Dimensionality reduction expression method of mapping knowledge domain on basis of sub-graph division
A knowledge map and expression method technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to accurately express entity and relationship information, ignoring local features of the map, etc., to achieve improved computing performance and growth speed maintain a smooth effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
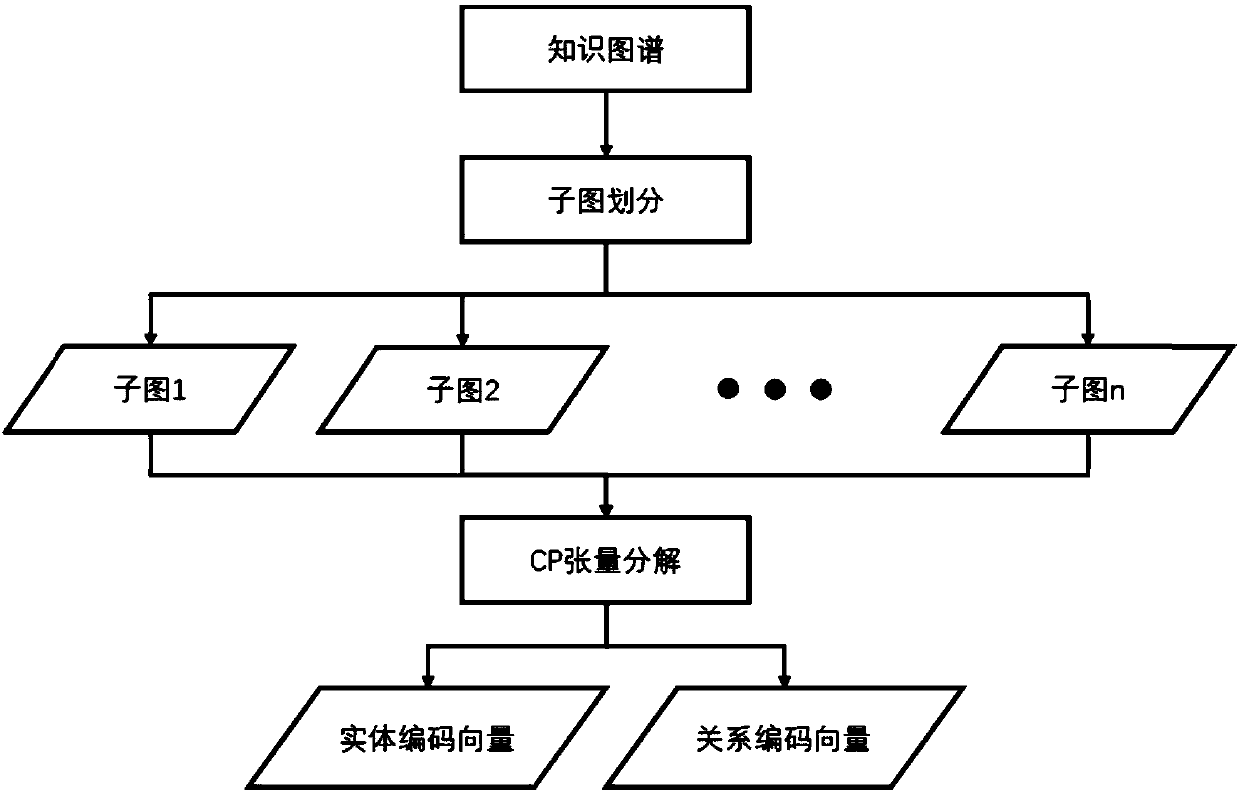
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method provided by the present invention includes the following contents: divide the knowledge map into subgraphs; perform CP tensor decomposition on the divided subgraphs, and obtain entity encoding vectors and relationship encoding vectors as the result output of dimensionality reduction expression.
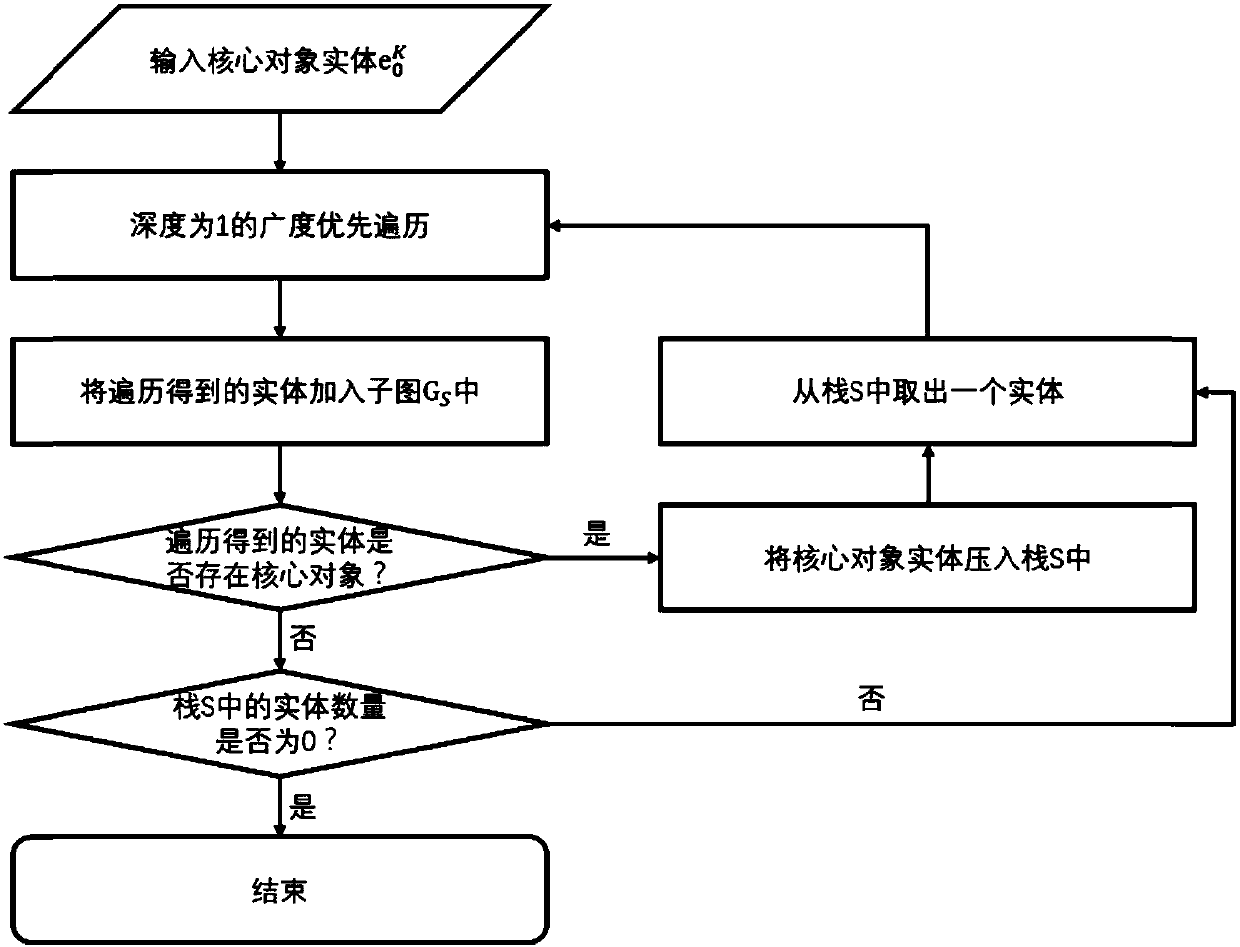
[0047] In this example, if Figure 8 As shown, the process of dividing the knowledge map into subgraphs is as follows:
[0048] S11. Manually mark the entities in the knowledge map, and mark different entities as core object entities and secondary object entities;
[0049] S12. Push all marked core object entities into the stack K
[0050] S13. Take a core object entity from the stack K as the traversal starting point to perform subgraph traversal;
[0051] S14. Remove the core object entity obtained through traversal from the stack K;
[0052] S15. Determine whether the number of entities in the stack K is 0, and if so, end the subgrap...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The commonly used indicator in the world to measure the encoding effect of entities is AUC (Area Under Curve). The encoded entities are classified into binary values. The better the classification effect, the more reasonable the encoding method, and the higher the value of AUC. The data set of this experiment is the Cora public data set, and the structure of the Cora data is as follows Figure 11 As shown, by comparing the AUC value obtained by this method with other mainstream methods for entity binary classification on the Cora knowledge graph, the histogram is drawn as Figure 12-Figure 13 shown.
[0074] Comparing the computing performance of the subgraph division method and the traditional method, Table 1 lists the four methods completed on the same computer (Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-6600K CPU@3.50GHz) and the same data set The computation time spent on entity encoding.
[0075] Table 1 Performance comparison between the subgraph partition method and the traditional ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com