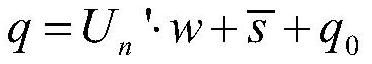A 3D reconstruction method of cardiac soft tissue based on sparse principal component analysis
A sparse principal component and 3D reconstruction technology, applied in the field of 3D reconstruction of cardiac soft tissue based on sparse principal component analysis, can solve problems such as inability to explain the meaning of principal components, reduce model complexity, and heart damage, and achieve reduced computational complexity. The effect of improving calculation speed and improving success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
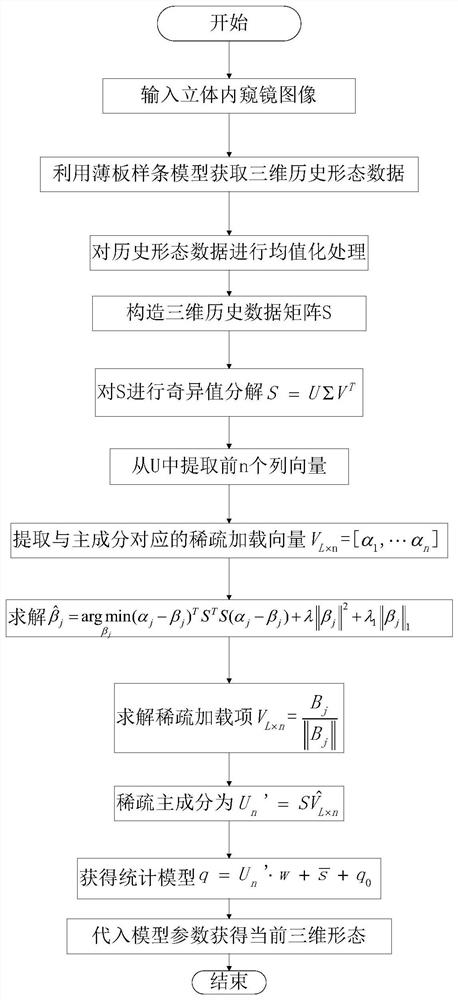
[0034] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the three-dimensional reconstruction method of cardiac soft tissue based on sparse principal component analysis in the present invention.
[0035] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, a method for three-dimensional reconstruction of cardiac soft tissue based on sparse principal component analysis of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0036] S1. Obtain 600 frames of images on the surface of the beating heart from the stereoscopic endoscope system as historical image data;
[0037] S2. Utilize the traditional high-complexity thin-plate spline model TPS to extract the three-dimensional historical shape data of the region of interest in the historical image data; in this embodiment, the size of the region of interest is set to be a pixel region of 120*120, and the total N= 14400, N is the total number of points in the target region on the surface of the heart, extract L=600 frames of three-dimensional historical shape d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com