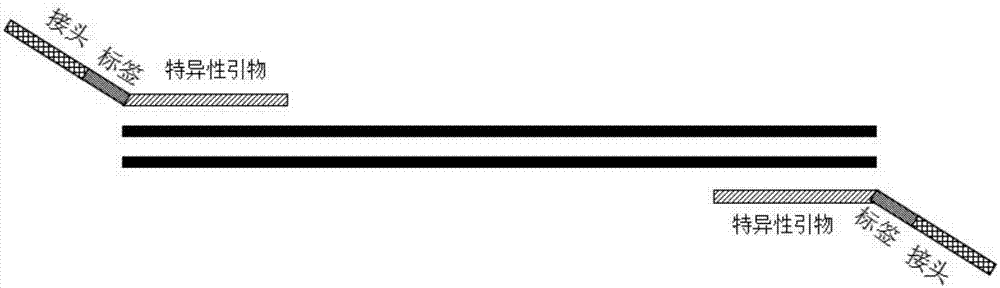Method for detecting rearrangement clonality of correlative genes of lymphocyte
A clonality and gene technology, applied in the field of clonal detection of lymphocyte-related gene rearrangements, can solve the problems of increasing detection costs, inability to detect somatic hypermutation at the same time, and inability to analyze rearrangements in depth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] The specific operation process that the present invention takes in order to realize the above object is:
[0072] (1) Selection and verification of target fragment-specific primers:
[0073] The BIOMED-2 gene rearrangement primer detection system has been proved to have good specificity and sensitivity through a large number of clinical experiments. The gold standard for gene clonality rearrangement. However, with the development of next-generation sequencing, there have been no reports of applying such high-specificity and high-sensitivity primer combinations to the detection of next-generation sequencing. Therefore, BIOMED-2 classic primers (such as JJM vanDongen, Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspectedlymphoproliferations: Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936, Leukemia (2003) 17, 2257–2317) as the specific amplification primers of this method...
Embodiment 2
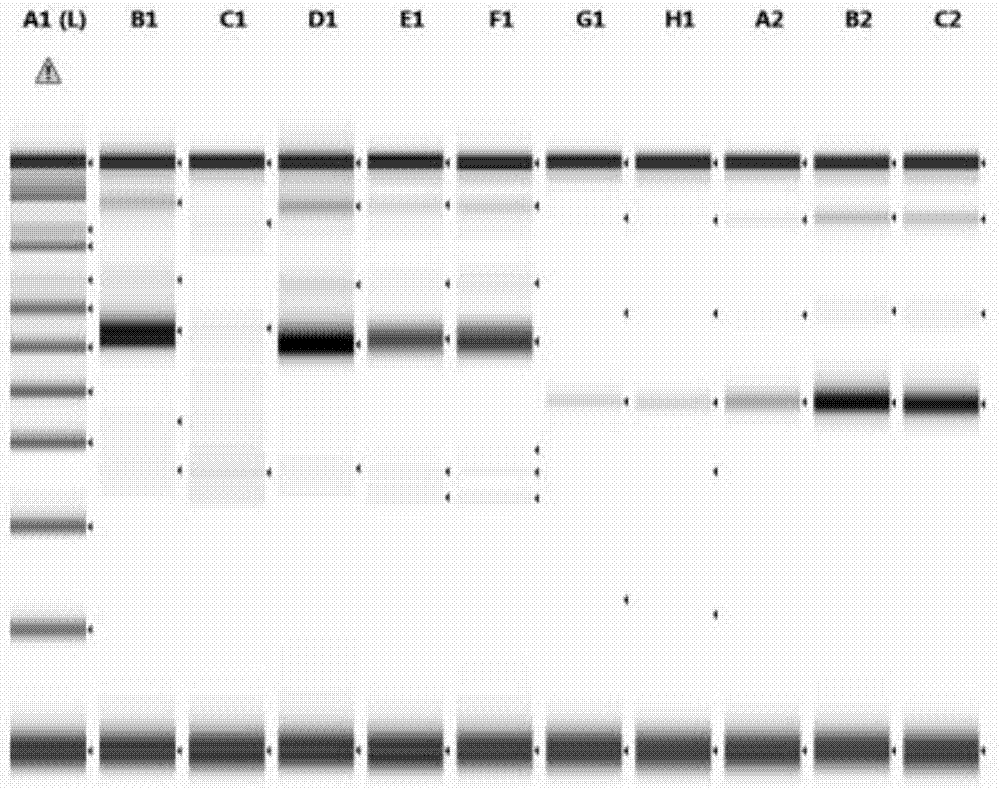
[0097] 1. Materials
[0098] 1.1 Sample selection:
[0099] 3 cases of nucleic acid were extracted from paraffin sections of clinical samples of unknown type; 1 case of nucleic acid extracted from ATCC CRL-2959 cell line was used as a positive control; 1 case of clinically excised tonsil tissue frozen section was used as a negative control; 1 case of pure water was used as a blank control
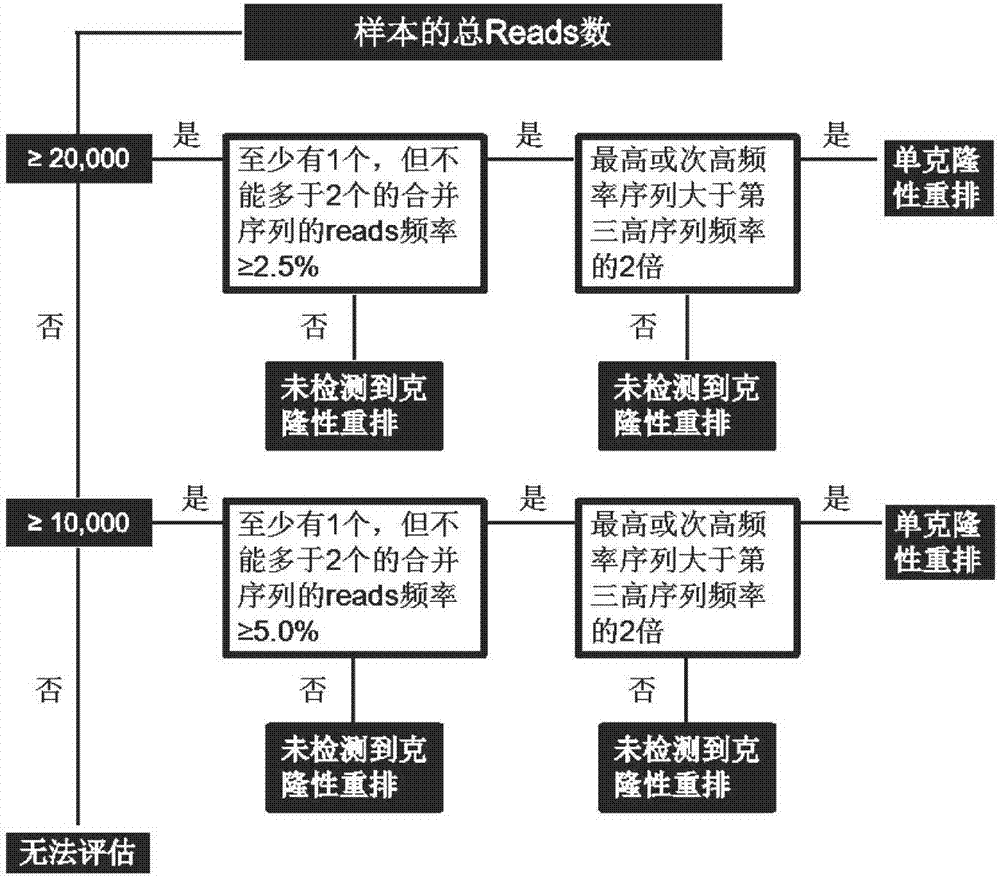
[0100] 1.2 Detection of genes:
[0101] Choose to perform clonality detection on IGH gene rearrangement, and use primers that match the sequence of the target region of the sample as shown in the table below:
[0102] Table 2
[0103]
[0104] Choose to perform clonality detection on TCRG gene rearrangement, and use primers to match the sequence of the target region of the sample as shown in the table below:
[0105] table 3
[0106]
[0107]
[0108] 1.3 PCR reagents
[0109] Including AntiTaq enzyme (Roche) and Buffer for amplification, dNTP and MgCl 2 the solution
[0110...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com