Migratory locust mesenchymal epidermal protein gene 6 and application thereof in locust control
A technology of epidermal proteins and internodes, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, and plant genetic improvement, can solve problems such as non-target biological hazards, environmental pollution, and drug resistance, and achieve the goal of reducing the number of eggs laid by pests and the number of offspring populations Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] 1. Acquisition of the full-length sequence of the epidermal protein gene of the migratory locust intersegmental membrane
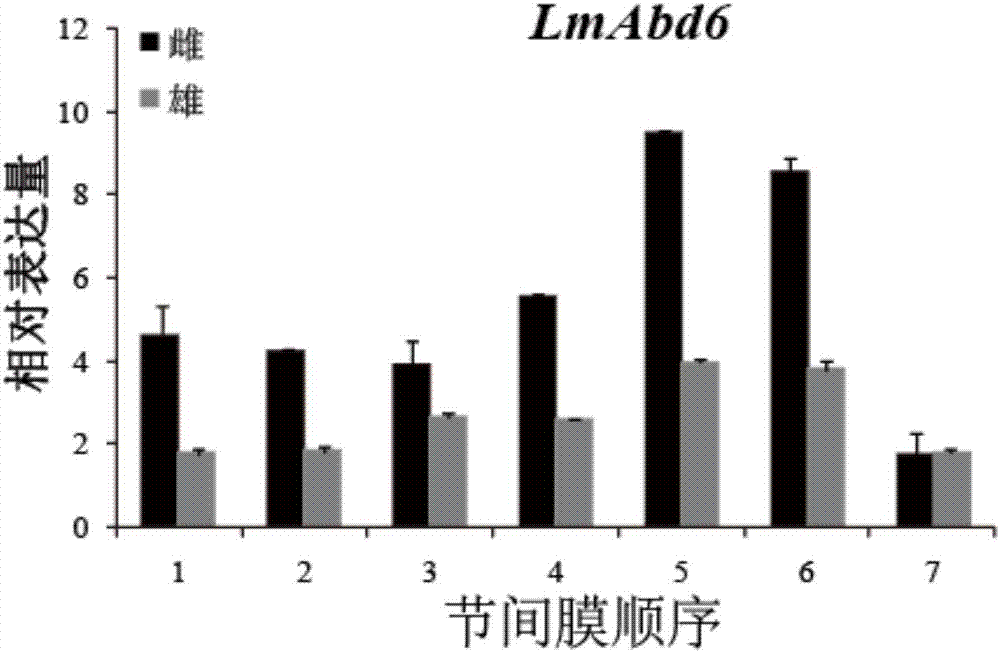
[0016] Based on the transcriptome database of migratory locusts, the epidermal protein gene of migratory locusts was searched using bioinformatics methods, and after sequence analysis combined with genome sequence splicing and comparison of migratory locusts, an intersegmental membrane epidermal protein gene of migratory locusts (LmAbd6 ) sequence, using primer premier5.0 software to design upstream and downstream primer sequences and send them to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for synthesis. Healthy adult migratory locusts of the same size were selected, and the intersegmental membrane tissue was dissected and frozen in liquid nitrogen. The first 6 biological replicates, 4 biological replicates were set up, and the total RNA was extracted according to the TaKaRa Trizol kit. Using M-MLV reverse transcriptase, the extracted total RNA was...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: Experiment of killing migratory locusts by dsRNA of intersegmental membrane epidermal protein gene of migratory locusts
[0025] 1. Injection of dsRNA gene of migratory locust intersegmental membrane epidermal protein
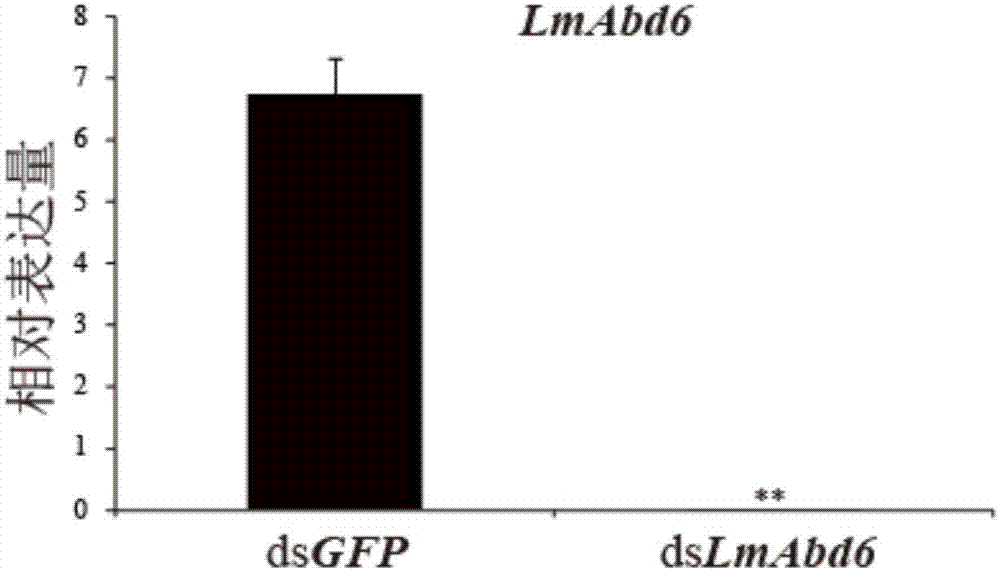
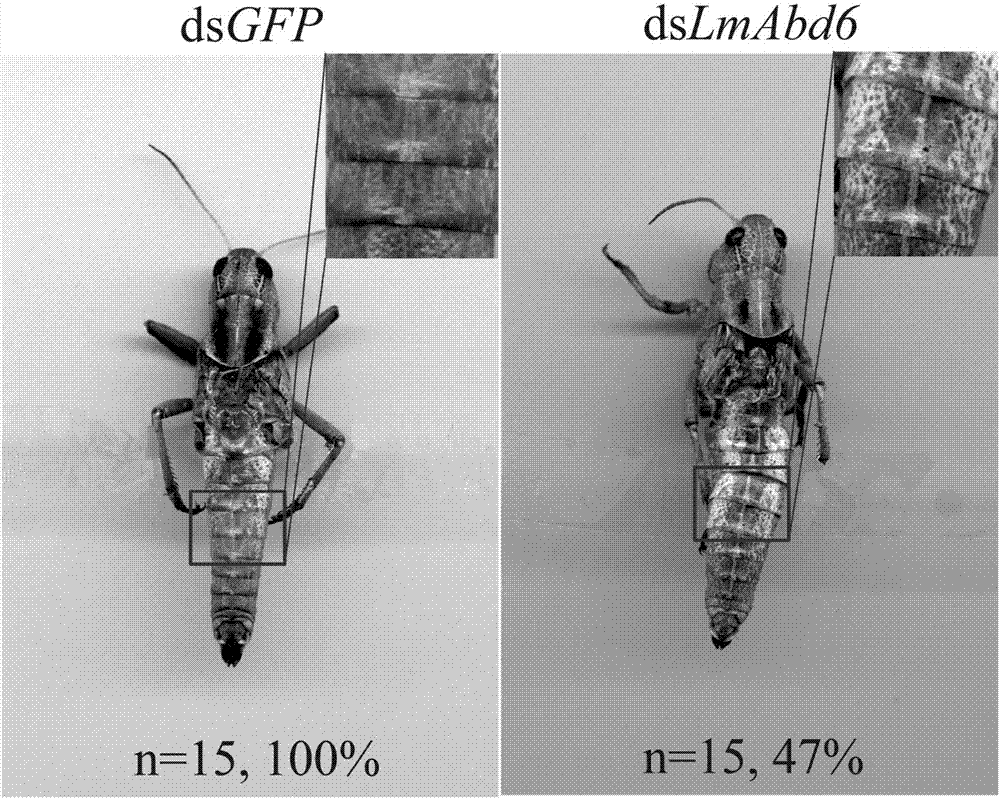
[0026] Thirty female nymphs of the 5th instar and the 2nd day of age were selected for the experiment. 5 μl (10 μg) of dsRNA of SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4 were gently injected with a 25 μl micro-syringe along the blood flow between the second and third abdominal segments of the lateral abdomen of the nymph. At the same time, 30 female nymphs were selected as the control group. Inject the same volume and concentration of dsGFP into the control group. Pick equal amounts of males that grow healthy and have the same size and mix with the injected female migratory locusts respectively and place them in a constant temperature biochemical incubator at 30°C to raise (light: dark time = 14h:10h, temperature 30±2°C, humidity 60% ), fed fresh wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com