Semi-annular-wing aircraft
An aircraft and ring-wing technology, applied in the field of aircraft, can solve the problems of lack of large-scale popularization, insufficient surplus power, and high maintenance costs, and achieve the effects of high reliability and safety, stable attitude, and large carrying capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Takeoff
[0042] 1. Slide mode
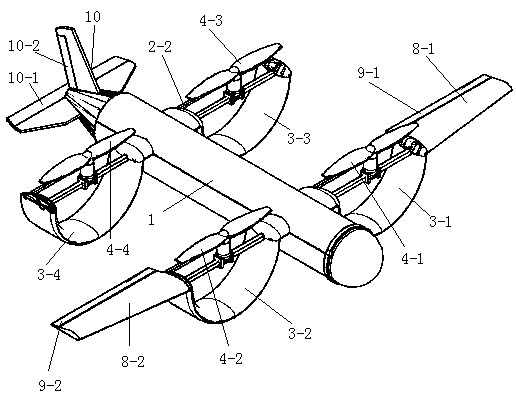
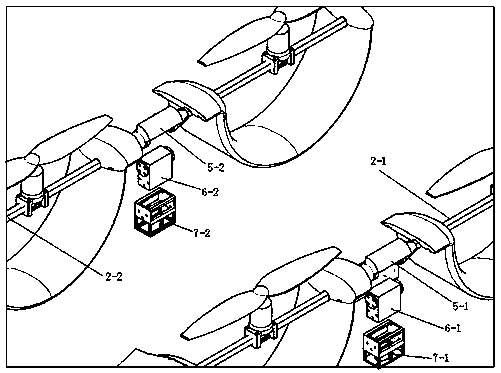
[0043] Use the landing gear to take off on the runway, and the steering gear 18 controls the flaps 9 to turn down to increase the lift. At this time, the angle of the rotating device 2 is at 0°, and the propeller 4 generates backward thrust, and the steering gear 18 controls the elevator. 10-1 turns downward, the aircraft generates a head-up moment, and the aircraft leaves the ground. As the flight speed of the aircraft gradually increases, the steering gear 18 controls the elevator 10-1 to turn upward, and the aircraft generates a head-down moment to balance the attitude of the aircraft. Steering gear 18 controls flap 9 to retract, thereby enters level flight state.
[0044] 2. Short takeoff
[0045] The angle of the rotating device 2 is adjusted by the controller, usually between 0° and 90°. The steering gear 18 controls the flaps 9 to turn down to increase the lift. At this time, the thrust generated by the propeller 4 is...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Attitude in the air
[0049] 1. Hover
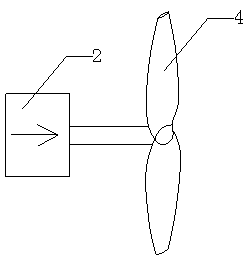
[0050] The angle of the rotating device 2 is adjusted by the controller. At this time, the rotating device 2 is in the 90° position, and the thrust produced by the propeller 4 is vertically downward. When the control thrust is the same as the weight of the aircraft, the aircraft is in a hovering state.
[0051] 2. Somersault in the air
[0052] In the hover attitude, by increasing the thrust of the left propeller (4-1, 4-3) of the aircraft, and reducing the thrust of the right propeller (4-2, 4-4), at the same time, the steering gear 18 controls the rudder 10-2 Flip to the right, because of the power difference on both sides of the aircraft, a rightward yaw moment will be generated on the aircraft, otherwise, a leftward yaw moment will be generated, and it can also turn back and forth.
[0053] 3. Normal flight
[0054] Same as the roll take-off, the rotation device 2 angle of the aircraft is at the 0° position, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3: Landing
[0061] 1. Vertical landing
[0062] By adjusting the angle of the rotating device 2, the rotating device 2 is at a position of 90° at this time, and the thrust produced by the propeller 4 is vertically downward, and by reducing the thrust, the thrust is gradually smaller than the weight of the aircraft, so that the vertical landing of the aircraft is realized.
[0063] 2. Short-distance landing
[0064] Adjust the angle of the rotating device 2 through the controller, usually between 0° and 90°. At this time, the thrust generated by the propeller 4 is obliquely rearward, and the thrust can be decomposed into forces in two directions, forward and upward, and then gradually lower the propeller. 4 thrust, while the steering gear 18 controls the elevator 10-1 to turn upwards, and the aircraft produces a nose-down moment to realize the short-distance landing of the aircraft.
[0065] 3. Rolling and landing
[0066] At this time, the angle of the rotat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com