Method for reducing influence of random frequency offsets of lasers in flexible grid elastic optical network
An elastic optical network and flexible grid technology, applied in electromagnetic wave transmission systems, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of inflexible frequency grid allocation and waste of spectrum resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0038] Figure 4 It is a flow chart of the first embodiment of the method for reducing the influence of random frequency offset of lasers in the flexible grid elastic optical network of the present invention. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific steps of the method for reducing the influence of laser random frequency offset in the flexible grid elastic optical network of the present invention include:
[0039] S401: frequency raster division:
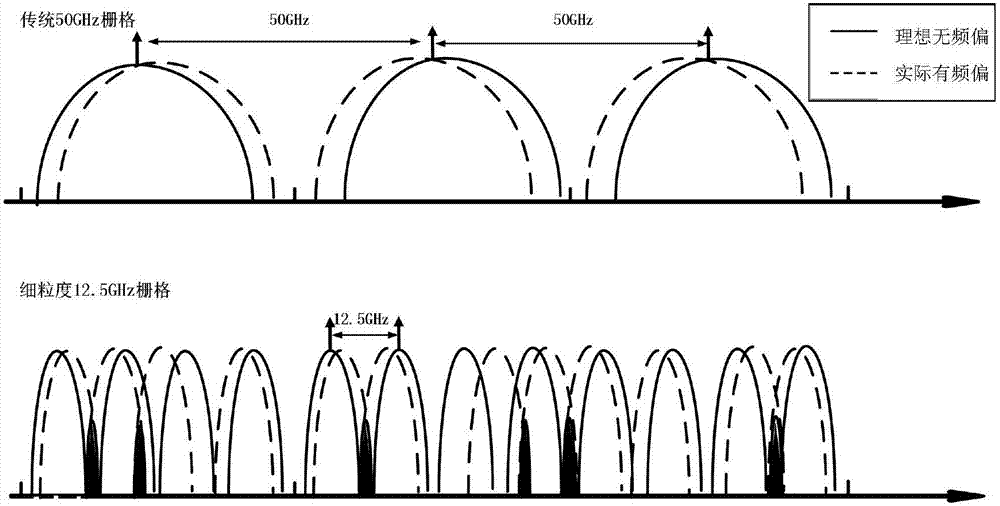
[0040] The fixed frequency grid is divided into several fine-grained frequency grids to obtain the initial reuse frequency of each frequency grid. The specific division parameter, namely the number of fine-grained frequency grids, is determined according to actual needs.
[0041] S402: Routing and wavelength allocation:
[0042] According to the source and sink nodes of the business, the traffic demand of the business and the current network resources, the routing and wavelength allocation are carried out for the business. The fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com