Method, device and storage medium for point mutation detection and filtering based on next-generation sequencing
A next-generation sequencing and point mutation technology, applied in genomics, sequence analysis, proteomics, etc., can solve the problems of large sample consumption, low throughput, and low detection specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] In this embodiment, the samples used are standard products purchased from Horizon, and the samples to be tested include 3 positive standard products Q1, Q3 and Q5, and the theoretical VAFs corresponding to the positive sites are 1%, 3% and 5% respectively; There is also a negative control sample Q0. The specific steps of paired sample detection in this embodiment are as follows:
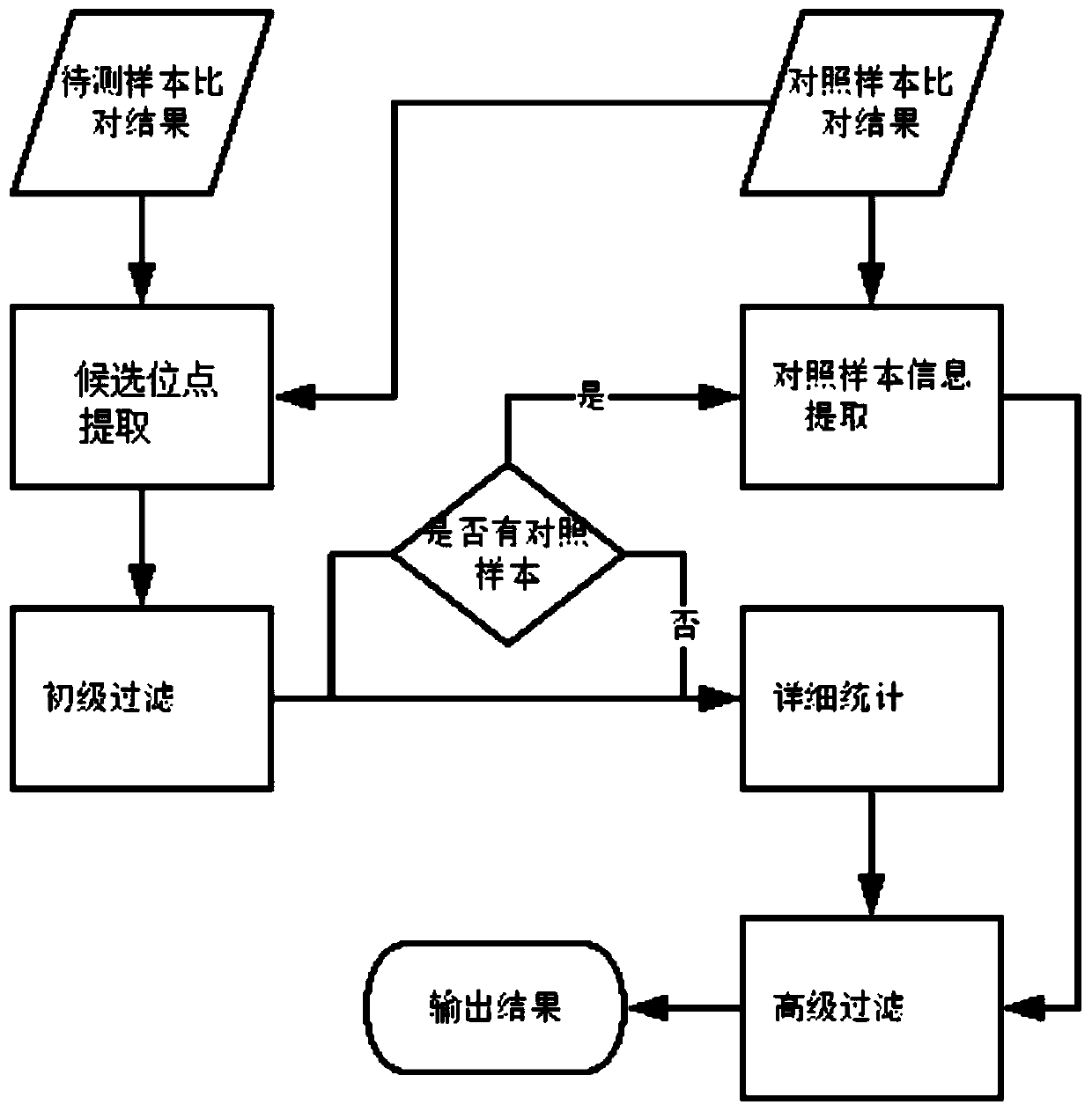
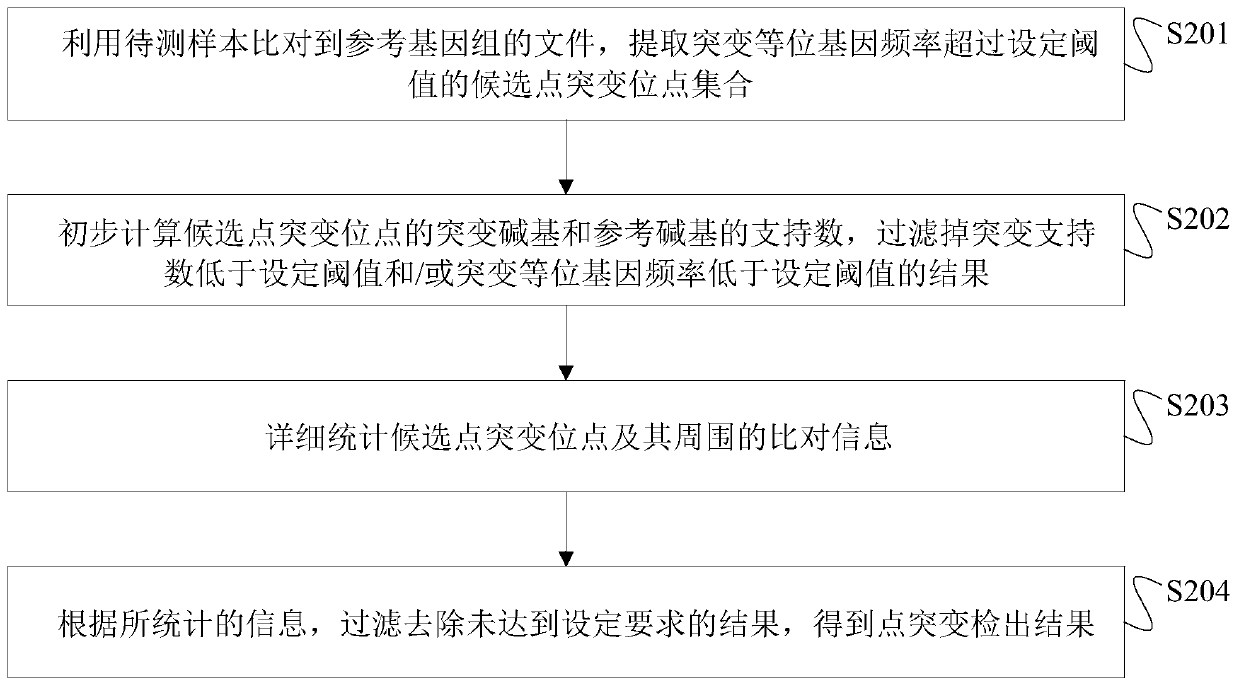
[0113] (1) Using the BAM files of the positive standard products Q1, Q3, Q5 and the control sample Q0 respectively, obtain the set of candidate somatic point mutation sites of the three samples to be tested.
[0114] (2) Obtain the unfiltered point mutation results of the three samples to be tested through the primary filtering step, and then count the number of mutation supports and VAF at the corresponding positions in the control sample.
[0115] (3) Statistically compare detailed information at and around the site obtained after the primary filtering step in the three samples to be tested...
Embodiment 2
[0129] In this embodiment, the sample to be tested is a quality-assessed point mutation-positive sample, including 3 positive point mutation sites, and the VAF is 1%-20%. The specific steps of single-sample detection in this embodiment are as follows:
[0130] (1) Using the BAM file of the sample to be tested, a set of candidate point mutation sites is obtained.
[0131] (2) Obtain the unfiltered point mutation result of the sample to be tested through the primary filtering step.
[0132] (3) Statistically compare detailed information at and around the site obtained after the primary filtering step in the sample to be tested.
[0133] (4) Through the advanced filtering module, the unfiltered point mutation detection results in the samples to be tested are finally obtained.
[0134] The sensitivity of the final detection result of this embodiment to the 3 positive sites is 100%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com