Compound microbial fertilizer for preventing continuous cropping of ginseng and preparation method thereof
A compound microorganism and continuous cropping technology, applied in the field of organic fertilizers, can solve the problems that it is difficult to meet the requirements of ginseng growth, development and high yield, unfavorable soil physical and chemical properties and soil microflora, and little research on microorganisms that degrade ginseng allelochemicals. Preventing the harm of ginseng from repeated cropping, improving the yield of ginseng, and the effect of significant application effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
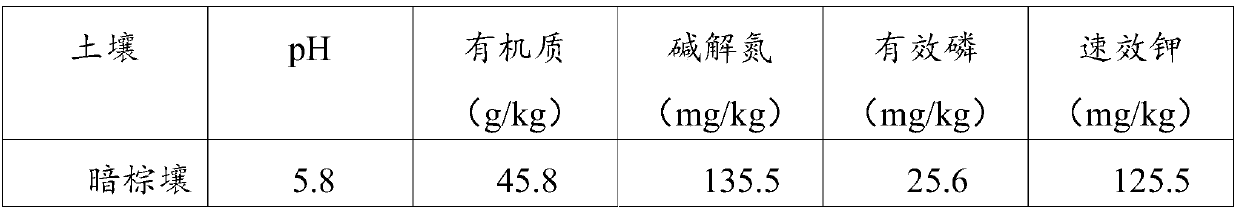
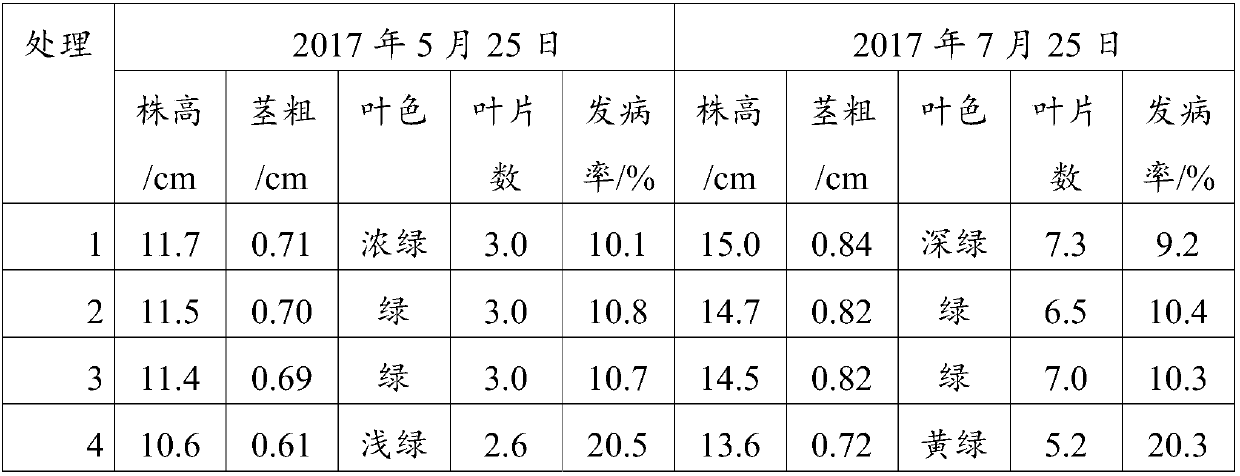
[0064] This embodiment prevents the compound microbial fertilizer of ginseng from repeated cropping, including organic fertilizer, inorganic fertilizer and composite functional bacteria;
[0065] Wherein, the organic fertilizer includes 60 parts by weight of traditional Chinese medicine residue, 15 parts by weight of humic acid, 8 parts by weight of diatomaceous earth, 5 parts by weight of volcanic rock, 5 parts by weight of bentonite, 5 parts by weight of zeolite, 15 parts by weight of biochar, and 5 parts by weight of bran. parts by weight, 1 part by weight of white sugar, 2 parts by weight of ferment bacteria and 55 parts by weight of water;
[0066] Described inorganic fertilizer comprises 40 weight parts of potassium nitrate, 8 weight parts of urea, 20 weight parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 40 weight parts of potassium sulfate and 0.2 weight part of potassium fulvic acid;
[0067] The composite functional bacteria include 35 parts by weight of Acinetobacter, 35 p...
Embodiment 2
[0145] This embodiment prevents the compound microbial fertilizer of ginseng from repeated cropping, including organic fertilizer, inorganic fertilizer and composite functional bacteria;
[0146] Wherein, the organic fertilizer includes 50 parts by weight of traditional Chinese medicine residue, 10 parts by weight of humic acid, 5 parts by weight of diatomite, 4 parts by weight of volcanic rock, 3 parts by weight of bentonite, 2 parts by weight of zeolite, 10 parts by weight of biochar, and 2 parts by weight of rice bran. part, 0.5 parts by weight of brown sugar, 1 part by weight of ferment bacteria and 50 parts by weight of water;
[0147]Described inorganic fertilizer comprises 35 parts by weight of potassium nitrate, 4 parts by weight of urea, 13 parts by weight of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 35 parts by weight of potassium sulfate and 0.05 parts by weight of potassium fulvic acid;
[0148] The composite functional bacteria include 25 parts by weight of Acinetobacter, 2...
Embodiment 3
[0226] This embodiment prevents the compound microbial fertilizer of ginseng from repeated cropping, including organic fertilizer, inorganic fertilizer and composite functional bacteria;
[0227] Wherein, the organic fertilizer includes 55 parts by weight of traditional Chinese medicine residue, 12 parts by weight of humic acid, 6.5 parts by weight of diatomite, 4.5 parts by weight of volcanic rock, 4 parts by weight of bentonite, 3.5 parts by weight of zeolite, 12.5 parts by weight of biochar, 3 parts by weight of bran parts by weight, 0.5 parts by weight of white sugar, 1.5 parts by weight of ferment bacteria and 52 parts by weight of water;
[0228] Described inorganic fertilizer comprises 37 parts by weight of potassium nitrate, 6 parts by weight of urea, 16 parts by weight of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 37 parts by weight of potassium sulfate and 0.1 part by weight of potassium fulvic acid;
[0229] The composite functional bacteria include 30 parts by weight of Acine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com