Method for creating and authenticating chromosome translocation line between peanut genomes A and B
A technology of chromosomal translocation and identification method, which is applied in the field of creation and identification of chromosomal translocation lines between peanut A and B genomes, and can solve the problems of unseen peanut chromosomal translocation and lack of research on peanut genome chromosomal translocation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1, the creation method of chromosomal translocation line between peanut A and B genomes
[0047] Experimental materials: peanut cultivar "Si Li Hong" (allotetraploid 2n=4x=40), preserved by the Economic Crops Research Institute of Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
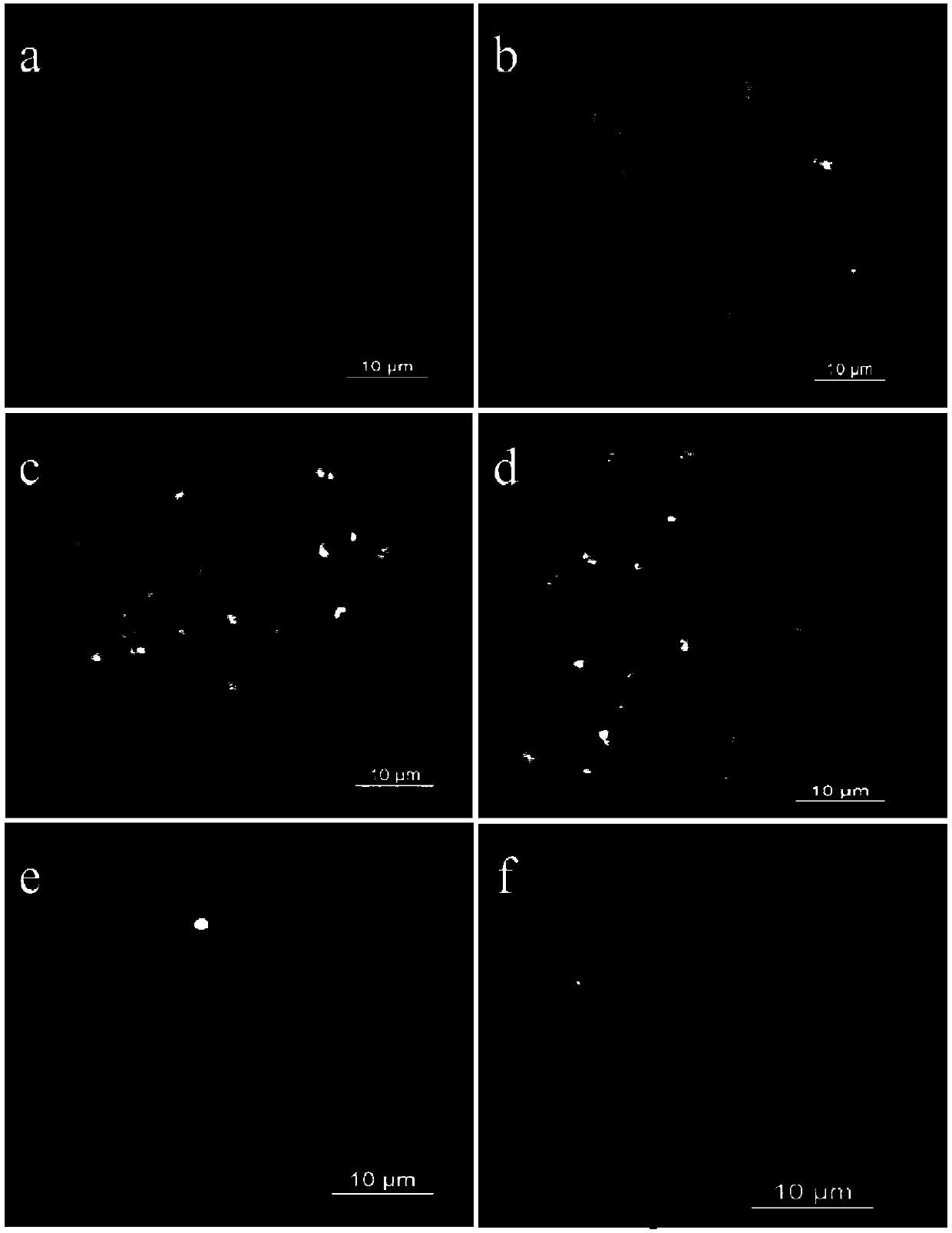
[0048] The experimental materials were planted in flower pots, using Co 60 - Gamma ray irradiation and identification by genome fluorescence in situ hybridization to obtain the chromosomal translocation line between the A and B genomes. The specific method is as follows:
[0049] (1) Plant the peanut cultivar "Si Lihong" in a flowerpot, and from the first day of flowering of the plant, pinch off the newly opened flowers from the base of the flower stalk every morning to control the fruiting of the flowers; Flowering period (the flowering amount is 50% of the total flowering amount), using Co 60 - Irradiation of whole peanut plants with gamma rays, at Co 60 - γ-ray (Henan Academy of Scien...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2, identification method of chromosomal translocation line between peanut A and B genomes
[0052] The identification method of the chromosomal translocation line between the peanut A and B genomes, specifically:
[0053] (1) Probe labeling: Genome donor ancestor species A. duranensis and A. duranensis and A. Whole genome DNA, and A. duranensis whole genome DNA was labeled with fluorescein by the nick translation method to obtain a fluorescein-labeled A. duranensis DNA probe; for A. The whole genome DNA was labeled with digoxin to obtain digoxin-labeled A. DNA probe; the specific method is:
[0054] Fluorescein-labeled A. duranensis DNA probe: First prepare the reaction solution in a 0.2mL eppendorf tube, add 800ng / μL A.duranensis DNA 3μL, 10×DNA Polymerase I Buffer 2.5μL, 1.3mMdNTP mix 2.5μL, 5U / μL DNaseI 0.5μL, 1mM Fluoresceint-12-dUTP 0.7μL, 5U / μL DNAPolymerase I 1μL, 14.8μL ddH 2 O, mix the reaction solution evenly, incubate at 16°C for 25 minutes,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com