Scaled inter-domain metrics for link state protocols
A router and network technology, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve problems such as uneven deployment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
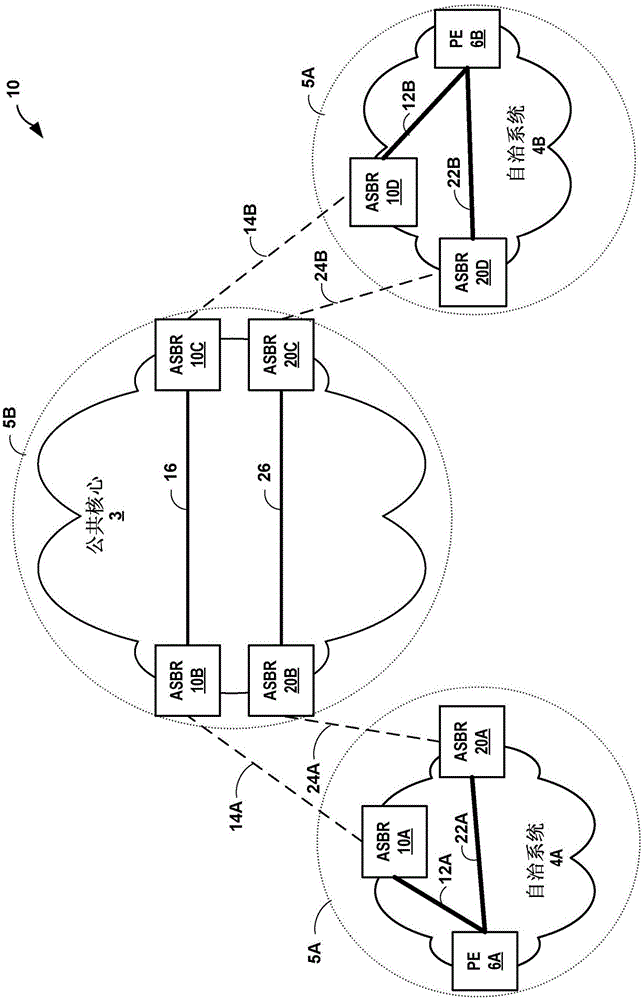
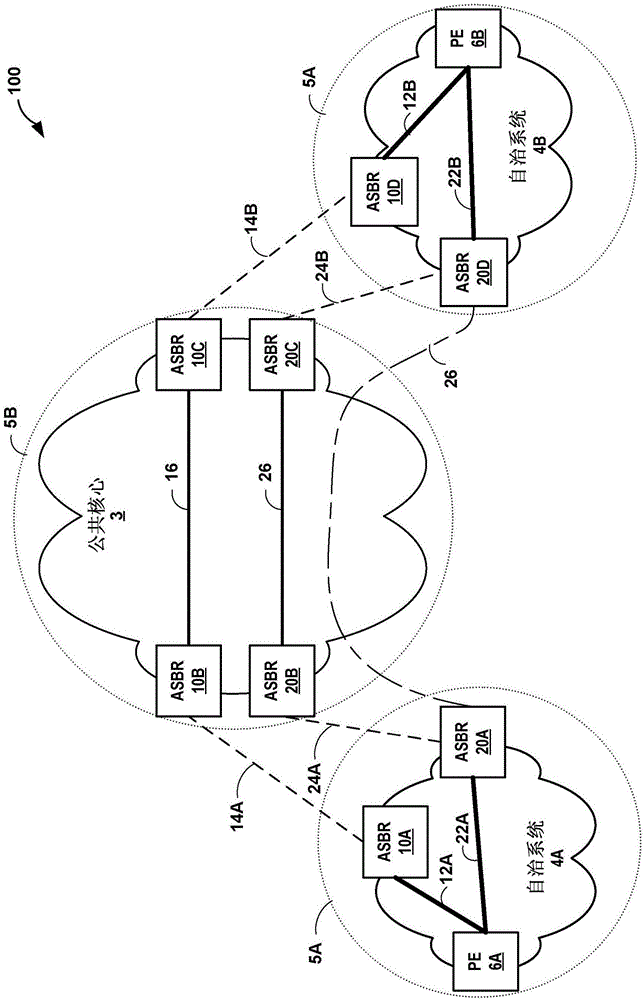
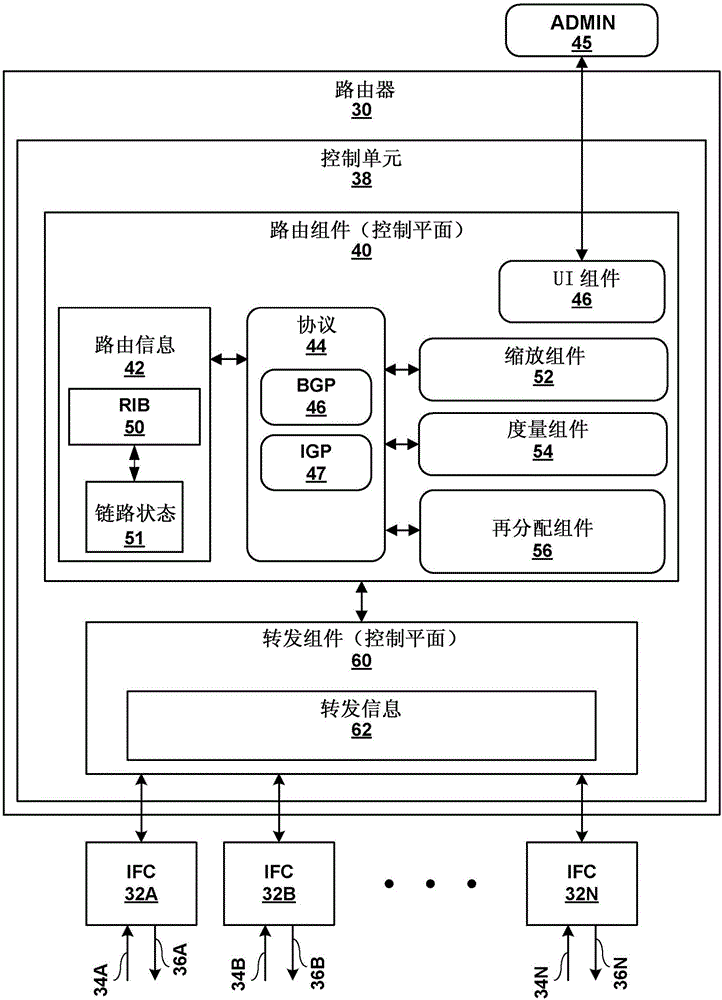
[0108] Example 1. A method comprising: receiving, by a network device located on a boundary of a second interior gateway protocol (IGP) domain, link metrics assigned to links within a first IGP domain; scaling, by the network device, the metrics assigned to the the link metric of the link in the first IGP domain, so that the link metric assigned to the link in the first IGP domain is consistent with the metric scale of the second IGP domain; and through the The network device updates a representation of a topology of a network including the first IGP domain and the second IGP domain to include the scaled link metric.
example 2
[0109] Example 2. The method of example 1, further comprising: selecting, by the network device, a path through the network based on the updated representation of the topology of the network; and following the selected path, by the network device Forward network traffic.
example 3
[0110] Example 3. The method of example 1, wherein receiving the link metric comprises receiving an accumulated IGP (AIGP) attribute of the first IGP domain, the accumulated IGP attribute comprising The link metric for the link.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com