Bacterium capable of degrading buprofezin and bifenthrin as insecticides and bacteriostat produced by using bacterium
A bifenthrin and insecticide technology, applied in the field of biological high-tech, can solve the problems of unfavorable industrial production, unstable degradation properties, easy loss of degradation genes, etc., achieve wide application potential and value, good removal effect, and protect people health effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The isolation and identification of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0026] The invention provides a stable and highly efficient bacterial strain for degrading buprofezin and bifenthrin and the bacterial agent D-6 produced therefrom, which is isolated from a soil polluted by buprofezin for a long time in Jiangsu Province. The screening method of bacterial strains is as follows: take 5g soil sample and add to 100mL containing 50mg·L -1 In the shaking flask of the basal salt medium of buprofezin (hereinafter referred to as BMM), place 30 ℃, 150rpm in the shaker culture, after 5 days, transfer to the shaking flask containing fresh BMM with 5% inoculation amount, carry out continuously Three enrichment cultures. Dilute the enrichment solution from the last passage and spread it on the BMM solid medium. After culturing at 30°C for 5 days, pick a single colony that formed a transparent circle and culture it in a 4 mL LB test tube. After the bacterial cells grow thick, a part...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2 laboratory degradation experiment
[0029] 2.1 Preparation of seed solution
[0030] Pick a single colony that has been activated on the plate, inoculate it in LB medium, and culture it in a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm until OD 600≈1.0. Collect the cells by centrifugation (4°C, 6000rpm for 5min), wash twice with basal salt medium and resuspend the cells to OD 600 ≈2.0, this is the seed solution.
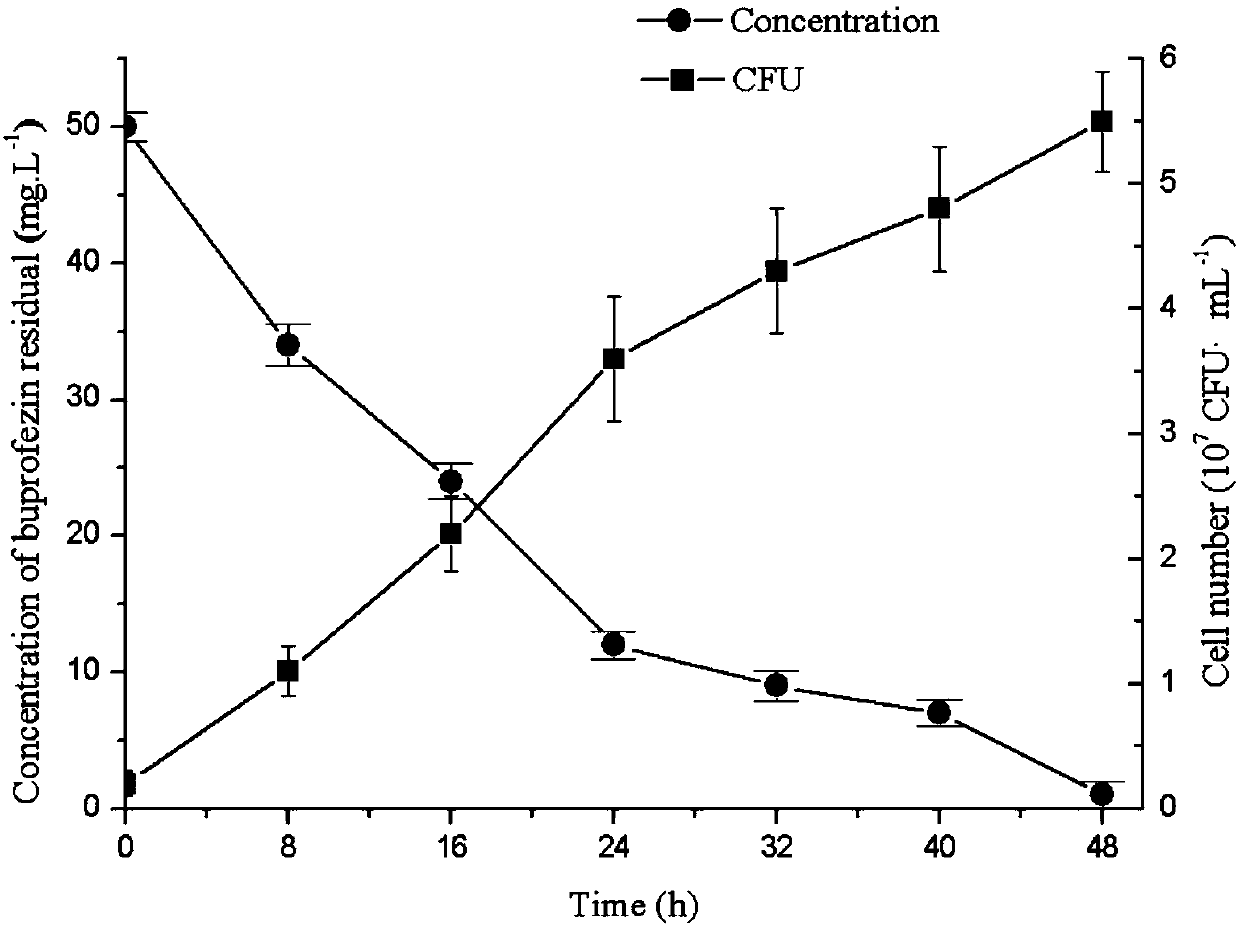
[0031] 2.2 Degradation of buprofezin by strain D-6
[0032] The seed liquid of strain D-6 was inoculated into BMM with an inoculum amount of 2%, and placed in a shaker at 30° C. at 150 rpm for 48 hours. Take 3 mL of culture solution every 8 hours, detect and calculate the concentration and degradation rate of remaining buprofezin in the culture medium by HPLC, and at the same time, dilute the regularly sampled culture solution and apply LB solid medium, calculate the growth of bacteria, and draw the strain D -6 to the growth degradation curve of buprofezin (as ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3 degradation stability experiment
[0042] Since the reported strain Rhodococcus qingshengii YL-1 (CCTCC AB 2017132) has unstable degradation properties of buprofezin, it is necessary to evaluate the stability of the degradation properties of strain D-6. Pick freshly activated single colonies of strain D-6 and strain YL-1 on the BMM plate and form a transparent circle, inoculate them into test tubes containing 4 mL of LB medium, and culture them in a shaker at 30°C and 150 rpm until OD 600 ≈1.0. Transfer this bacterial solution to another test tube containing 4mL LB medium with 1% inoculum, and cultivate to OD under the same culture conditions. 600 ≈1.0, this is the first passage. Dilute the bacterial solution of the first passage to an appropriate multiple (10 -4 ~10 -6 ) after coating the BMM flat plate, and after the colony grows out, count the percentage of the colony number that cannot form a transparent circle to the total number of colonies. Per...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com