Distributed energy allocation method for small cell networks based on game theory
An energy distribution and distributed technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as multi-cell situation and co-frequency interference, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing system energy consumption, high speed, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiments of the present invention are applied in a wireless network, including the following steps:
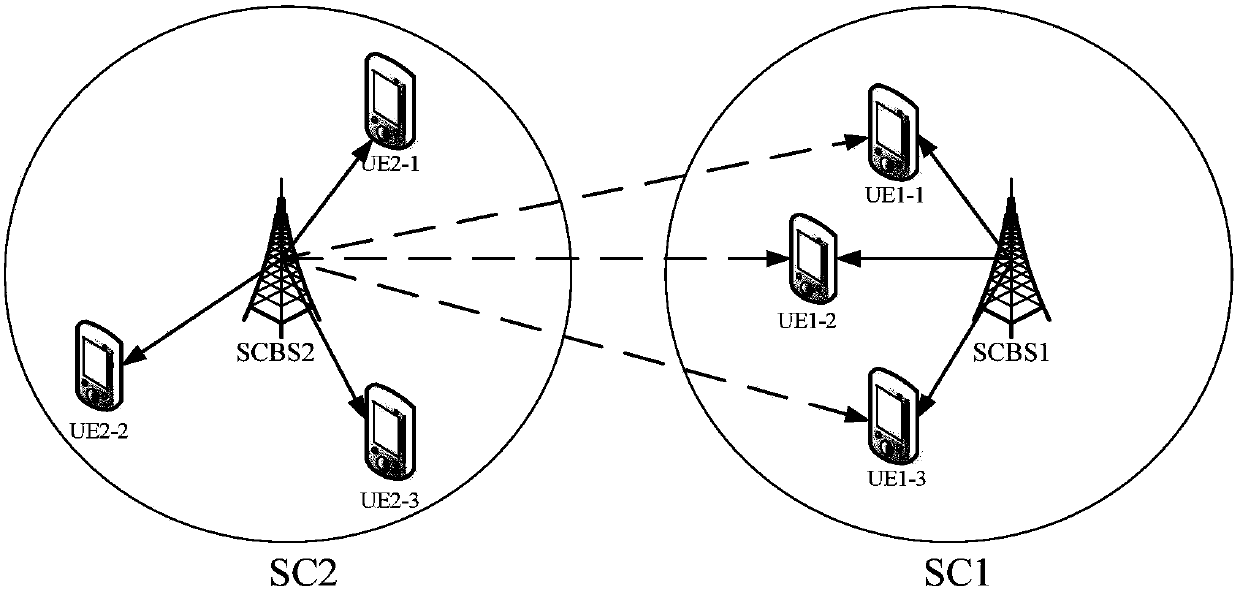
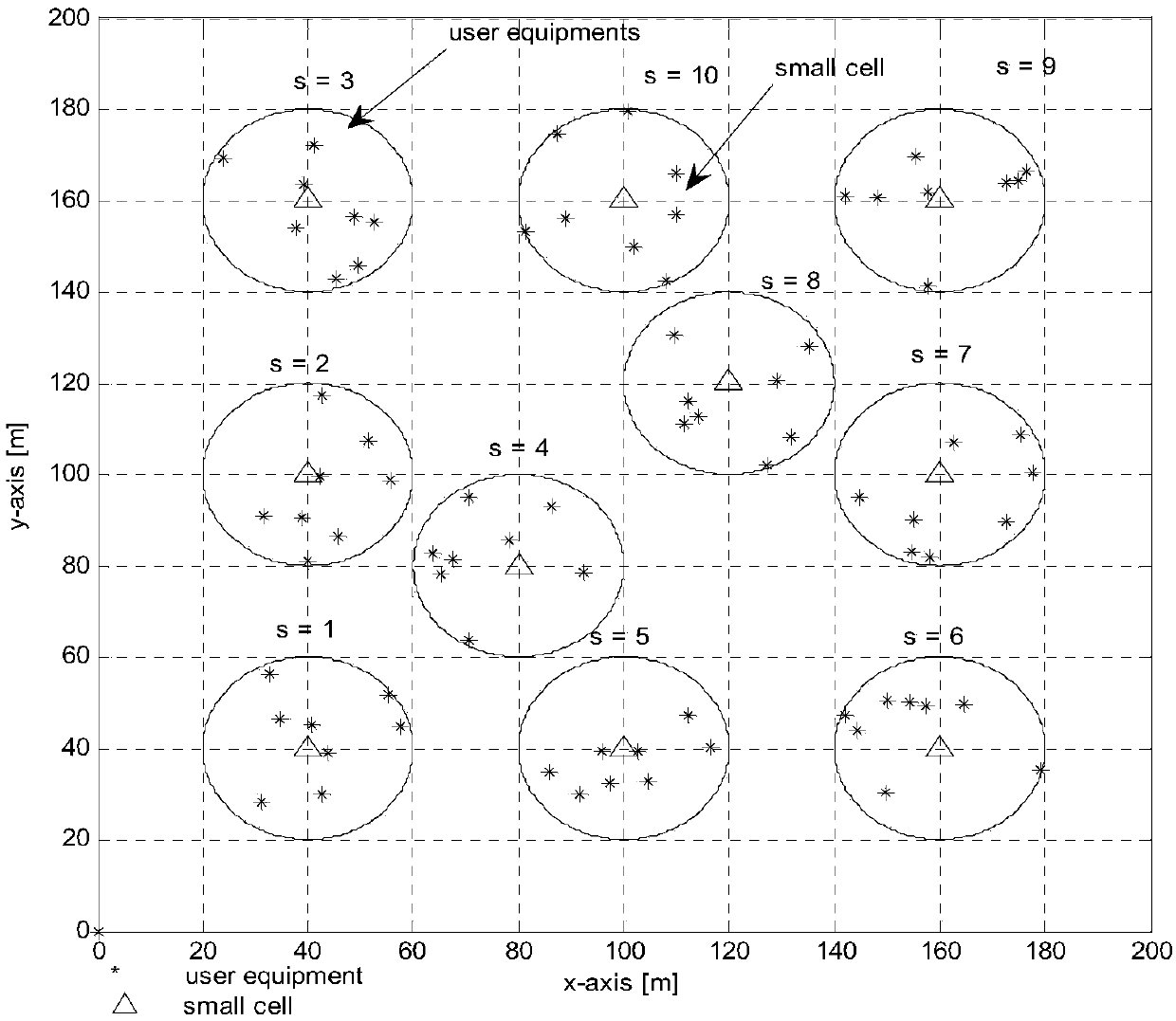
[0043] The first step is to set up an LTE cellular system network model that includes S adjacent cells (S represents a cell), and when S=10, it is as follows figure 2 As shown, the system divides N sub-channels (n) in total, and each cell shares these sub-channels, and K=8 users are evenly distributed in each cell, and the cell ownership of each user is determined, and K is the user set in cell S .
[0044] Define μ s,n is the interference factor of cell s on the nth subchannel, namely:
[0045]
[0046] where: g s,n is the channel gain of cell s on the nth subchannel, g i,n is the channel gain of other cell i on the nth subchannel, p i,n is the transmit power of other cell i on the nth subchannel, σ 2 is Gaussian white noise.
[0047] Define η s,n is the signal-to-noise ratio of cell s on the nth subchannel during information transmission, that is:
[0...
Embodiment 2
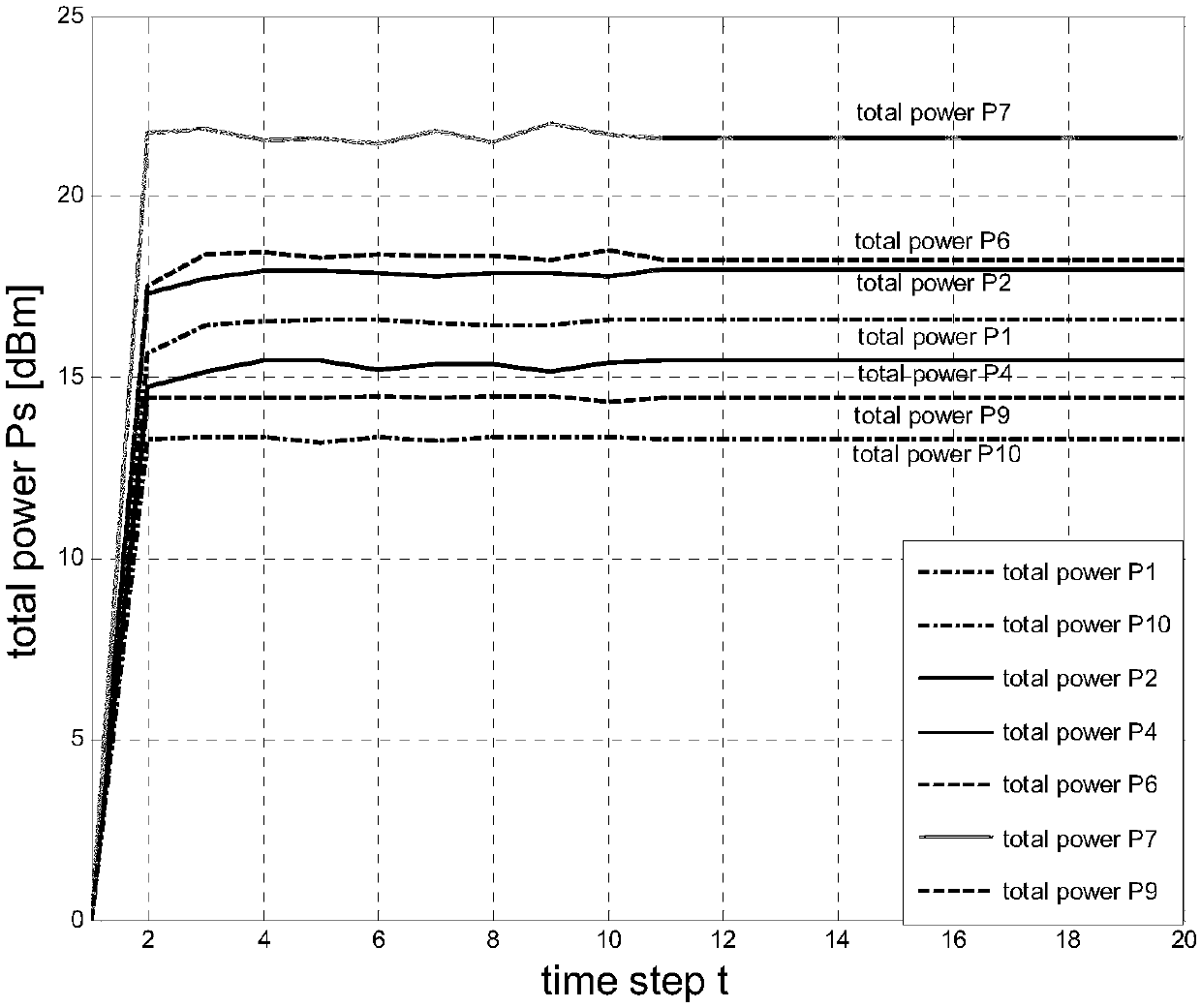
[0069] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the present invention provides a game theory-based small cell network distributed energy allocation method, the method includes the following steps:
[0070] The first step is to set up an LTE cellular system network model that includes S adjacent cells (S represents a cell), and when S=10, it is as follows figure 2 As shown, the system divides N sub-channels (n) in total, and each cell shares these sub-channels, and K=8 users are evenly distributed in each cell, and the cell ownership of each user is determined, and K is the user set in cell S .
[0071] In the second step, in the non-cooperative cell power control game model of the present invention, the cell S participating in the decision-making is called a player in the game (Player); The behavior of maximizing one's own utility is called a strategy (Strategy), and the set p of all available strategies s =[p s,1 ,p s,2 ...,p s,n ] is called a strategy space (that is, Strategy Spac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com