Novel lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei k56
A technology of para-cheese and Lactobacillus, applied in the direction of bacteria, biochemical equipment and methods, food science, etc., can solve the problems of lethality and easy side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Identification of 16s rRNA and pheS gene sequences
[0028]K56 was isolated from the feces of children in Taiwan. The isolated strain K56 was cultured with MRS based on 37°C for one day, and its genomic DNA was extracted. In order to confirm the status of isolate K56 in microbial classification, 16S rRNA and pheS gene primers (as shown in Table 1) were used to perform polymerase chain reaction (Polymerase Chain Reaction, PCR) on the genomic DNA of isolate K56, and sequenced Nucleotide fragments after propagation.
[0029] Table 1, 16S rRNA and pheS gene primer sequences
[0030]
[0031] The K56 nucleotide fragment of the sequenced isolate was compared with the strains belonging to Firmicutes by using the comparison software in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database to compare the 16S rRNA and pheS gene fragments. The typical 16S rRNA and pheS gene fragments were compared manually. For comparison, the typical 16S rRNA and pheS...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: the fermentability test of Lactobacillus paracasei K56
[0041] In order to further confirm the subspecies of the isolate K56, the fermentability of the isolate K56 on various carbohydrate substrates was tested using the API 50CHL rapid identification kit (bioMerieux, France). The results are shown in Table 4. The results of the fermentation ability analysis of the API50CHL rapid identification kit showed that the biochemical characteristics of the isolate K56 were highly similar to Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. Lactobacillus is still a new species.
[0042] After identification and confirmation of the species of the isolate K56, Lactobacillus paracasei subspecies K56 was deposited at 7B, Yinghaofeng Street, D-38124, Braunschweig, Germany on June 27, 2013 according to the Budapest Treaty. German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures (Inhoffenstr. 7 B, D-38124 Braunschweig, Germany), and the DSMZ deposit number DSM27447 was given by the Internati...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: the acid production ability test of Lactobacillus paracasei subspecies K56
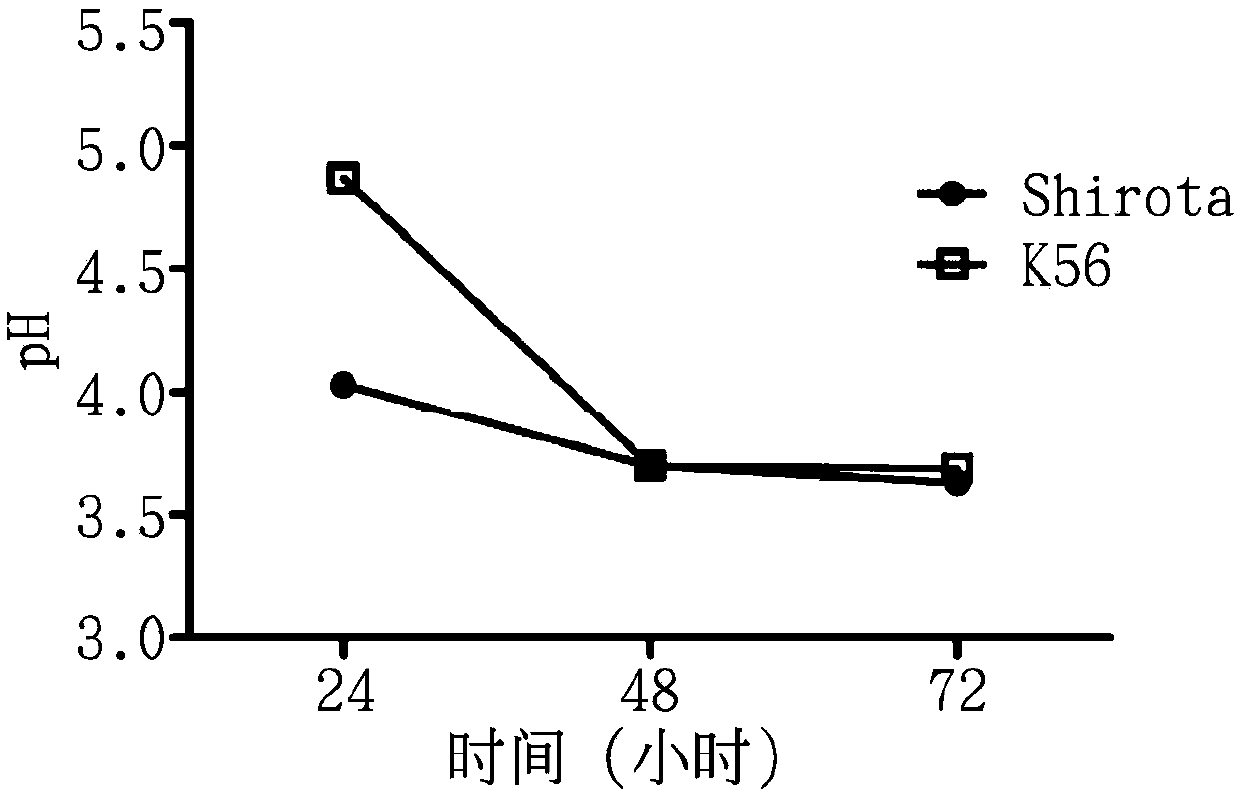
[0046] The Lactobacillus paracasei subspecies K56 cultured in MRS medium (Man, Rogoa, Sharpe medium) was taken out, and transferred to a culture medium based on skim milk, and cultivated at 37°C for 24 hours, 48 hours and After 72 hours, take out the culture liquid (fermentation liquid) after fermentation, detect the pH value of the culture liquid (fermentation liquid) and carry out acid titration test.
[0047] In the description of the following examples, "Shirota bacteria" means that the strain to be tested is Lactobacillus casei Shirota strain (Shirota) isolated from the famous lactic acid bacteria drink Yakult. Shirota bacteria are known to have good immunomodulatory ability.
[0048] In the acid titration test, every 5 grams of fermented culture solution was mixed with 20 milliliters of pure water, and titrated with 0.1N sodium hydroxide to calculate the acid production o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com