Water system secondary battery
A secondary battery and water system technology, applied in the field of electrochemical energy storage, can solve the problem of secondary hybrid batteries failing to get rid of them, and achieve the effects of low production cost, high operational safety, and reduced overpotential for hydrogen evolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
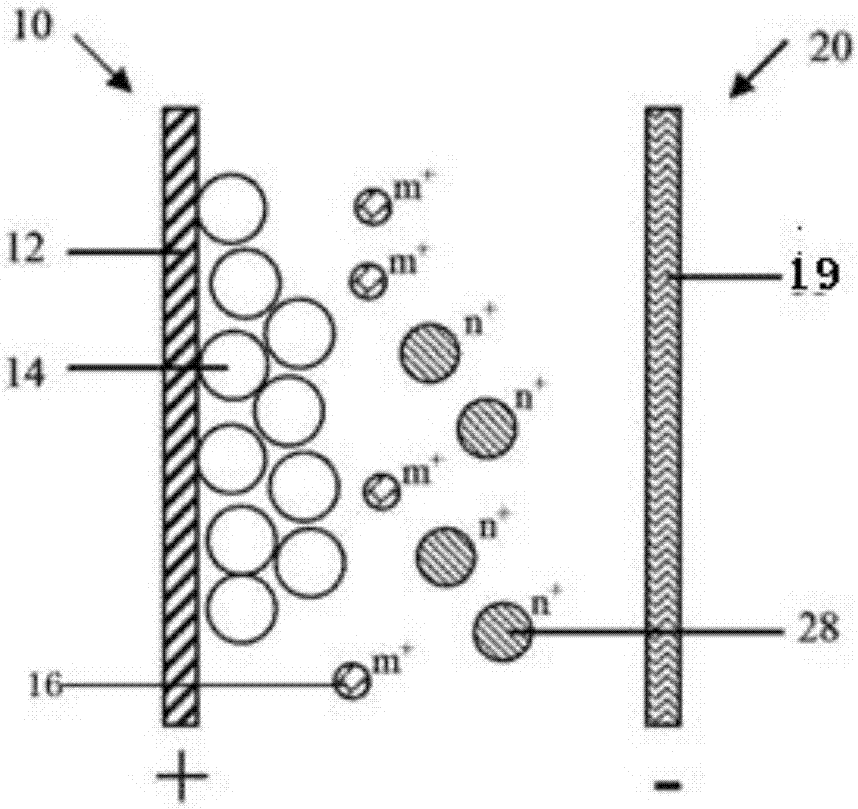
[0041] An aqueous secondary battery, such as figure 1 As shown, a positive electrode 10, a negative electrode 20, and an electrolyte (not shown) are included. The positive electrode 10 includes a positive electrode current collector 12 and a positive electrode active material 14 that participates in an electrochemical reaction. The positive electrode active material 14 can reversibly extract and intercalate ions; the negative electrode 20 includes a negative electrode 19 that includes metal zinc or metal zinc and oxide A mixture of zinc; the electrolyte includes at least one solvent capable of dissolving and ionizing the electrolyte; the electrolyte includes at least one ion 16 capable of reversible extraction-intercalation of the positive active material; the pH of the electrolyte is >8.
[0042] refer to figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the battery structure of the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0043] The positive electrode active...
no. 2 approach
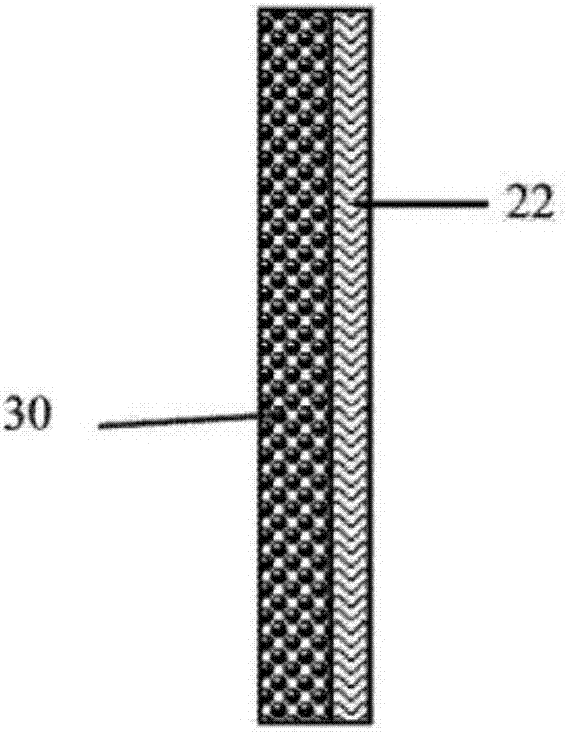
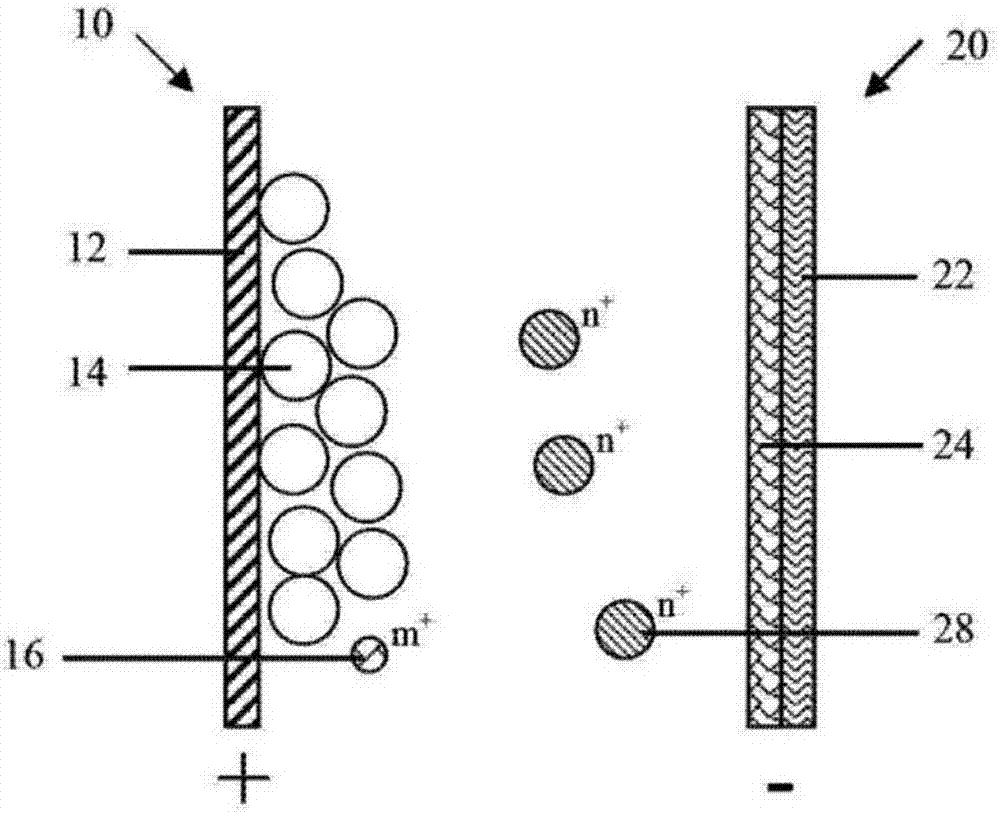
[0085] Please refer to image 3 As shown, the second embodiment of the present invention provides a battery, and the difference from the battery described in the first embodiment is: in the second embodiment, the negative electrode active material 24 is formed on the surface of the negative electrode current collector 22, and the negative electrode active material 24 Can be oxidized-dissolved into active ions 28 during discharge.
[0086] The negative electrode collector 22 is only used as a carrier for electron conduction and collection, and does not participate in the reaction of the negative electrode 20. The negative electrode active material 24 is formed on the negative electrode collector 22 by coating, electroplating or sputtering. The sputtering method includes but is not limited to magnetron sputtering. Specifically, the negative electrode current collector 22 is copper foil, the negative electrode active material 24 is zinc, and the zinc is formed on the surface of ...
Embodiment 1-1
[0108] Take LiNi 1 / 3 co 1 / 3 mn 1 / 3 o 2 As the positive electrode active material, mix the positive electrode active material, conductive agent graphite KS6, binder CMC and SBR in water according to the mass ratio LMO:KS6:CMC:SBR=86.5:10:1:2.5 to form a uniform positive electrode slurry. The positive electrode slurry is coated on the positive electrode current collector graphite foil to form an active material layer to make a positive electrode with a surface density of 25 mg / cm 2 .
[0109] Zinc foil was used as the negative electrode, and glass fiber (AGM) was used as the separator.
[0110] Weigh a certain quality of zinc sulfate and lithium sulfate, add them to dissolve in water, configure an electrolyte solution with a concentration of zinc sulfate of 1mol / L and a concentration of lithium sulfate of 1.5mol / L, mix LiOH to adjust the pH value of the electrolyte to 12 to obtain electrolysis solution, assemble the positive electrode, negative electrode and diaphragm into ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com