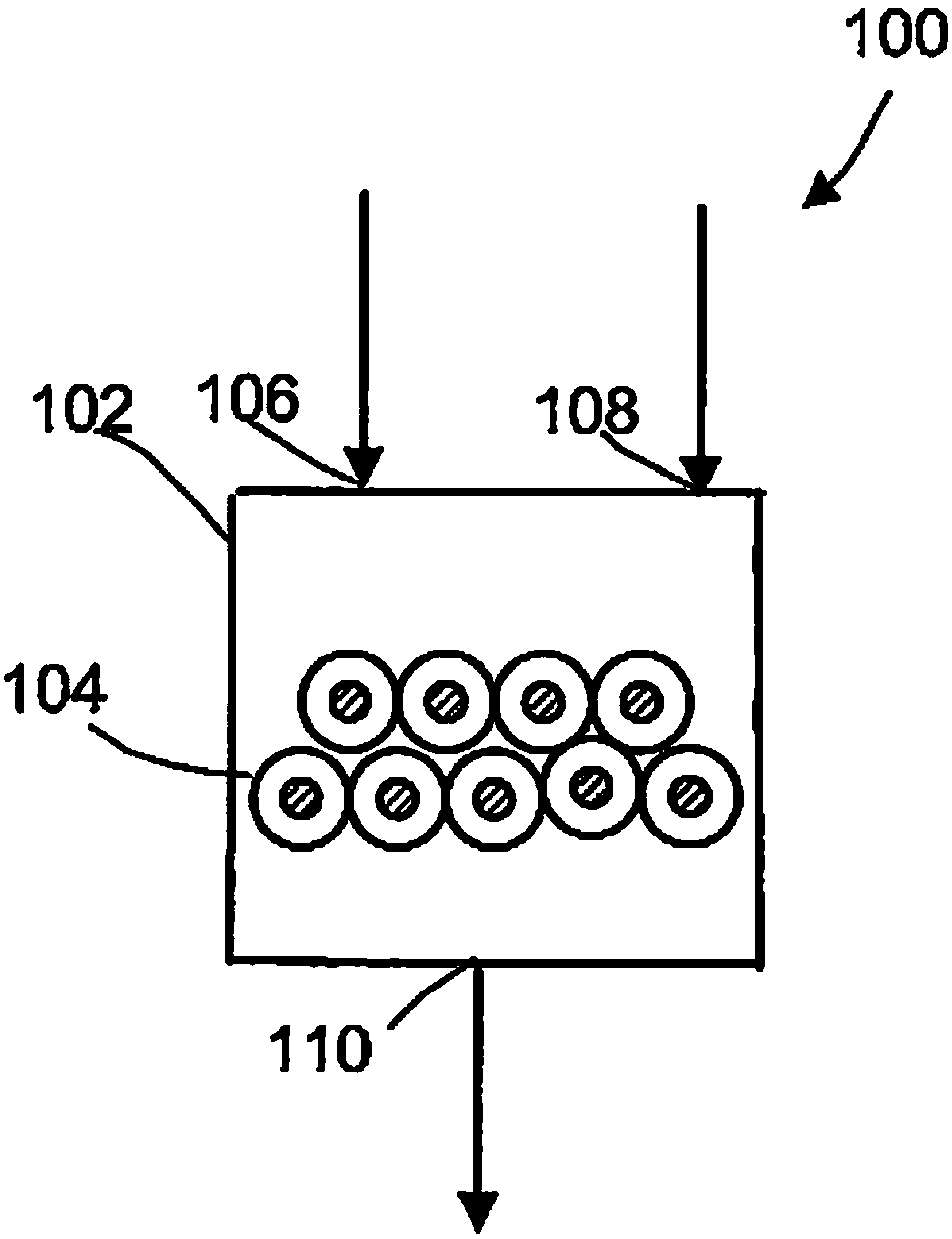
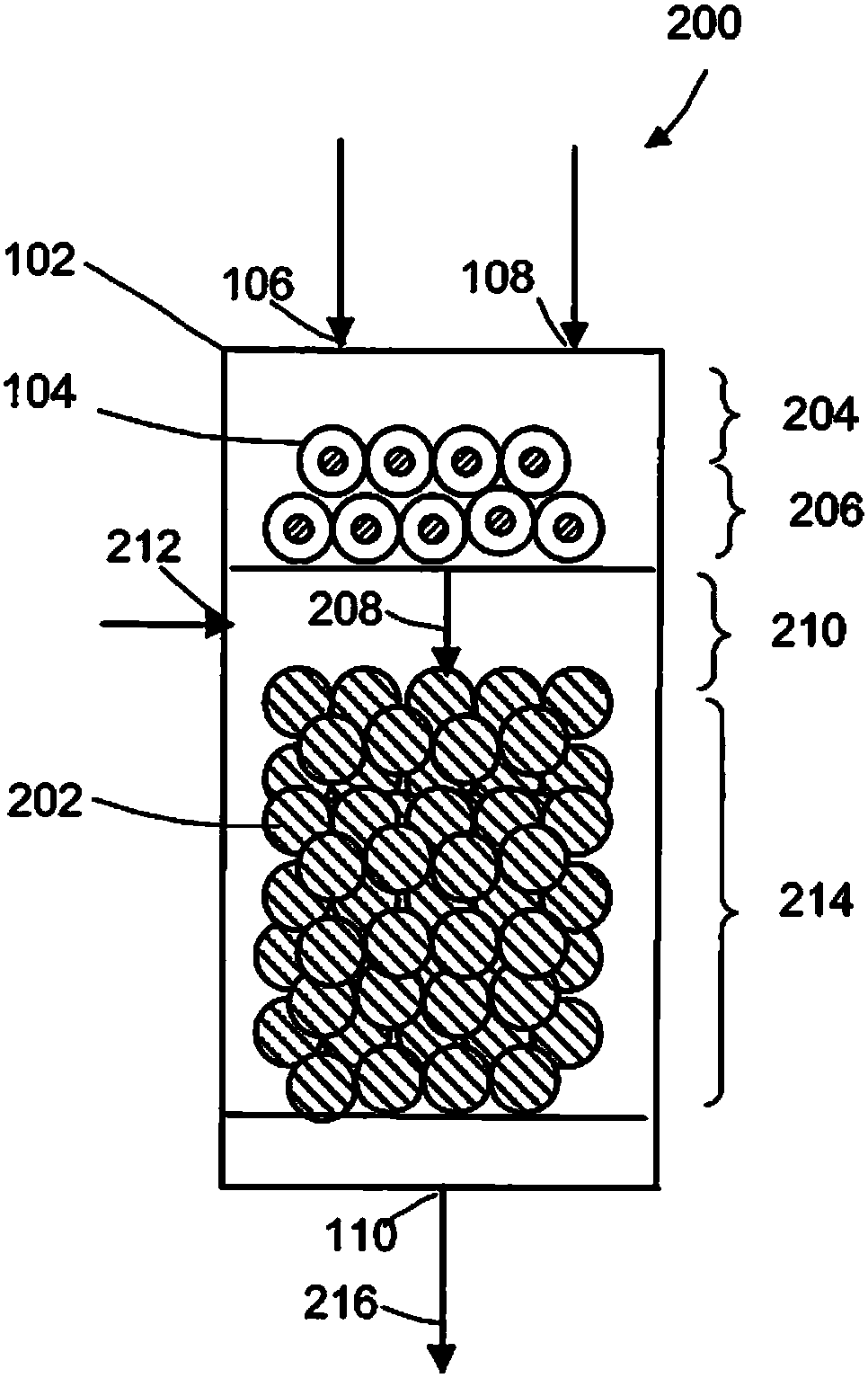
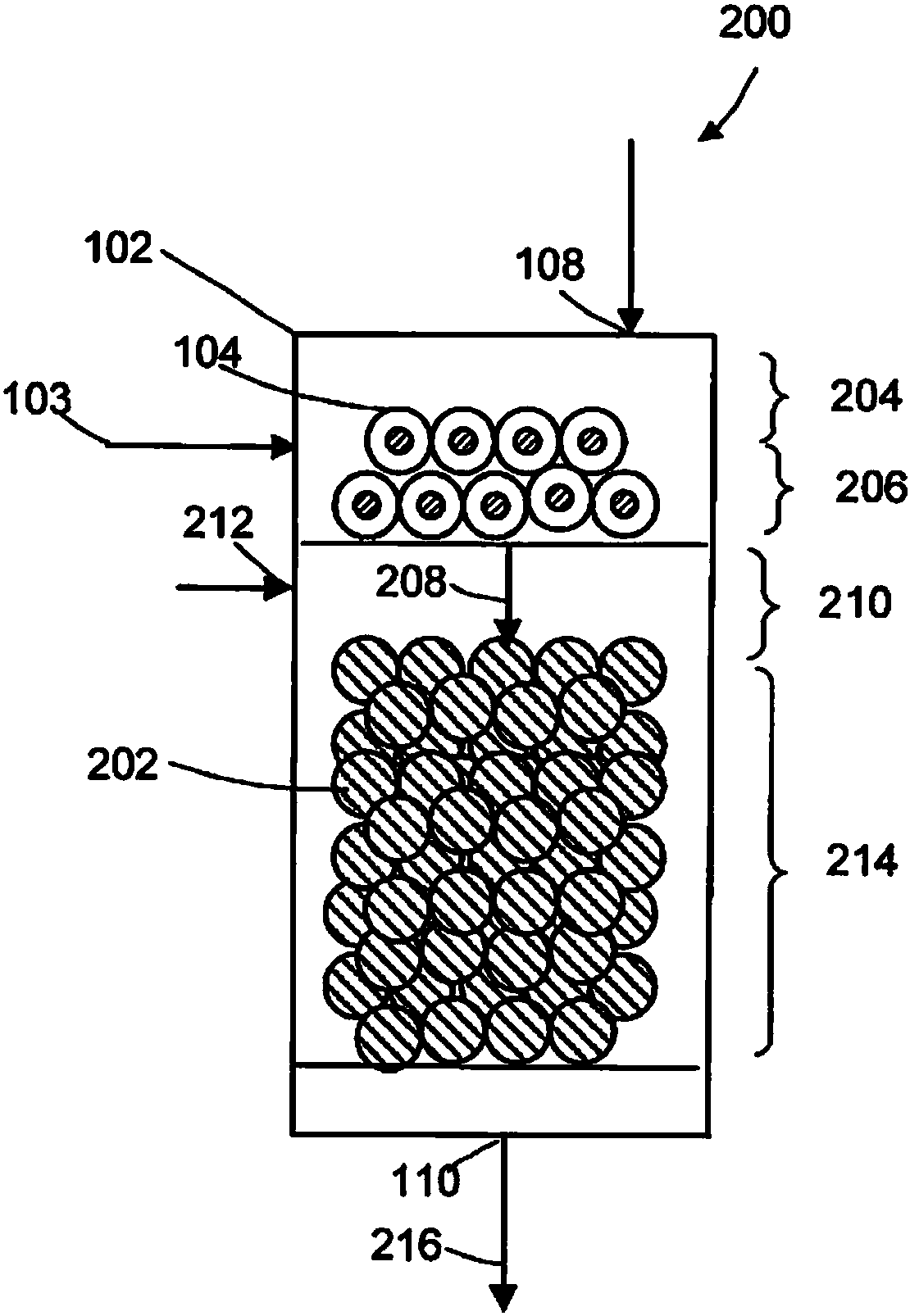
Methane oxidative coupling with la-ce catalysts
A technology of oxidative coupling reaction and catalyst, which is applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, catalyst, heterogeneous catalyst chemical elements, etc., which can solve the problems of affecting and increasing the total cost of preparing catalysts, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0064] (catalyst synthesis)
[0065] All materials used in the synthesis of bulk metal oxide catalysts were obtained from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, USA).
[0066] Block metal oxide catalyst. Lanthanum nitrate (La(NO 3 ) 3 ) and cerium nitrate (Ce(NO 3 ) 3 ) was dissolved in deionized water with stirring. The mixture was then dried overnight at 125°C. The dried material was then calcined at 625°C for 5 hours at a ramp rate of 1°C / min. image 3 is to show La(OH) 3 X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the bulk metal oxide catalyst of the present invention (sample 3 in Table 1) for the phase. The inverted triangle indicates that it belongs to La(OH) 3 peak. Such as image 3 Shown, La(OH) 3 phase is the main phase in the catalyst. Figure 4 is the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of sample 5, which does not include La(OH) 3 Mutually.
[0067] Table 1
[0068] Sample serial number
example 2
[0070] (Methane Oxidative Coupling)
[0071] A fixed bed catalyst reactor was filled with the catalytic material of Example 1 (10 mg). The reactor was heated to the desired temperature and methane (CH 4 ) and oxygen (O 2 ) into the reactor. The ignition temperature, methane conversion, oxygen conversion, and C 2+ Product selectivity. Methane conversion was calculated based on the difference in methane inlet and outlet concentrations. Selectivity is based on C 2+ The concentration of the product is calculated compared to all converted methane. From the analytical data it can be concluded that the La(OH) 3 Catalysts in crystalline phase than do not contain La(OH) 3 Catalysts in the crystalline phase have higher C 2+ selective.
[0072] Table 2
[0073]
[0074] Figure 5 is the O of sample 1 (La:Ce ratio 10:1) in the methane oxidative coupling reaction 2 conversion percentage, CH 4 conversion percentage and C 2+ Plot of percent selectivity versus temperature in...
example 3
[0076] (oxidative coupling of methane with a second catalyst)
[0077] The fixed bed catalyst reactor was filled with supported catalyst (100 mg, MnNa 2 WO 4 / SiO 2 ). The reactor was heated to the desired temperature, and methane and oxygen were fed into the reactor at a flow rate of 33.3 sccm. CH for each sample is listed in Table 3 4 :O 2 ratio, methane conversion, oxygen conversion, and C 2+ Product selectivity. Methane conversion was calculated based on the difference in methane inlet and outlet concentrations. Selectivity is based on C 2+ The concentration of the product is calculated compared to all converted methane.
[0078] table 3
[0079]
[0080] From the analysis of the data in Table 3, it was determined that the selectivity of the second catalyst in the presence of oxygen was higher than that obtained with the catalyst used in Example 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com