Breeding method of brassica napus radish cytoplasm sterile restorer line and application to brassica napus breeding
A technology of Brassica napus and cytoplasm, which is applied in the fields of application, botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of uncertain source of recovery, difficulty in transgenic recovery, unstable genetics, etc., to improve selection Efficiency and accuracy, avoid selfing depression, increase the effect of probability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
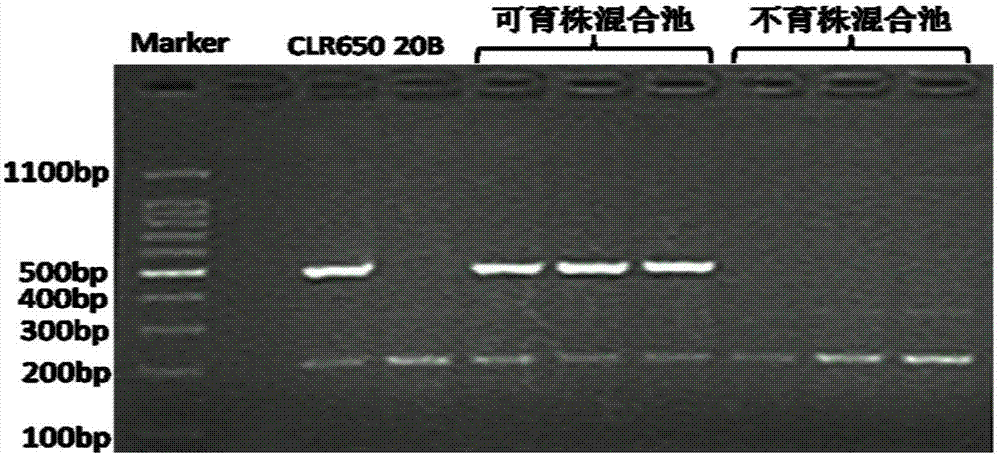
[0037] The breeding method of the cytoplasmic sterile restorer line CLR095 of Brassica napus radish in the embodiment of the present invention is shown in the attached figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps.
[0038] 1. Development of specific molecular markers and linkage markers of radish cytoplasmic male sterility restorer gene
[0039] 1.1 Implementation materials
[0040] Brassica oleracea radish sterility recovery material CLR650 (it is radish male sterile cytoplasm, leaf edge is zigzag, leaf tip is sharper, leaf color is dark green, siliques are thick and short, see literature: Chen Weijiang et al., Brassica oleracea radish Creation of cytoplasmic male sterility restoration material, Agricultural Sciences of China, 2012, 45(8): 1465-1474), the material is a hybrid of Raphanobrassica (AACCRR, 2n=56) and Brassica napus through grafting technology Breeding, the number of chromosomes is between 38-40. Its cytoplasm is radish male sterile cytoplas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com