Method for identifying purity of varieties or germplasm of conventional varieties of wine making glutinous sorghum
A technology for sorghum and varieties, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of narrow genetic basis and high similarity, and achieve the effects of good repeatability, strong specificity and wide identification range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1 Screening of SSR molecular marker sites and primers
[0056] Experimental steps:
[0057] Step 1. According to Gramene database (http: / / archive.gramene.org / cmap / ) published sorghum SSR molecular marker information to synthesize primers, it is required to randomly select SSR sites and primers on the 10 chromosomes of sorghum for synthesis. The synthesized primers are shown in Table 1;
[0058] Step 2. Collect the main wine-growing sorghum varieties in the country, and extract the genomic DNA of sorghum varieties;
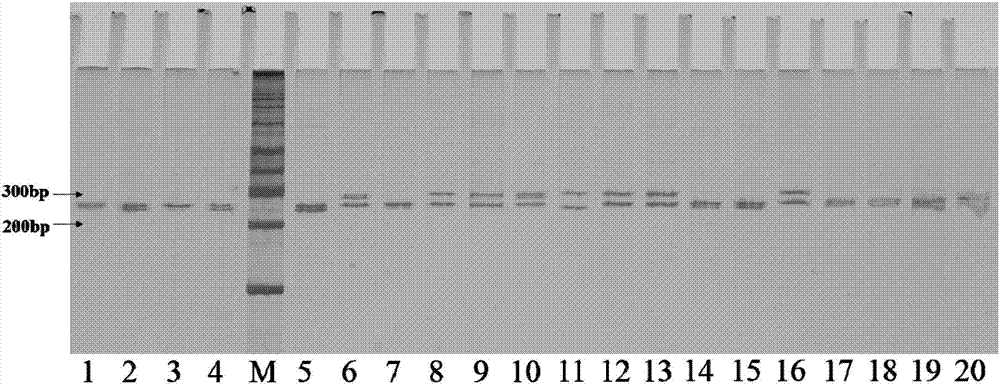
[0059] Step 3. Screening of variety-specific primers. Use the synthesized primers (Table 1) to perform PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and electrophoresis analysis on the genomic DNA of different sorghum varieties, and finally screen out the sorghum varieties that can be used for winemaking. Specific SSR molecular markers identified;
[0060] Among them, the specific extraction of sorghum genomic DNA is:
[0061] Extract Hongyingzi, Qiangao 7, Q...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2 Identification of variety / germplasm purity in different mixed samples of sorghum
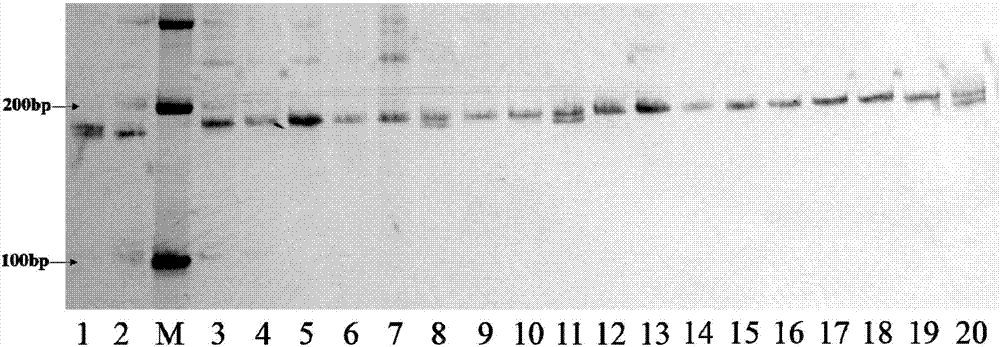
[0087] In order to illustrate the amplification of a single molecular marker in two mixed samples of sorghum, the inventors mixed different sorghum varieties in pairs and then accelerated the germination, then extracted DNA, amplified with marker txp287 and analyzed by gel electrophoresis, the results are as follows Figure 13 Shown.
[0088] Table 2
[0089]
[0090] Numbers 1-5 are two sorghum varieties mixed at a ratio of 1:1, and numbers 6-14 are two sorghum varieties mixed at a ratio of 4:1.
[0091] Taking the red tassel sorghum as an example, the results of mixed samples of No. 6 and 7 containing red tassel sorghum varieties showed that even if a small amount of components were present, obvious difference bands could be amplified. Among them, Hongyingzi and Liaoza 37 can only amplify bands with a size of 250 bp at the txp287 labeling site, while control 1 can amplify bands with a...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3 Identification of variety / germplasm purity in different mixed samples of sorghum
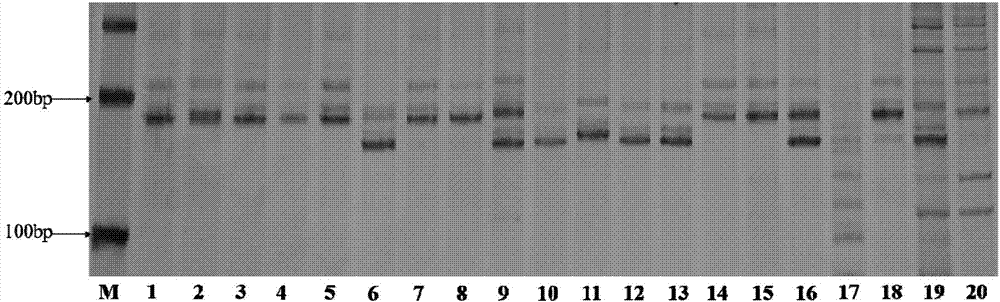
[0093] In order to illustrate the amplification of a single molecular marker in different sorghum mixed samples, the inventors mixed two or three different sorghum varieties and then accelerated the germination, then extracted DNA, amplified it with txp36 and analyzed it by gel electrophoresis. The results are as follows Figure 14 Shown.
[0094] table 3
[0095]
[0096] Numbers 1-4 are two sorghum varieties mixed at a ratio of 1:1, and numbers 5-10 are three sorghum varieties mixed at a ratio of 1:1:1.
[0097] Figure 14 Only 195bp bands were amplified in the two mixed samples of No. 1 and 3, the 190bp band in No. 2 was the result of Jinza 22 marker, the 190bp band in No. 4 was the amplification result of Jinza No. 103, and No. 5 was red. Both Yingzi and Jinza 22 were able to simultaneously amplify 190bp and 195bp bands. The 190bp and 195bp bands in No. 6 are the marker results of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com