Structured biological samples for analysis by mass cytometry
A biologically sampled, structured technology for application-specific bioreactors/fermenters, analytical materials, biomass post-processing, etc., which can solve problems such as limiting flushing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
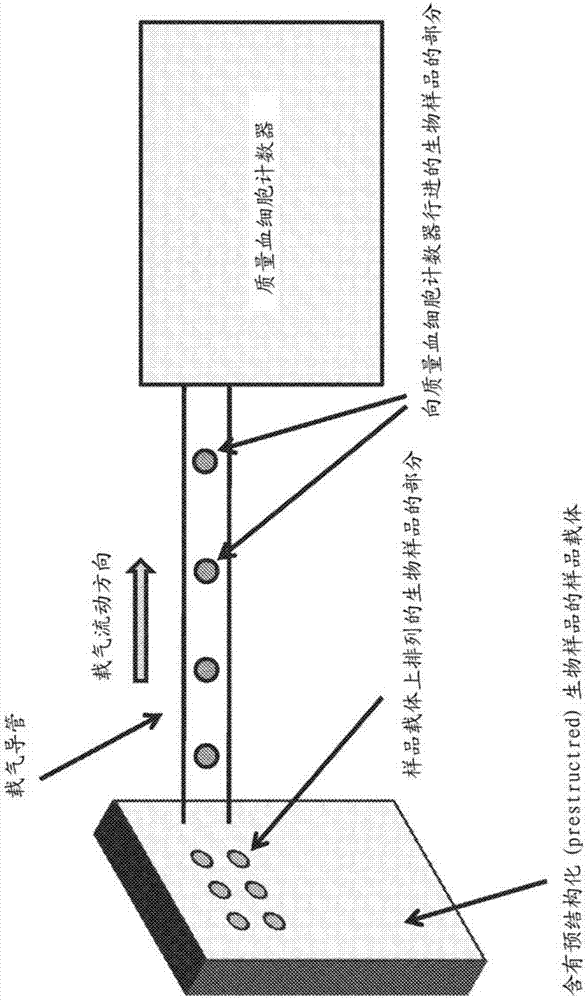
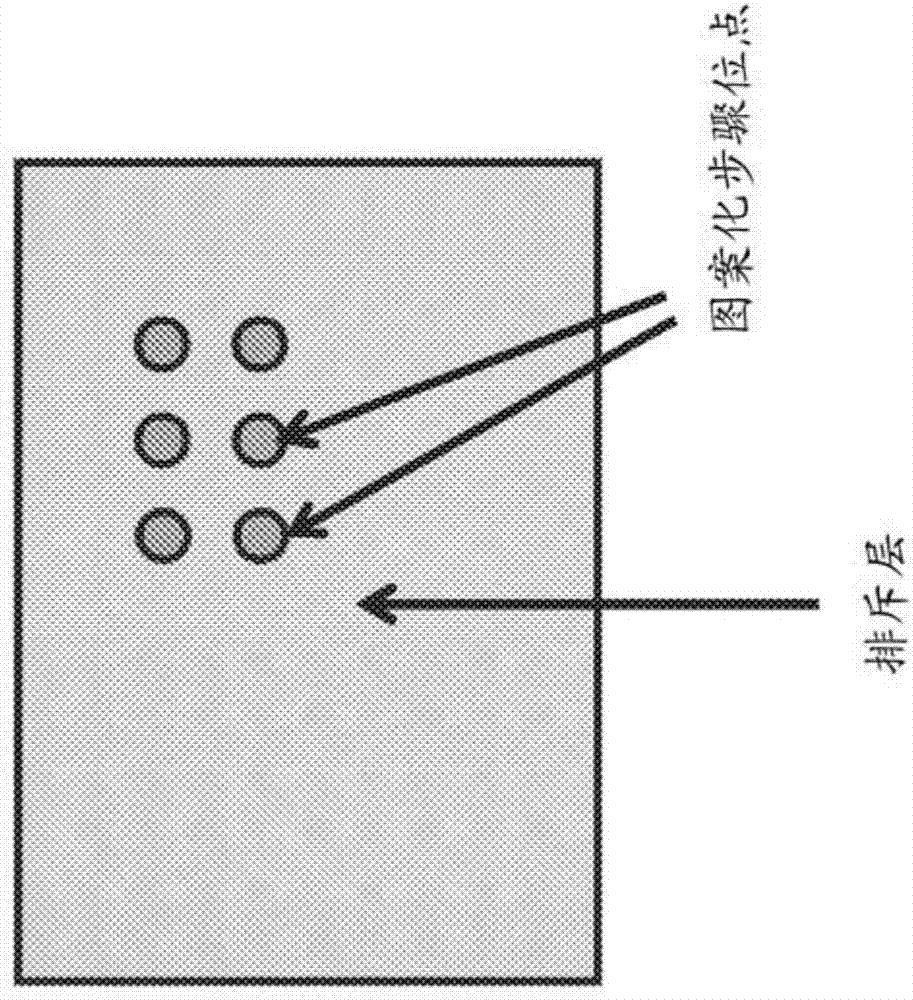
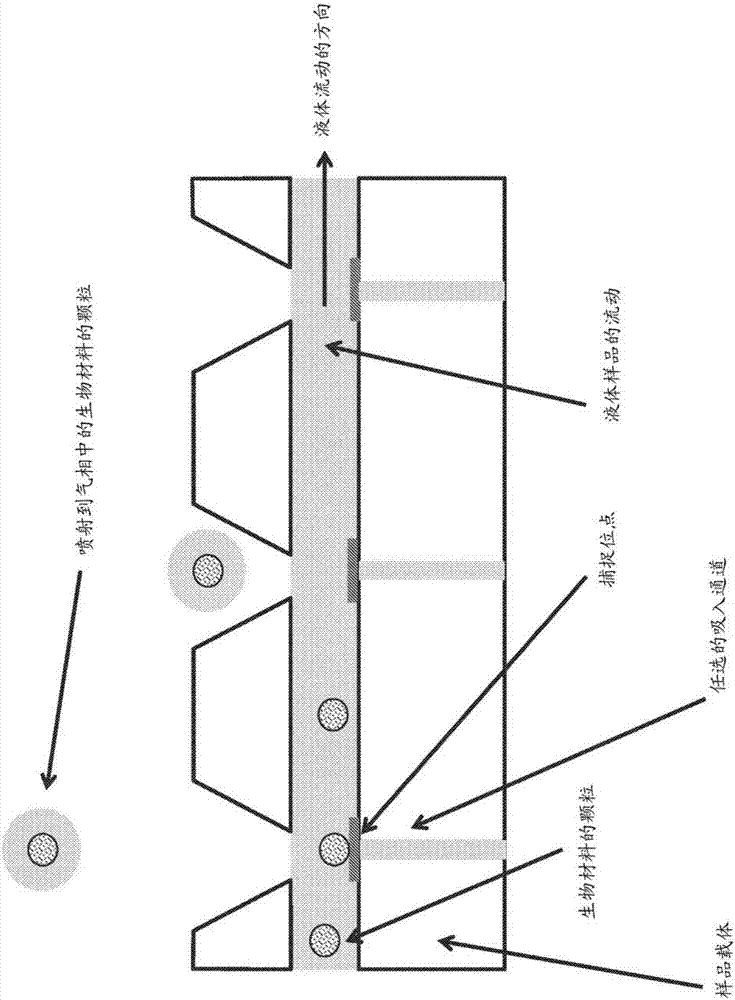
[0030] Structured biological materials are used to introduce discrete samples or pixels of biological material into the ionization source of a mass cytometer or mass spectrometer, such as an ICP source. Structured biomaterials refer to materials arranged in discrete addressable sites on a support, such as individual cells, tissue parts, or other aggregates of biological material. The structured biomaterial can be released from the carrier and each discrete pixel of material introduced sequentially into a mass cytometer or mass spectrometer for analysis. In contrast to random introduction of biological samples as in conventional mass cytometry or mass spectrometry, advantages of sequential introduction of discrete material pixels include higher sample processing rates and elimination of multimers caused by simultaneous arrival of multiple entities, Such as dimers, trimers, etc. Handling and analysis of data can also be simplified by eliminating multimers.
[0031] "Pixel" ref...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com