A method for rapidly reducing antibiotics and resistance genes in organic solid waste
A technology of organic solids and resistance genes, applied in the removal of solid waste, methods based on microorganisms, preparation of organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of expanding pollution and spreading, ARGs and antibiotic pollution, lack of efficient and economical treatment technologies, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
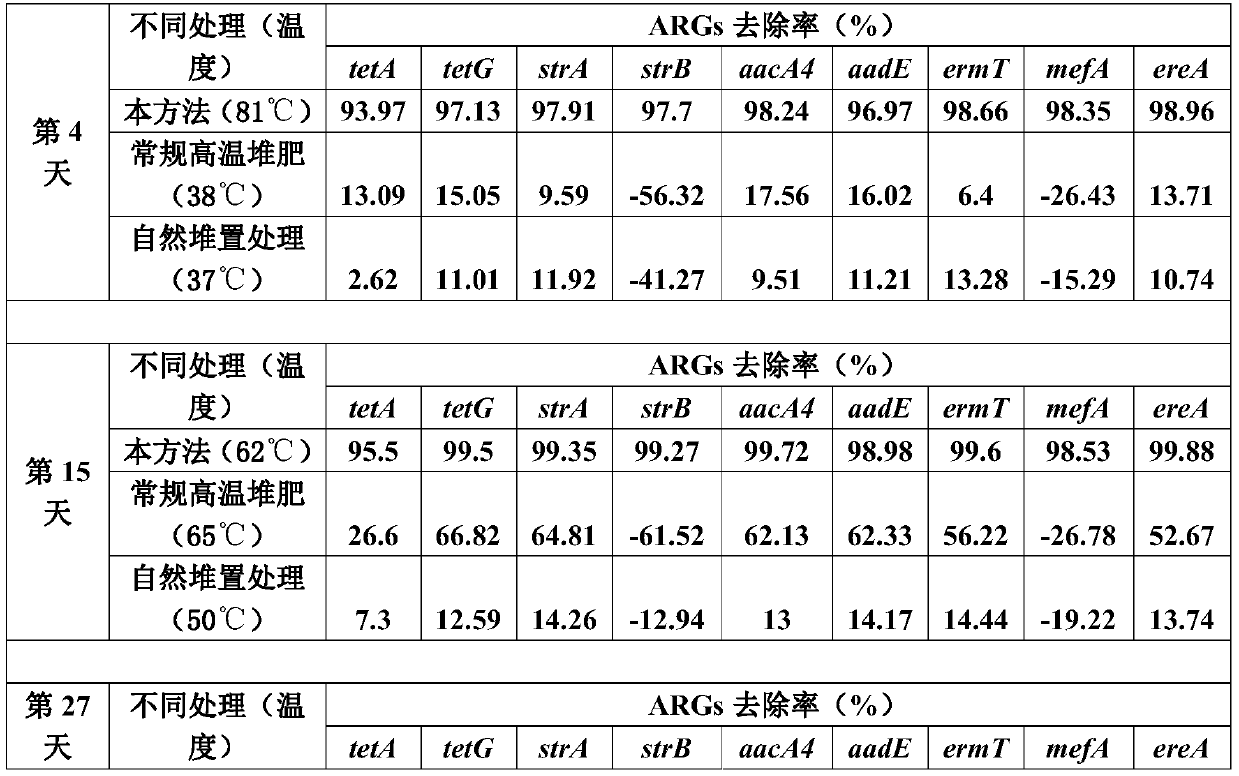
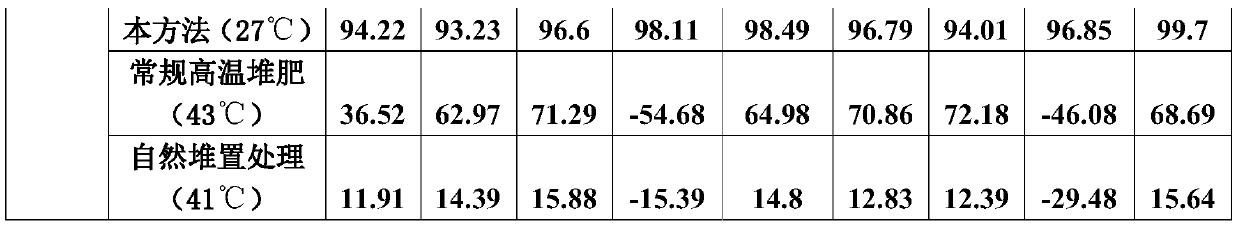
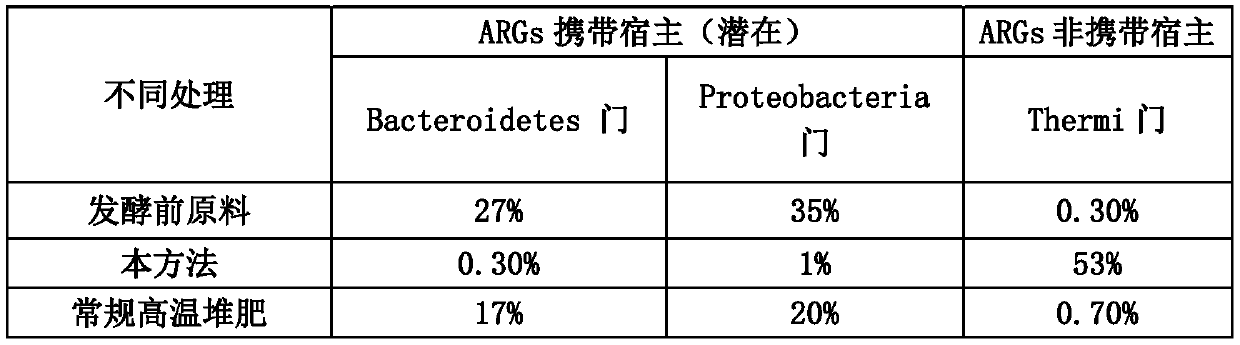
[0054] 1) The configuration of the ultra-high temperature fermentation liquid bacterial agent: hyperthermophilic bacteria Calditerricola yamamurae UTM801, thermophilic bacteria Thermus thermophilus FAFU013, thermophilic Bacillus geobacillussp.UTM801, methylotrophic Bacillus Bacillus methylotrophicus UTM401, Bacillus sp.UTM03 was respectively activated and cultivated until the logarithmic growth phase, and the bacteria were mixed evenly according to the mass ratio of 1:1:1:1:1 for later use.
[0055] 2) Material blending: Mix sludge (moisture content 80%) and auxiliary material rice husk (moisture content 15%) according to the volume ratio (1:4). At this time, the moisture content of the mixed material is about 55%, and add 0.05% The ultra-high temperature aerobic fermentation bacterial agent, mash some agglomerates with a diameter greater than 10cm, and stir evenly.
[0056] 3) Ultra-high temperature aerobic composting: stack the mixed materials into the fermentation tank for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com