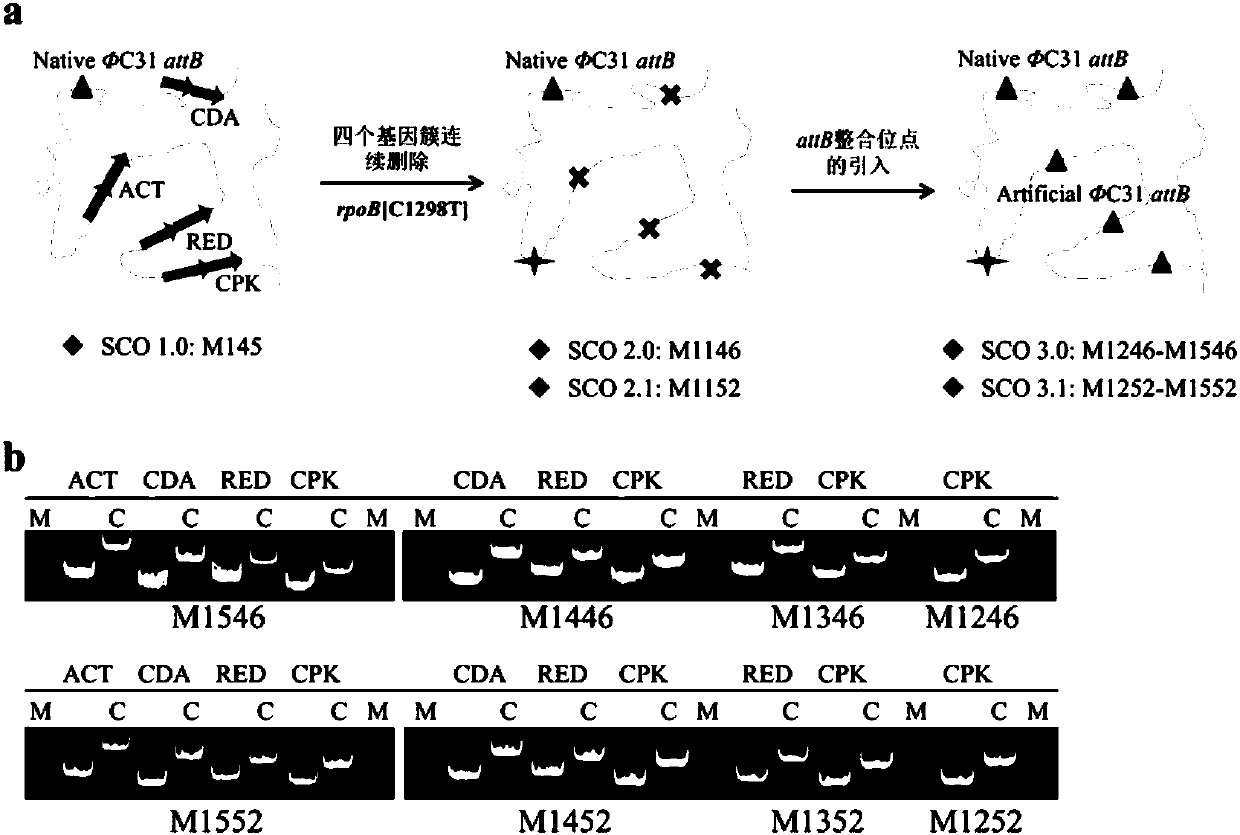
[0089] Since the four active biosynthetic gene clusters have been knocked out in M1146 and M1152, the present invention directly introduces the attB site (see SEQ ID NO: 54) at the knocked out site, and the introduced sequence is respectively The sites of the deleted yCPK, RED, ACT and CDA synthetic gene clusters ( figure 1 A). The detailed steps of engineering strain construction are as follows: Taking the deleted yCPK synthetic gene cluster site as an example to introduce an attB integration site, first use primers yCPK-up-fw\rev, yCPK-down-fw\rev and yCPK-sgRNA- fw\DM-sgRNA-rev was amplified by PCR to obtain the knockout upstream and downstream homology arms yCPK-UP, yCPK-DOWN and the gRNA expression element yCPK-sgRNA targeting yCPK, and then yCPK-up-fw and sgRNA- Rev is the primer, using the above three PCR products as templates, the yCPK-UP-DOWN-sgRN...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2: Systematic identification of chloramphenicol and YM-216391 synthetic gene cluster insertion efficiency
[0093] In order to explore whether the above-mentioned 8 strains of chassis bacteria can effectively realize the amplification of exogenous secondary metabolite synthesis gene clusters, the present invention selected chloramphenicol and a kind of anti-cancer small molecule YM-216391 synthetic gene clusters for identification (gene clusters respectively in cosmids pAH91 and pST85). Using conjugative transfer, they were introduced into M1152-M1552, respectively. Except when there was no zygote when M1552 was introduced, more than 10 zygotes grew out in all the others. As the copy number increases, the number of zygotes gradually decreases. We randomly selected 10 of them for identification of multi-copy insertion efficiency, and the experiment was repeated twice. The results showed that the two gene clusters could be efficiently integrated into M1252-M145...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Example 3: Test of heterologous expression of chloramphenicol and YM-216391 in M1152-M1452
[0098] By effectively inserting chloramphenicol and YM-216391 synthetic gene clusters into M1152-M1452, we obtained engineering bacteria containing different gene cluster copy numbers. The specific fermentation process is as follows: After obtaining a sufficient amount of fresh bacteria in MS medium, transfer to 2×YT medium at 30°C and 200rpm for 7-10h, then directly transfer the culture solution to GYM medium for 30 Cultivate at 200 rpm, and sample every other day.
[0099] The fermentation results showed that with the increase of the copy number, the yield of the two compounds gradually increased. On the 5th day of fermentation, the chloramphenicol yield of M1452 / pAH91 (containing 4 chloramphenicol synthetic gene clusters) reached the maximum (110.4 mg / L), compared to M1152 / pAH91 (containing 1 chloramphenicol synthetic gene cluster, which The chloramphenicol output is 36.3mg...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com