Pauli decomposition and depth residual network-based polarimetric SAR image classification method
An image classification and residual technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as poor universality, affecting classification results, feature loss, etc., to achieve the effect of improving classification accuracy, improving learning ability, and enhancing generalization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
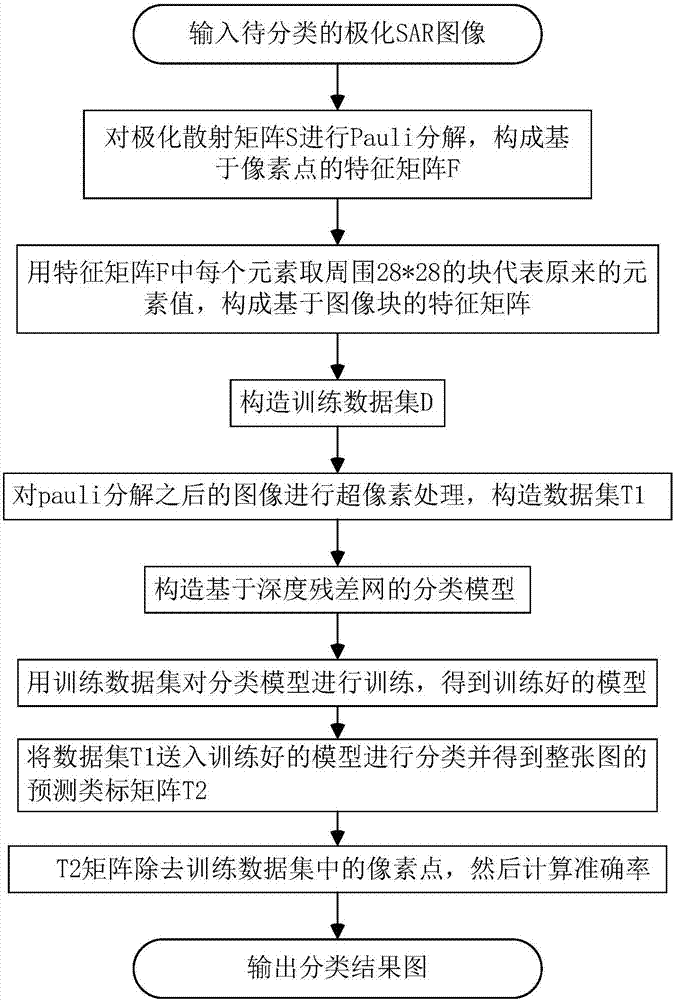
[0054] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, implementation steps and experimental effects of the present invention are described in further detail:
[0055] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
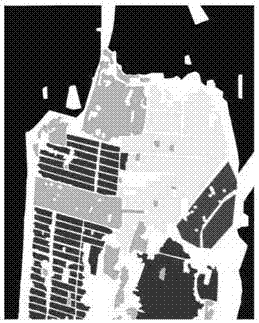
[0056] Step 1, input the polarimetric SAR image to be classified, perform Pauli decomposition on the polarimetric scattering matrix S (polarimetric scattering matrix S is used to describe the properties of the polarimetric SAR image), and obtain the odd scattering, even scattering, and volume scattering coefficients, Use these three coefficients as the 3D image features of the polarimetric SAR image to form a pixel-based feature matrix F:
[0057] (1a) Define the Pauli basis {S 1 ,S 2 ,S 3} The formula is as follows:
[0058]
[0059] where S 1 Indicates odd scattering, S 2 Indicates even scattering, S 3 Indicates volume scattering;
[0060] (1b) According to the definition of Pauli decomposition, the fol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com