Distributed multihop broadcast protocol for maximizing relay forwarding probability based on Internet of vehicles
A forwarding probability, broadcast protocol technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve a lot of redundancy, broadcast information delay, discarding and other problems, to achieve the effect of ensuring real-time, saving network overhead, and preventing infinite spread
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
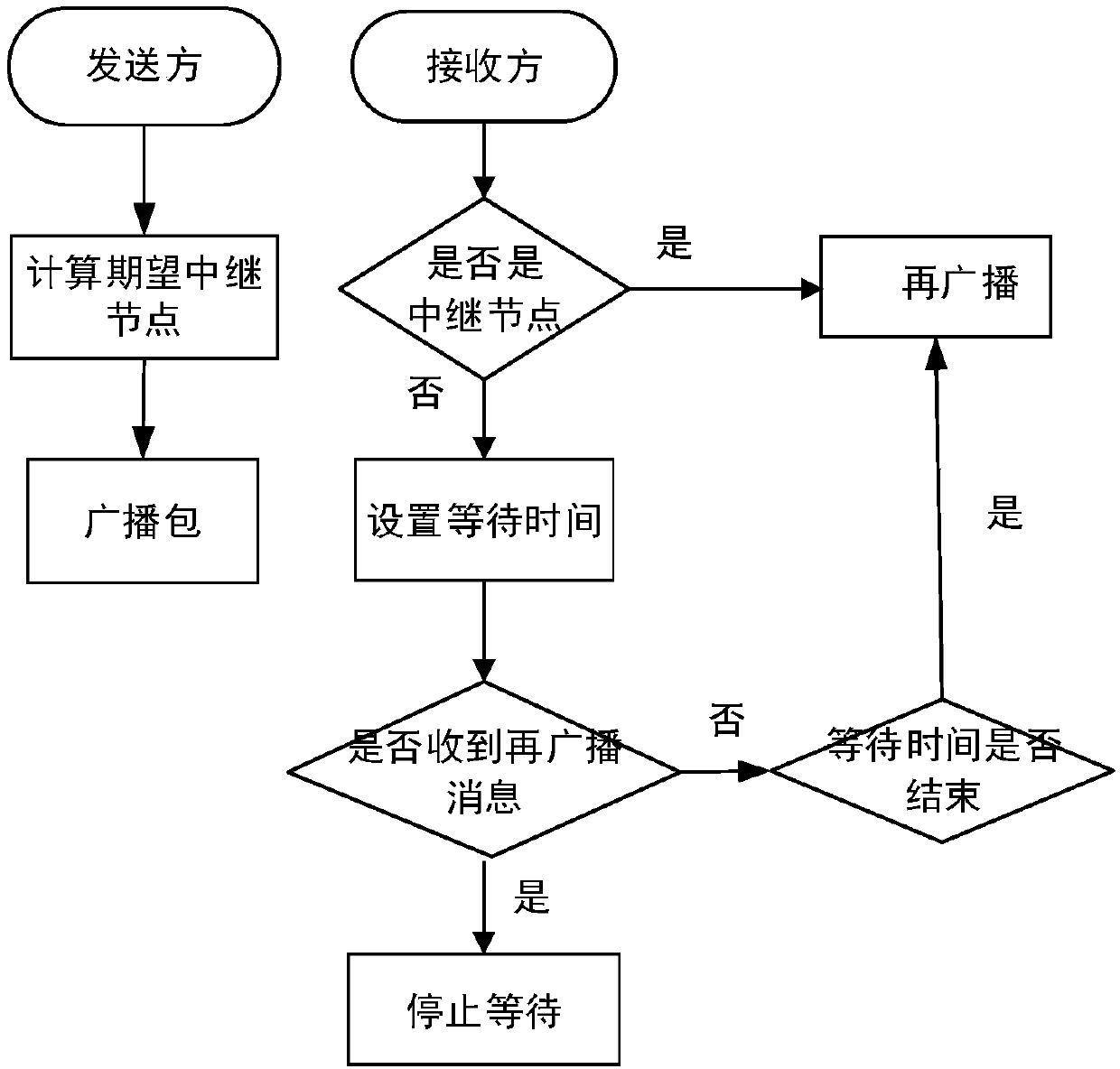
[0026] Because the existing technology is easy to cause broadcast storm and information delay, the node will judge whether the ID is the same message when receiving the message. If the message is the same, it will discard the message and not re-broadcast, and cannot continue to send emergency messages. This method is not conducive to Broadcast delivery of emergency messages.
[0027] The Internet of Vehicles is an application on traffic roads. It is a special mobile ad hoc network. Each vehicle in the network can obtain its position and speed through the Global Positioning System, and the location of the destination can also be known through the location management system. All Vehicles know neighbors' information through periodic Hello messages, and the considered situation includes road segments at intersections, each road segment has multiple lanes, and vehicles travel in different directions.
[0028] The present invention proposes a distributed multi-hop broadcast protocol...
Embodiment 2
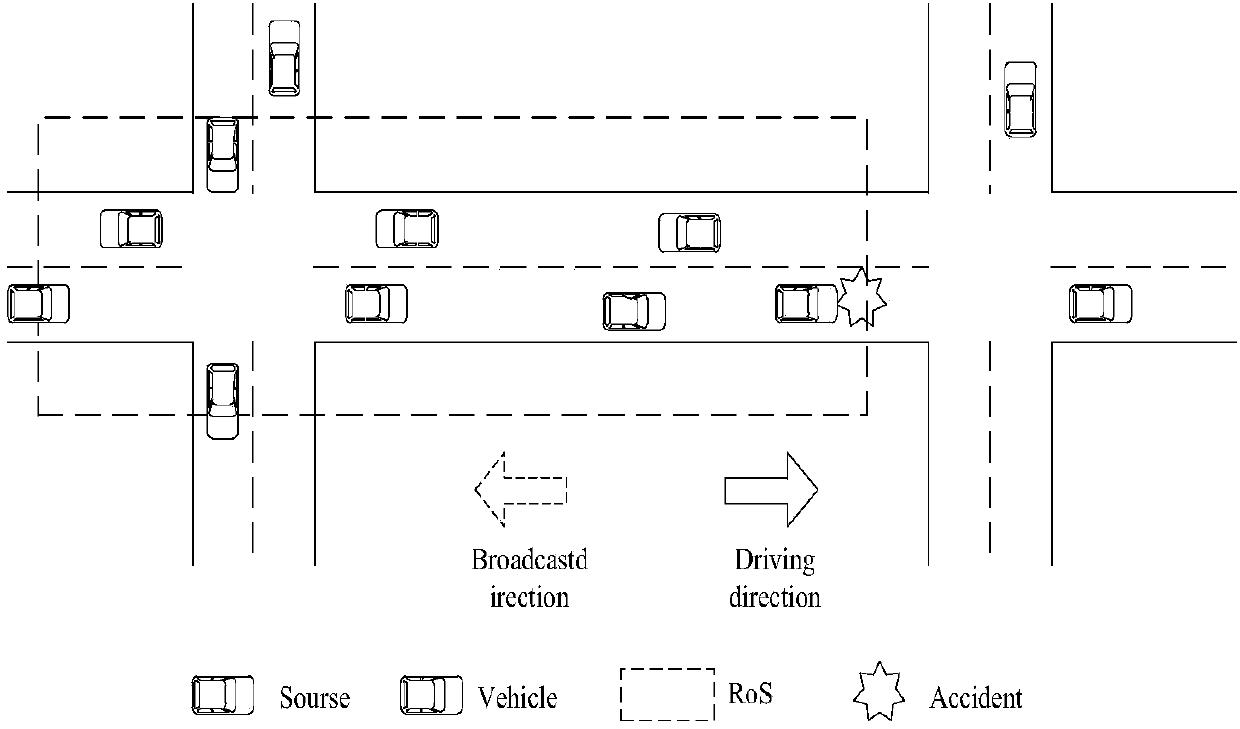
[0040] The distributed multi-hop broadcast protocol based on the maximized relay forwarding probability of the Internet of Vehicles is the same as that in Embodiment 1, see figure 2 , the protocol of the present invention defines a RoS (region of sensitivity) area, figure 2 The dotted line area in is the RoS area defined in the present invention. RoS acts as a selection-guiding region model for desired relay nodes, assigning weights to each candidate relay node according to each hop progress, link availability, and packet reception probability.
[0041] Abstract the map of the city as a directed graph composed of street topology, see figure 2 , where the dotted line area is the RoS area defined by the present invention, and the RoS area is represented as S=L∪M, the section length of the dotted line part in the figure is L, and the intersection is M, the place where the accident occurred is marked in the figure, and the explosion is attached in the figure The accident vehi...
Embodiment 3
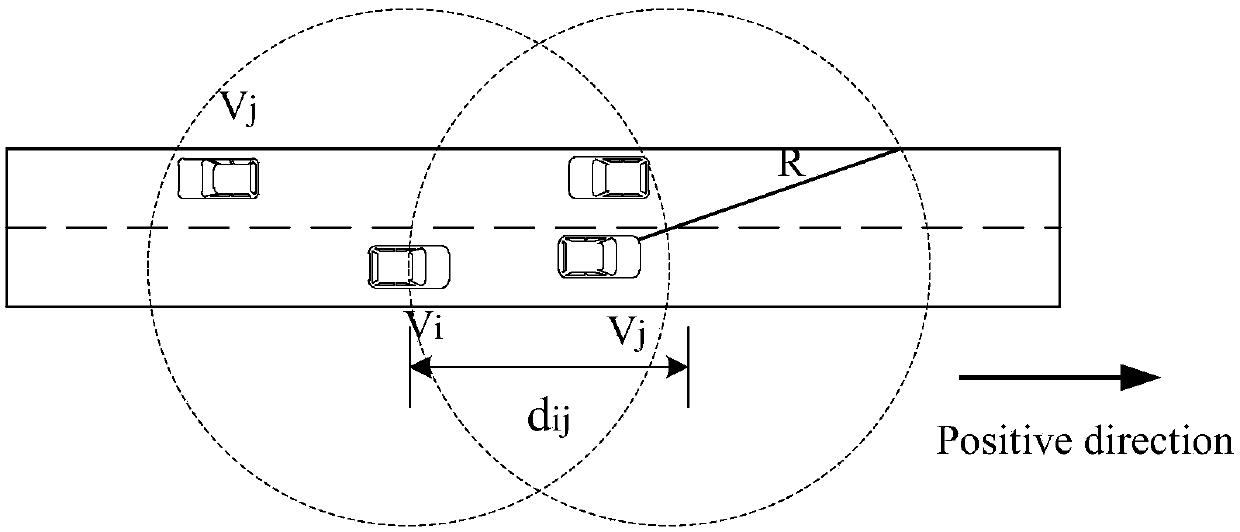
[0044] The distributed multi-hop broadcast protocol based on the maximized relay forwarding probability of the Internet of Vehicles is the same as that of Embodiment 1-2, and the successful transmission probability in step 2 of the present invention The calculation formula (1) of is as follows:
[0045]
[0046] is the transmitter V under the influence of channel fading i and the receiver V j Probability of successful reception: f d (r T ; m; Ω) represents the cumulative distribution function of the received signal power; is the acceptance threshold of the signal; is the given average power intensity; p t is the transmission power, R is the communication radius; G is a constant, see the Nakagami-m distribution model for the value; the attenuation parameter m is a parameter about d ij The function:
[0047]
[0048] p l is the vehicle V i and vehicle V j The connection probability between, such as formula (2):
[0049]
[0050] R is the communication ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com