Overcurrent protection circuit, control method and device, and terminal
An overcurrent protection circuit and control method technology, applied in the electronic field, can solve problems such as burning terminals, safety risks, and user property losses, and achieve the effects of overcurrent protection, improved reliability, and reduced after-sales maintenance costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
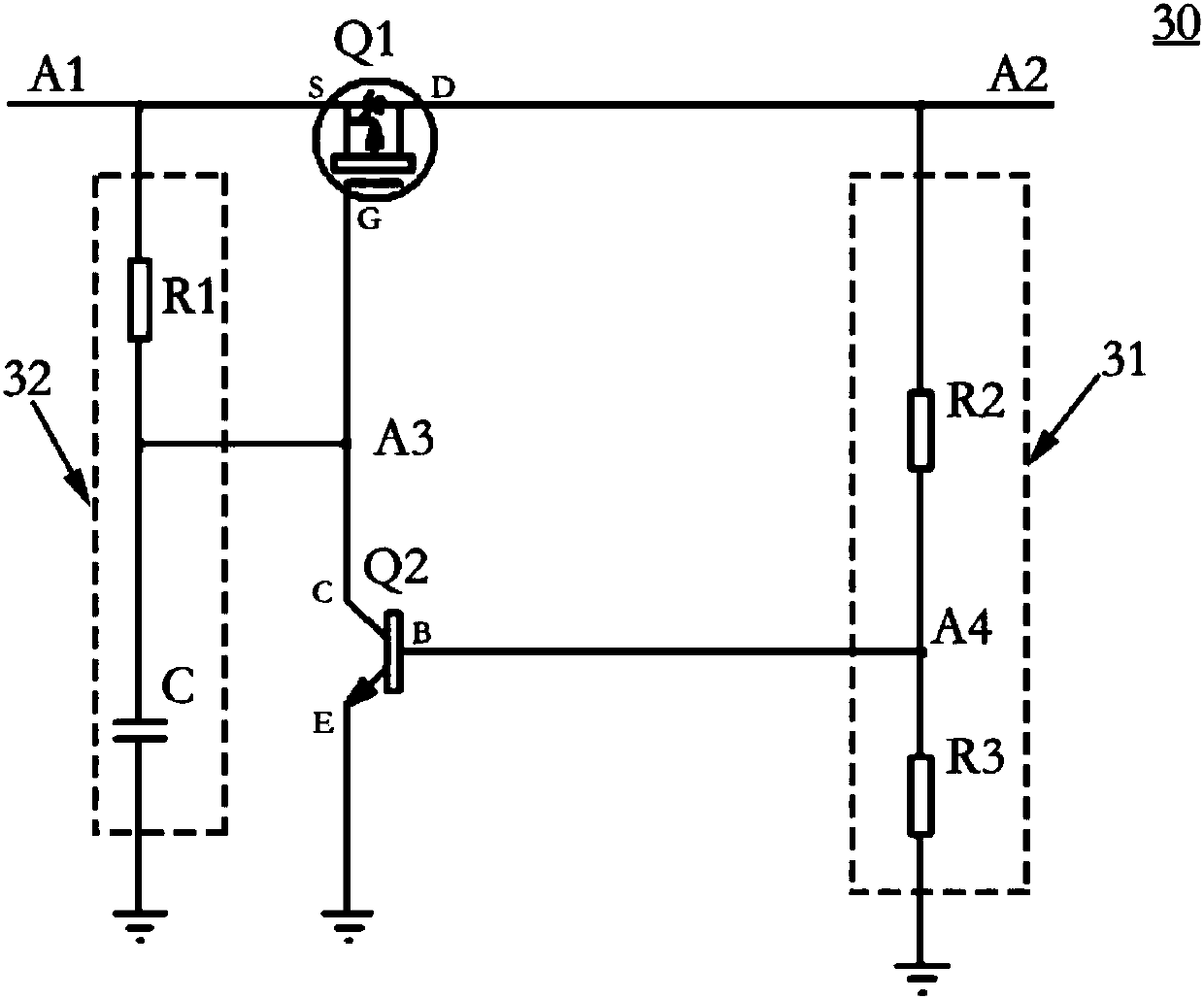
[0064] Such as image 3 as shown, image 3 An overcurrent protection circuit provided in the first embodiment of the present invention, the overcurrent protection circuit 30 includes a power switch tube and a voltage divider circuit 31;
[0065] The power switch tube includes a first power switch tube Q1 and a second power switch tube Q2;
[0066] The first end of the first power switch tube Q1 is connected to the third end of the second power switch tube Q2, and the second end of the first power switch tube Q1 is connected to the output end of the terminal power supply (represented by A1 in the figure shown) connection, the third end of the first power switch tube Q1 is connected to the power supply pin (shown in A2 in the figure) that the terminal supplies power to the OTG device;
[0067]The first end of the voltage dividing circuit 31 is connected to the power supply pin of the OTG device, and the second end of the voltage dividing circuit 31 is connected to the ground; ...
no. 2 example
[0087] The second embodiment of the present invention provides a terminal, and the terminal includes the overcurrent protection circuit described in the first embodiment. For the overcurrent protection circuit, reference may be made to the above content, and details are not repeated here.
[0088] The following combination figure 1 Explain the working process of the overcurrent protection circuit in the terminal:
[0089] When point A1 gradually rises from 0V to 5V, capacitor C is charged through resistor R1, the voltage at point A3 rises from 0V, and the voltage at point A1 rises faster than point A3, so the first power switch tube Q1 starts to conduct, thus The voltage at point A4 also starts to rise. When the voltage at point A4 reaches above 0.7V, the second power switch tube Q2 is turned on, causing the voltage at point A3 to drop, the first power switch tube Q1 is completely turned on, and the voltage at point A2 is equal to point A1. The terminal starts to supply powe...
no. 3 example
[0093] Based on the overcurrent protection circuit of the first embodiment, please refer to Figure 4 , Figure 4 A method for controlling an overcurrent protection circuit provided in the third embodiment of the present invention, the method includes the steps of:
[0094] S41. Acquire the voltage value of the voltage divider circuit.
[0095] S42. If the voltage value of the voltage dividing circuit is lower than the preset voltage value, control the first power switch tube and the second power switch tube to be cut off, so that the terminal power supply output end is disconnected from the OTG device.
[0096] In one embodiment, the method also includes the steps of:
[0097] If the voltage value of the voltage divider circuit is higher than the preset voltage value, then control the first power switch tube and the second power switch tube to be turned on, so that the terminal power output terminal is established with the OTG device connect.
[0098] As an example, the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com